This is an automatically translated article.
While enjoying alcoholic beverages regularly is unlikely to harm your health, drinking in excess can have significant negative effects on your body and health. So when does drinking become harmful to health, as well as how much is considered heavy drinking.
1. Recommended drinking
Beverage standards and drinking recommendations vary from country to country.
In the United States, a standard drinking unit is about 14 grams of alcohol, which is the amount commonly found in 355ml of regular beer, 150ml of regular wine, or 45ml of spirits.
However, the concentration of alcohol in the blood/breath when drinking alcohol depends on the health status and location of each person. Although there are standards for alcohol content, in reality different drinks have different alcohol levels.
According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, the United States Department of Agriculture and the United States Department of Health and Human Services, moderate alcohol consumption is up to one drink per day for women and maximum up to two drinks per day for men.
Research shows that only about 2% of drinkers within these limits have an alcohol use disorder. Drinking alcohol can lead to many related problems, such as binge drinking, heavy drinking, alcoholism.
American Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) defines binge drinking as drinking four or more drinks for women and five or more drinks for men in the same moment or drink in a few hours.
Heavy drinking is defined as binge drinking for 5 or more days within a month. Whereas, alcoholism is when you have a reduced ability to control alcohol, get preoccupied with its use and continue to use it despite the adverse consequences it causes.

Uống nhiều rượu có thể dẫn đến suy giảm khả năng kiểm soát rượu
2. Effects of alcohol on the body
Drinking too much affects your health and almost every part of your body. Not only does it damage vital organs in your body, but it also affects your mood and behavior.
2.1 Brain
Drinking too much alcohol can have devastating effects on the central nervous system.
Several factors govern how alcohol affects you and how it affects your brain, including how much and how often you drink, the age you start drinking, your gender, and some other issues other.
Early effects of alcohol on the central nervous system include slurred speech, impaired memory, and impaired hand-eye coordination.
Many studies have shown a link between chronic heavy alcohol use and memory impairment. Alcohol dependence is a major risk factor for Alzheimer's disease, especially in women. In addition, it is estimated that alcohol-related brain damage may account for 10% of cases of early-onset dementia.
Although brain damage is likely to be partially reversed after a long period of sobriety, prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption can permanently impair brain function.
2.2 Liver
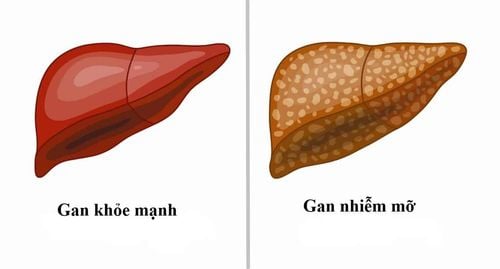
Liver damage is another consequence of chronic drinking. Most of the alcohol you consume is metabolized in the liver. This creates potentially harmful byproducts, which can damage your liver cells. As you continue to drink over time, liver health will deteriorate.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is the earliest stage of alcoholic liver damage. This condition can occur over time as drinking too much alcohol leads to the accumulation of body fat in the liver cells, which can interfere with liver function.
This is the most common bodily response to chronic alcohol use and can develop in 90% of people who regularly drink more than 5 drinks per day.
When you drink a lot of alcohol, fatty liver disease is at risk of progressing to hepatitis, cirrhosis and even liver failure, which is a life-threatening condition.

Rượu bia ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến chức năng gan
2.3 Dependence on alcohol
The harmful effects of alcohol can be mentally and physically addictive.
Feelings of wanting to drink, always thinking about where and when you will have your next drink, finding it difficult to feel comfortable without alcohol are all common signs of alcohol dependence.
The cause of this dependency can be complex. It can be caused in part by genetics and family history, but your surroundings can also play a big role.
2.4 Other effects
Chronic drinking can cause many other side effects. Although health effects vary between subjects, alcohol consumption is often associated with depression and feelings of anxiety.
Some people may use alcohol as a way to improve their mood and reduce anxiety, but this usually only helps in the short term. In the long run, it can undermine your overall physical and mental health.
Alcohol consumption can also affect weight and body composition (percentage of body fat, bone, water and muscle). Although research on the effects of alcohol on body weight is multi-dimensional, it is reported that alcohol use is associated with weight gain.
Drinking alcohol in moderation is considered quite safe, but drinking too much alcohol and its abuse can have adverse effects on your physical and mental health.

Uống nhiều rượu có thể dẫn đến trầm cảm
3. Gender and genetics affect alcohol metabolism
Gender and genetics can affect how quickly your body metabolizes alcohol. The main enzymes involved in alcohol metabolism are alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH).
Women generally have lower ADH activity than men. As a result, women may metabolize alcohol at a slower rate, making them more susceptible to the effects. In addition, some men also have low ADH activity.
The effects of alcohol on your body can also vary based on your body composition. For example, the average woman's body has more fat and less water than a man's body. This can lead to higher blood alcohol levels in women, even if they drink the same amount as men.
4. Some subjects should abstain from alcohol
For most people, the occasional use of alcohol is usually not harmful to health. However, in certain situations and in specific populations, alcohol should be avoided:
4.1 Pregnant and lactating women
Research has shown that there is no safe level of alcohol use for pregnant women.
Many studies have concluded that alcohol use during pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage, birth defects, and cognitive and developmental problems.
One study found that birth defects were 4 times more likely if the mother drank a lot of alcohol during the first trimester.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), alcohol use during pregnancy is the leading cause of birth defects, developmental disabilities, and intellectual disability in the United States.
It's important to note that alcohol can also pass into breast milk if you're breastfeeding. Nursing mothers should wait to completely eliminate alcohol from their breast milk after drinking. This process takes about 2 to 2.5 hours per drink, depending on the individual's condition.

Sản phụ uống rượu làm tăng khả năng mắc dị tật bẩm sinh ở thai nhi
4.2 Other cases
Several other people should abstain from alcohol, including:
Chronic conditions: Alcohol can worsen pre-existing health conditions such as liver disease, diabetes and kidney disease.
Drugs: Alcohol can interact with over-the-counter herbal and prescription drugs, including antidepressants, antibiotics, and opioids.
Underage drinking: Underage drinking, especially heavy and frequent drinking, is associated with immediate and chronic consequences.
Current and recovering alcoholics: Recovery from an alcohol use disorder can be difficult. Alcoholics in recovery should stop drinking altogether and avoid triggers of abuse.
Alcohol use during pregnancy increases the risk of birth defects. You should also abstain from drinking if you have certain pre-existing medical conditions, are underage, or take certain medications. While drinking in moderation is safe for most individuals, heavy and chronic alcohol use can have devastating consequences for your mental and physical health.
Many factors play a role in alcohol metabolism, and the effects of alcohol vary from person to person, making it difficult to make recommendations on drug intake.
The American Dietary Guidelines recommend limiting alcohol to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men. However, some people, such as those with certain medical conditions and pregnant women, should avoid alcohol altogether.
If you are a frequent drinker, you should have regular health check-ups to detect alcohol-related diseases early and take early intervention measures.
Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
General health checkup package diamond Vip General Health Checkup Package Special General Health Checkup Package Comprehensive General Health Checkup Package Standard General Health Checkup Package Patient's examination results will be returned to your home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.
Reference source: healthline.com