This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Hong Phuc - Emergency Resuscitation Doctor, Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital. The doctor has nearly 20 years of experience in Emergency Resuscitation.BMI is a measure of a person's weight. The BMI formula is applicable to both men and women and applies only to adults (over 18 years of age), does not apply to pregnant women, athletes, the elderly, and varies from country to country.
Obesity not only makes you self-conscious about your appearance but also leads to many health consequences such as increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer,... To assess obesity status There are many different methods for obesity such as measuring subcutaneous fat, measuring body fat percentage, ... but the most common method recommended by the World Health Organization is based on BMI. Here is how to measure and calculate BMI according to the guidelines of the National Institute of Nutrition.
![[Infographic] Cách đo và tính BMI chuẩn theo hướng dẫn của Viện dinh dưỡng quốc gia](/static/uploads/large_20220128_071225_590892_220124_BMI_01_max_1800x1800_jpg_1d98722407.jpg)
1. Formula to calculate BMI
BMI is also known as body mass index. Based on a person's BMI, it is possible to know that person is fat, thin or has an ideal weight. This index was first proposed in 1832 by a Belgian scientist. The formula to calculate BMI is relatively simple, based on only 2 indicators: height and weight:
BMI = Weight/ [(Height)2] In which, height is in m and weight is in kg.
BMI does not apply to pregnant women, athletes, bodybuilders
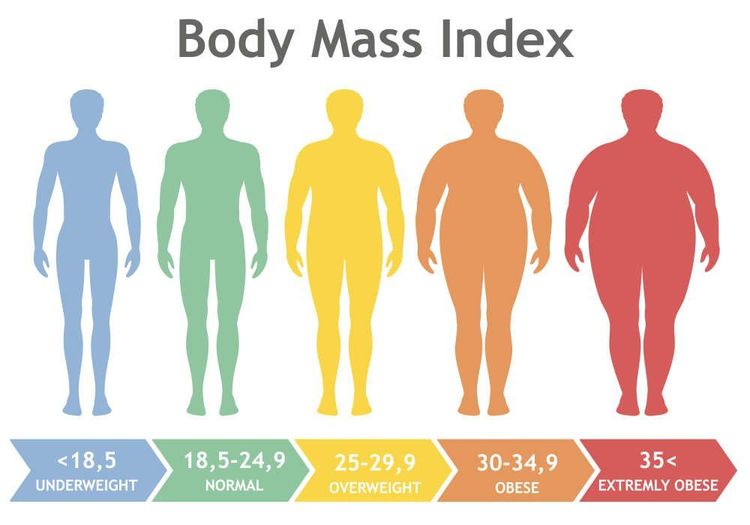
2. The classification of skinny-fat levels based on BMI
Below is a table to classify a person's lean - fat level based on BMI. The World Health Organization (WHO) grading scale for Europeans and the Diabetes Association of Asia (IDI & WPRO) grading scale are applied to Asians.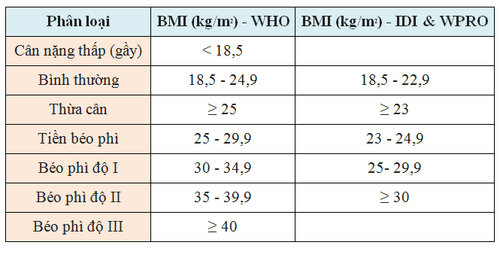
Ideal weight = Odd number of height (in cm) x 9 then divide by 10 Maximum weight = In numbers odd of height (in cm) Minimum weight = Odd number of height (in cm) x 8 then divide by 10 So, if you are 1.7m tall, ie 170cm then:
Ideal weight your weight is: 70 x 9:10 = 63kg Maximum weight is: 70kg Minimum weight is: 70 x 8 :10 = 56kg So just based on the odd number of height, you can immediately determine the level maximum allowable weight. If you exceed your maximum weight, you are overweight.
3. Waist/butt ratio
To assess the distribution of body fat, the Waist Hip Ratio WHR (Waist Hip Ratio WHR) can be usedWHR = [Waist circumference (cm)] / [ Hip circumference (cm)] Where : Waist is measured at navel and buttock circumference is measured across the widest point of the buttocks
WHR for men should be 0.95 or less, and women should be 0.85 or less.
WHR is a useful tool to help support BMI, because BMI can only classify the degree of leanness based on the correlation between height and weight, not reflecting the fat distribution. in the body. Fat concentration in the abdomen and waist warns of the risk of many dangerous diseases such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, etc. Based on the location of fat distribution on the body, there are The following types of obesity are present:
If the fat is evenly distributed over the whole body, it is called generalized obesity. If fat is concentrated in many areas of the abdomen and waist, it is an "egg" shaped human organ. This is “central” or “upper” obesity. People with this type of obesity are at risk of many diseases. If fat is concentrated in the area around the buttocks, thighs and groin: this is called "pear" obesity or "lower" obesity. People with this type of obesity have a lower risk of disease than those with central obesity. In short, being too fat or too thin both have adverse effects on health, so you need to regularly monitor your height and weight to promptly take reasonable corrective measures. Changing your diet and increasing exercise are effective measures to help you have a balanced and healthy body.
If there is a need for consultation and examination, please make an appointment with the Hospitals of the National Health System for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: National Institute of Nutrition