Scalp fungus not only causes itching, flaking, and hair loss, which significantly affects aesthetics, but it also impacts the quality of life of the patient. The disease is often confused with other scalp conditions such as ringworm, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, and there are many types of fungi that cause the disease. In reality, many cases of scalp fungus, including children treated with folk remedies, result in severe scalp inflammation, hair loss, and permanent scarring.
1. Types of Scalp Fungus
1.1 Scalp Fungus Caused by Trichophyton
Scalp fungus begins with small, scattered nodules on the scalp. The lesions have thin scales, with healthy hair interspersed with hair cut close to the scalp (due to fungal infection making the hair brittle and easy to break).
The scales peel off the scalp, creating a temporary bald patch. This condition causes itching, and the patient may have fungal infections in other areas (groin, buttocks, nails).
1.2 Hair Shaft Fungus (Black Piedra) Caused by Pierdraiahortai and Trichosporon beigelii
The characteristic manifestation is along the hair shaft, from 2-3 cm from the hair root, with round, soft nodules (about the size of millet seeds), black or brown, and can be removed like lice eggs. This condition does not cause hair loss because the fungal spores only develop on the hair shaft, causing mild discomfort or itching. It often arises from poor personal hygiene.
The primary source of scalp fungus is humans, but it can also come from some animals like dogs and cats. The fungus can persist on contaminated objects. The disease spreads directly from skin to skin, but the most common way is indirectly through shared use of combs, hats, pillows, etc., with an infected person.
To diagnose, besides clinical symptoms, tests are needed: examining fresh samples of scalp scales or hair debris. Culturing in a protein-rich environment to accurately diagnose the type of fungus and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
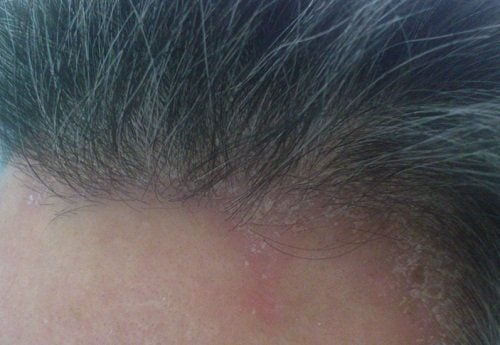
2. Effective Treatment for Scalp Fungus
For mild cases, daily shampooing with selenium sulfide or Nizoral shampoo is effective.
If the condition is more severe, after shampooing, cover the hair with a towel (note not to scratch or rub the scalp hard to avoid bacterial superinfection).
Alternatively, shave the hair in the affected area and apply antifungal medication daily. If the lesion is superinfected with bacteria, apply topical antiseptics and possibly use systemic antibiotics.
Medication Options:
When topical treatment with antifungal creams and shampoos is ineffective, doctors will prescribe oral antifungal medications.
Griseofulvin is taken for 6-8 weeks. Patients should take Griseofulvin with a fatty meal to enhance absorption. Griseofulvin may cause nausea or abdominal pain in children.
Terbinafine, Itraconazole, and Fluconazole are popular antifungal medications. However, the treatment duration for some of these medications may be shorter, from 2 to 4 weeks. Both Ketoconazole and Fluconazole can cause abdominal pain in children, so use with caution.
For seborrheic dermatitis caused by Microsporum spp., Griseofulvin has been proven to be the best treatment, while Terbinafine is better for Trichophyton spp. infections.
3. Measures to Reduce Scalp Fungus

To prevent the spread of the disease, maintain cleanliness, especially in places like homes, schools, dormitories, etc. Use clean shampoo daily, avoid scratching or rubbing the scalp hard, rinse thoroughly with clean water when shampooing, and always keep hair dry and clean. Dry hair immediately after shampooing and when returning from the rain.
Avoid wearing tight hats or wearing hats for too long, as it makes the hair damp, creating favorable conditions for fungal growth.
Avoid contact with infected pets, and take pets to the vet for regular check-ups to check for fungus. Avoid sharing personal items with others to prevent the risk of spreading the disease. Do not share towels, combs, or hats with others, especially those with dandruff or symptoms of scalp fungus.
Scalp fungus is easily spread, so if you notice any signs of the disease, seek medical attention promptly. Early detection and proper treatment, along with a reasonable shampoo regimen, can cure scalp fungus. If there is excessive dandruff along with symptoms like itching, sticky hair, and odor, or red pimples, see a dermatologist immediately to find the cause and appropriate treatment.
Do not scratch or rub the scalp hard to avoid causing injury and spreading dandruff and fungus. Do not self-medicate without a doctor's prescription or advice. Maintain a nutritious diet and always enhance the body's resistance as a way to prevent the disease.
To arrange an appointment, please call … or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.