This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Thanh - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Cervical cancer is a dangerous disease in women, ranking third in the world in terms of mortality, after breast and ovarian cancer. All women are at risk for sexually transmitted infections. However, with the Pap smear test, women can completely screen for cervical cancer early. So what is a Pap smear and how often should it be repeated?
1. What is a Pap smear?
A Pap smear (also called a Pap test or pap smear), is a cytological test to screen for cervical cancer in women. On the other hand, whether cervical cancer is curable depends on whether the patient detects the disease early or late. A Pap smear is done by collecting and examining cells in the area of the cervix - a narrow passage below the uterus, just above a woman's vagina.
2. How is the Pap test done?
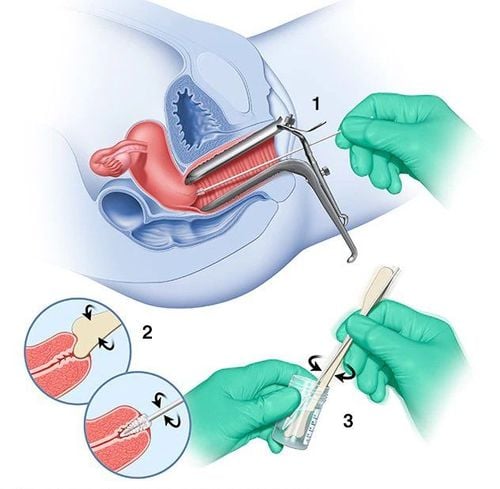
Cervical smears are performed in a dedicated women's sampling room, directly performed by the doctor, and the procedure takes only a few minutes. Often your doctor will ask you to partially strip off, from the waist down. The first time you have such tests, you may feel a little embarrassed. However, rest assured, because the Pap smear is completely painless, very safe, and fast.To perform, you need to lie on your back on the hospital bed, in a relaxed position, knees bent. Next, the doctor will gently insert an instrument called a speculum inside the vagina. The speculum helps to widen and fix the wall of your vagina so the doctor can easily see the inner cervical area. Sometimes inserting a speculum into your vagina can cause a pinching sensation in your pelvic area.
3. How long after having a Pap smear should I do it again?
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, women should have a Pap test every three years between the ages of 21 and 29. For women age 30 and older, the question of how often to have a Pap smear again depends on the results of the HPV test.HPV test helps detect the presence of HPV virus, one of the common agents leading to cervical cancer. Therefore, you may choose to have both the Pap test and the HPV test done at the same time (these two tests are collectively known as Co-testing).
There are 2 cases that occur with HPV subclinical results as negative or positive.
In case of HPV negative (no HPV infection): You should prioritize Co-testing every 5 years, or continue to have Pap smear every 3 years. In case of HPV positive (with HPV infection): The patient needs to perform Co-testing in the next 12 months. HPV testing can be done on a sample of cells from a woman's cervix, similar to a Pap smear. This type of procedure is called a “differential HPV test”, which detects the two main types of HPV that cause cervical cancer, HPV 16 and HPV 18. For HPV positive, you need to do more differential HPV testing to check if it's the two types of HPV that cause cervical cancer.
If certain risk factors are identified, your doctor will recommend more frequent Pap tests, regardless of your age. These risk factors include:
Having a diagnosis of cervical cancer or a Pap test showing the presence of precancerous cells Taking the drug diethylstilbestrol (a synthetic estrogen) ) before birth HIV infection Weakened immune system due to organ transplant surgery, chemotherapy or long-term use of corticosteroids Have a habit of smoking Thus, the question of "how often should I do Pap smears?" do it again” depends on the doctor's decision and the woman's consideration of her own risk factors.
4. Why do Pap smears need to be repeated many times?
The Pap smear is a safe and effective way to screen for cervical cancer. However, no test is perfect. In fact, although it's rare, a pap smear can still get a false-negative result - that is, the test results don't detect any signs of cancer, when the truth is. You have abnormal cells in your body.When a test result is a false negative, it does not mean that there is a problem with the procedure. In general, there are still objective factors that cause false-negative results that we cannot control, including:
The number of cervical smears obtained is too small Not enough detection threshold Cells abnormalities are obscured by blood cells. While the germ of cancer may not be detected by a single Pap test, you still have plenty of time. Cervical cancer takes several years to develop. Besides, it is very likely that these abnormal cells will not be able to "escape" in the next test.
Moreover, the Pap smear test periodically for cervical cancer screening many times to promptly detect the risk of disease, thereby deploying treatment as soon as possible.
5. When can Pap smears be stopped?
In the following cases, your doctor will stop performing a Pap smear:5.1. Women after total hysterectomy
If you have a total hysterectomy (including your cervix) for some reason, your doctor will consider stopping the Pap test. Specifically:If your hysterectomy is caused by a non-cancerous condition, such as uterine fibroids, you will no longer have to have a Pap smear. But if you have a hysterectomy to remove precancerous or cancerous cells from the cervix, your doctor will recommend that you continue with the Pap smear.
5.2. Elderly women

Screening Screening and early detection of gynecological cancer with the Pap smear test is considered the "golden key" for effective treatment results. Thereby, patients reduce the risk of death and significantly reduce costs.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Acog.org