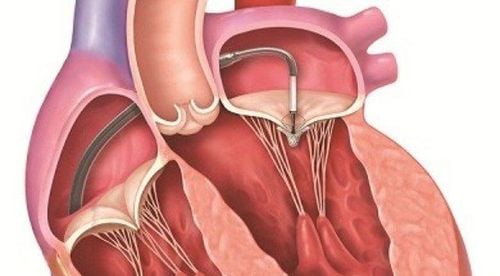
This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Cao Thanh Tam - Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Aortic stenosis accounts for up to 25% of all heart valve diseases, with 80% of sufferers being men. Cardiovascular diseases in general have similar symptoms, so are there ways to detect aortic stenosis?
1. Doppler echocardiography
Doppler echocardiography is the method of choice for the definitive diagnosis and assessment of the severity of aortic stenosis. Doppler ultrasound allows the assessment of the degree of aortic stenosis in most patients by measuring the maximum flow velocity through the aortic valve, the mean differential pressure across the valve, the area of the orifice... Instrument Possible:
Evaluation of valve status, causes of valve stenosis and effects on the heart chambers: The leaflets are thickened, arch opening during systole seen in congenital aortic stenosis and rheumatic heart disease. Determining the number of valve margins, closure path and orifice shape allows diagnosis of congenital aortic stenosis types Left ventricular hypertrophy and dilatation, left atrial dilatation Hemodynamic assessment: Pressure differential across the aortic valve host: usually measured by continuous Doppler based on the modified Bernoulli formula (P = 4 V2). The degree of aortic stenosis is classified based on the mean and maximum differential pressure across the aortic valve. Aortic orifice area: determined on 2D and Doppler. The degree of aortic stenosis is classified based on the area of the orifice. Transesophageal echocardiography Stress ultrasound
2. Electrocardiogram
In this test, wires (electrodes) attached to pads on your skin measure the electrical activity of your heart. The electrocardiogram usually shows left atrial hypertrophy (80%) and left ventricular hypertrophy (85%). Arrhythmias rarely occur, mainly in the late stages and mostly in atrial fibrillation, especially in the presence of mitral valve disease. Atrioventricular block may be present in the presence of an annular abscess complicated by endocarditis.3. Chest X-ray
Chest X-ray film is of little diagnostic value because the image may be completely normal. Heart shadow resembles a boot if left ventricular hypertrophy is concentric. The heart shape is usually enlarged if left ventricular dysfunction is present or there is an associated HoC.
Chest X-ray can also help your doctor determine the condition of your lungs
4. Stress test
Exercise testing is not indicated in patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis. For asymptomatic patients, this method should only be performed under the close supervision of experienced specialists, with close monitoring of ECG and blood pressure.
Exercise tests help check if you have signs and symptoms of aortic valve disease during physical activity, determining the severity of your condition. If you are unable to exercise, medications that have the same effect as exercise on the heart may be used.
5. Aortic valve stenosis with low differential pressure - low flow
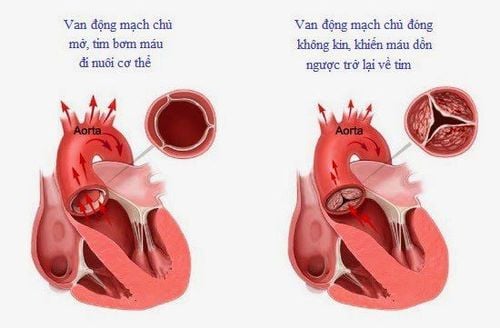
Patients with aortic stenosis with low pressure gradient - low flow through the aortic valve with left ventricular dysfunction need to determine the transvalvular pressure gradient and calculate the transvalvular area at rest, versus during physical exertion or drug exertion.
When you see any signs of aortic valve stenosis in your body, you should visit the hospital for the most accurate results, from which there can be timely treatment. If not detected and treated early, the patient's survival time can be reduced very quickly due to the risk of sudden death, so should not be subjective with any symptoms of aortic stenosis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.