This is an automatically translated article.
Melasma is a common skin condition in which brown patches appear on the skin, on the face, but can also appear on the forearms and neck. Melasma is not a serious disease but it can affect the appearance and psychology of the sufferer. So how to effectively treat melasma?
1. Causes of skin pigmentation
Currently, doctors have not found the exact cause of melasma. It can happen when the color-producing cells in the skin produce too much color. Anyone can get melasma, but melasma is more common in young women. This condition is usually related to the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. You have an increased risk of melasma if you are in the group of women who:
Take birth control pills . Have hormone replacement therapy. During pregnancy, melasma usually appears during pregnancy, in the second or third trimester. Being out in the sun for too long and too often also puts you at risk for this condition. Melasma is common in people living in tropical climates. People with darker skin are also more likely to develop melasma.
2. How to diagnose melasma?
In most cases of melasma, dermatologists can easily diagnose it by looking directly at the patient's skin. Alternatively, your doctor may use a special light (called a wood lamp) that emits ultraviolet light to examine your skin more closely. In rare cases, your doctor may take a very small piece of your skin for a biopsy.
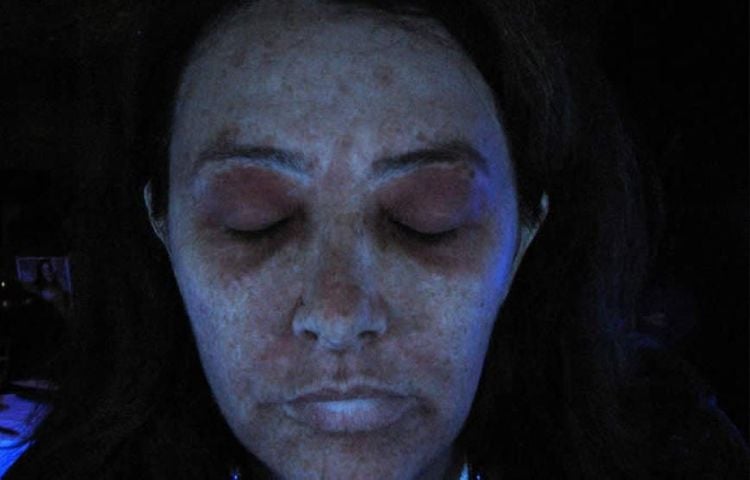
Nám da được phát hiện dưới ánh sáng của đèn wood
3. Melasma and how to treat it
Melasma does not always require treatment. If the cause of the melasma is due to hormonal changes, such as hormonal changes that take place during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills, have caused the melasma, then the melasma will fade after at birth or when the medication is stopped.
For others, melasma can last for years or even a lifetime. If melasma does not fade over time, you can seek treatment to help remove or fade the patches.
However, not all treatments work for everyone and melasma can return even after successful treatment.
Treatment options for melasma include:
Hydroquinone Doctors often use hydroquinone as the first line of treatment for melasma. Hydroquinone is available as a lotion, cream, or gel, and users can apply the hydroquinone product directly to the discolored patches of skin to make the patches lighter. Hydroquinone is available over the counter, but your doctor can also prescribe stronger creams.
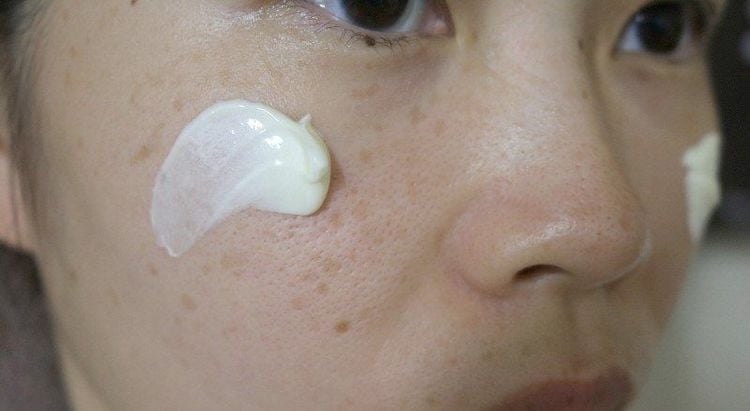
Hydroquinone kem bôi nám được sử dụng trong điều trị đầu tiên cho nám
Corticosteroids and tretinoin Corticosteroids and tretinoin are available as creams, lotions, or gels. Both corticosteroids and tretinoin can help lighten dark spots.
Combined creams In some cases, dermatologists may choose to prescribe combination creams that may contain hydroquinone, corticosteroids, and tretinoin in one product.
Topical Medications Used with or in place of other creams, a dermatologist may also prescribe azelaic acid or kojic acid. These acids work to lighten dark areas of the skin.
Medical techniques If topical medications do not work, the dermatologist can assign the patient to perform techniques such as:
Microdermabrasion Treatment Chemical peel Treatment laser treatment, light therapy, dermabrasion
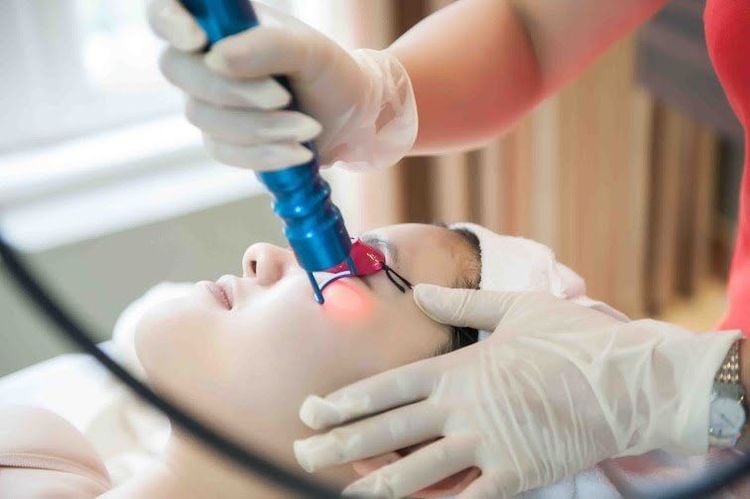
Điều trị bằng laser (laser treatment) được sử dụng trong điều trị nám da
Some of these treatment options have side effects or may cause additional skin problems. Therefore, it is best to consult your doctor or dermatologist about all the possible risks when performing the above methods of melasma treatments.
If you have had melasma before, you should try to avoid the factors that cause melasma by the following ways:
limit sun exposure, wear a hat when going out, use sunscreen, normal melasma, or hormonal melasma, Although it is not harmful to health, does not pose a risk to life, but it greatly affects facial aesthetics, creating a sense of inferiority for sufferers, but especially in women. Melasma is not too difficult to treat if you choose the right treatment method and know how to take care of your skin properly.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.
References: aad.org, medicalnewstoday.com, healthline.com