This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Tran Thi Vuong - Doctor of Microbiology - Laboratory of Laboratory - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.To reduce risk factors and limit the likelihood of BV, women should be aware of the signs of BV and be ready to perform the necessary diagnostic tests (e.g., microbiology). birth, vaginal examination, etc.).
1. What is a bacterial vaginosis?
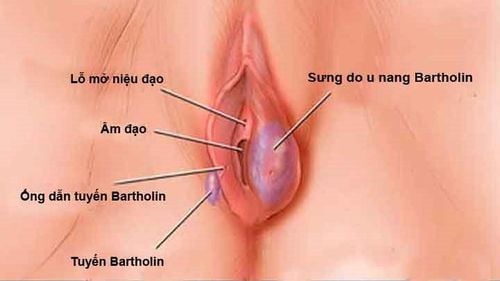
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) is a fairly common gynecological disease common in women aged 15 to 44 years. An estimated 75% of women have ever had a bacterial vaginosis.Bacterial vaginosis (also known as vaginitis) occurs when the amount of bacteria in the vagina overgrows, causing irritation, swelling, inflammation, excessive discharge and bad odor after sex. . Even the urethra, bladder and skin in the genital area can be affected.
Bacteria that cause bacterial vaginosis include Mobiluncus, Gardnerella, Bacteroides and Mycoplasma . During vaginitis, these microorganisms increase exponentially while the number of healthy microorganisms gradually decreases.
To identify bacterial vaginosis, a microbiological test is usually performed to remove fluid and cells from the vagina to evaluate for signs of infection.
2. Causes of bacterial vaginosis
The exact cause of vaginitis is not known at this time, but many statistics show that the infection is more common in women who have had sex. Having sex with a new or multiple sex partners, as well as improper douching, can affect the balance of vaginal bacteria, causing an imbalance between “good” and “good” bacteria. harmful" in the female vagina.Women rarely get bacterial vaginosis if they have never had sex. It is also not possible to get vaginitis from the toilet seat, bed sheet, or swimming pool.
If a woman has a bacterial vaginosis, she is at high risk for other STIs.
3. Time to test for bacterial vaginosis
The doctor may order a microbiological test to diagnose bacterial vaginosis when:The patient is about to undergo a hysterectomy or surgical abortion (to avoid an increased risk of post-operative infection due to bacterial vaginosis). The patient was pregnant and had a history of preterm birth (premature birth may be caused by vaginitis). The patient has a lot of abnormal vaginal discharge (gray or milky ...) Pain, itching in the vagina Vaginal area has a fishy smell, especially after sex Burning pain when urinating
4. Why should vaginal microbiology test?
Women should have a microbiological test when they have signs of risk, because bacterial vaginosis can cause serious health effects if left untreated, including:Increased risk of sexually transmitted diseases (Chlamydia infection and gonorrhea ...) if having unprotected sex. There is an increased risk of premature delivery if you have a bacterial vaginosis while you are pregnant. These bacteria can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which makes it difficult or impossible to have children.
5. Tests to identify bacterial vaginosis
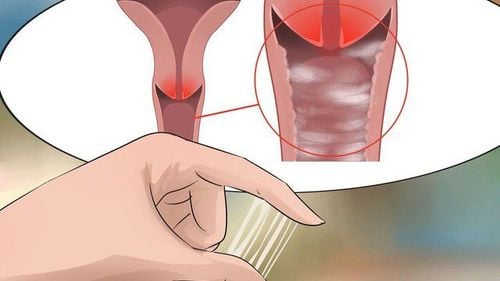
To diagnose a bacterial vaginosis, your doctor will take a medical history of your symptoms along with a vaginal exam and a sample of vaginal discharge. Common tests used to identify bacterial vaginosis include:5.1. The doctor will take a sample of the patient's vaginal discharge mixed with physiological saline and place it on a microscope slide, then observe for signs of infection, look for white blood cells and Trichomonas vaginalis to determine vaginal infection.
5.2. Whiff test Vaginal discharge samples will be added with KOH solution to determine if there is an odor. A foul odor formed after the Whiff test would be indicative of a vaginal infection caused by Gardnerella vaginalis. This method is currently only applied in a few places.
5.3. Measure vaginal pH. Normally, the vaginal pH of a normal person will be in the range of 3.8-4.8. Bacterial vaginosis will raise the vaginal pH above 4.5-7.0. This method is not currently used in many places.
5.4 Gram stain:
The swab containing the specimen will be spread on the slide, then Gram stained. This method targets the bacteria Gonorrhea, Gardnerella vaginalis, or the yeast Candida albicans.
5.5 PCR
With cases of chronic infection, subtle symptoms, difficult to detect bacteria or disease cause by the above methods, PCR method will be a very useful diagnostic tool to find Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, Mycoplasma...
6. Test procedure
To diagnose bacterial vaginosis, the doctor will do a pelvic exam, especially the vaginal area, to identify symptoms of the disease. Your doctor will also collect a sample of vaginal discharge with a cotton swab for microscopic examination and other tests.The process of performing a bacterial vaginosis test includes the following steps:
Step 1: The doctor or nurse will help the examiner sit in the correct position to do the test.
Step 2: The doctor will put a lubricated speculum into the patient's vagina. This funnel gently separates the wide vaginal wall to allow the doctor to see inside the vagina and cervix.
Step 3: The doctor will use a cotton swab to take a sample of the fluid inside the vagina.
For accurate test results, your doctor will usually ask you to:
Do not douche for 24 hours before the exam and test Do not use anything that irritates the vagina, for example such as vaginal sprays, vaginal suppositories.... Avoid not having sex for 24 hours before the exam Do not go to the doctor while you are on your period. Before performing medical techniques, the patient should clearly understand the warnings and precautions. If you have any questions, please consult your doctor for more information and specific instructions.

7. How to prevent bacterial vaginosis
To reduce your risk of BV, you can take the following basic preventive steps:Safe sex Don't douche Limit the number of sex partners Lifestyle and lifestyle habits The following will help you limit the progression of bacterial vaginosis:
Keep the vaginal area dry Use the medicine exactly as directed and prescribed by the doctor. like the state of your health. Do not have sex during treatment.

Basic gynecological examination and screening package for female customers, has no age limit and may have the following symptoms:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding Having menstrual problems: irregular menstrual cycle, irregular menstrual cycle Irregular vaginal discharge (smell, different color) Vaginal pain and itching Female clients have several risk factors such as poor personal hygiene, Unsafe sex, abortion,... Female customers have other symptoms such as: Abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, pain in the intimate area, abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.