This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Ngoc - General Internal Medicine - Endocrinology - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. Doctor has more than 10 years of studying, researching and working in the field of endocrinology.In humans, the salivary glands are exocrine glands whose main role is to produce saliva or secrete amylase. There are quite a few salivary glands scattered throughout the mucosa of the mouth, in which there are 3 main pairs of glands: parotid salivary glands, submandibular salivary glands and sublingual salivary glands.
1. Salivary gland anatomy
Salivary glands function because of a balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. When the parasympathetic fibers reach the salivary glands in the cranial nerves, the parotid glands receive fibers traveling in the pharyngeal cord through the auricular ganglia and the sublingual salivary glands, and the submandibular salivary glands receive the fibers that travel in the pharynx. facial cord through the submandibular ganglion.All parasympathetic and sympathetic stimulation increase salivation, which acts with the following role:
Endocrine role: With this role, the salivary glands ensure the proliferation of central organs tissues such as bones, teeth, cartilage, elastic fibers, connective and blood-forming organizations, reticuloendothelial system.... Digestive role: The salivary gland will have the role of wetting and dissolving food, and at the same time fortifying it. taste and starch hydrolysis. Protective role: The salivary gland ensures the role of washing away bacteria, creating alkaline pH, bactericidal substances, antibodies to protect and support remineralization of tooth enamel. Excretion role: Accordingly, foreign substances will be detected quickly when testing saliva.
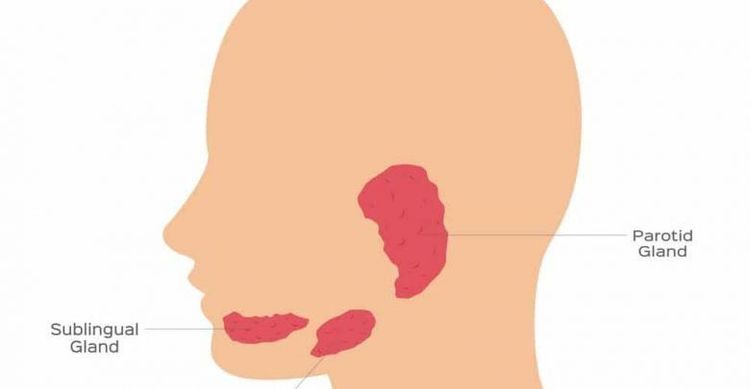
Mọi sự kích thích phó giao cảm và hệ giao cảm đều làm tăng tiết nước bọt
2. Major salivary glands
In terms of secretion, the human salivary glands are divided into 3 types of glands:Water glands: Parotid salivary glands Mixed glands: Submandibular salivary glands Mucus: Sublingual salivary glands 2.1 Parotid salivary glands Water glands The parotid gland, also known as the parotid gland, is one of the major salivary glands in many mammals. In humans, the parotid salivary glands are located on both sides of the mouth and in front of the ears. These are the two largest salivary glands. Each parotid salivary gland wraps around the upper jawbone and secretes saliva through the Stensen tube, to facilitate chewing, swallowing and the digestion of food.
In terms of external appearance and relation, the parotid salivary gland has 3 faces, 3 borders and 2 poles:
Outer surface: The outer surface is covered with skin and superficial fascia, in the subcutaneous tissue there are facial branches of The auricular nerve is large and the lymph nodes are superficial, this face is located very shallowly, so when there is inflammation and swelling, it can be very clearly seen. Anterior: The anterior aspect of the parotid salivary gland is pressed against the posterior border of the ascending branch of the mandible, the sphenoid muscle, the occipital muscle, and the sphenoid ligament. This anterior aspect is related to the maxillary vessel bundle and the ototemporal nerve at the level of the mandibular cervical defect. Posterior: The posterior surface of the parotid salivary gland is related to the mastoid process, bordering the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the stymoid process and the styloid muscles, the abdomen posterior to the biceps muscle. The external carotid artery, after slicing through the gap between the stylohyoid muscle and the lingual gyrus, will lie down and dig into the posterior surface of the parotid salivary gland and then enter the gland, vein, and internal carotid artery in and behind. More than separated from the parotid salivary gland by the styloid process and the styloid muscles, the facial nerve descending from the foramen magnum also enters the gland in the posterior superior portion of this face. Components located in the parotid salivary gland include the splenic nerve between the lobes and the blood vessels of the gland. The parotid ductal part is formed by the fusion of the two main branches in the anterior part of the gland, which exits from the gland at the anterior border.
2.2 Submandibular Salivary Gland The % volume contribution of the submandibular salivary glands will be reduced and at the same time the % contribution of the parotid glands will increase to 50%.
The submandibular salivary gland is the second largest gland after the parotid salivary gland, located in the submandibular triangle on the inner surface of the lower jaw bone, the submandibular salivary gland has 2 shallow and deep parts connected at the posterior border of the muscle. The jaw is hot and separated from the parotid gland by a fascia.
In terms of external appearance and relation, the superficial part of the submandibular salivary gland occupies most of the gland and is located in the submandibular triangle and has 3 faces and 2 ends:
The superior lateral surface of the gland lies close to the medial surface of the bone mandible and has a grooved facial artery in the posterior superior portion of this face. The inferior surface of the gland is covered with skin, the subcutaneous tissue and the superficial cervical fascia are covered. The medial surface of the gland lies close to the muscles of the supraclavicular region, related to the deep facial artery and sublingual nerve of the gland. The posterior part of the submandibular salivary gland is a reticular process extending anteriorly by the glandular duct, inferiorly related to the sublingual nerve and the submandibular ganglion.
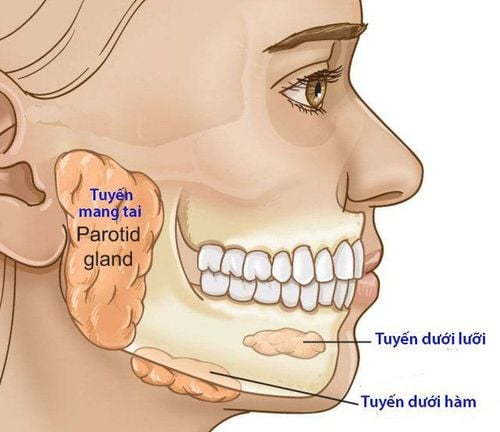
Tuyến nước bọt ở người được chia làm 3 loại tuyến: tuyến nước, tuyến hỗn hợp và tuyến nhầy
The salivary gland system in the human body is very susceptible to bacterial invasion and causes diseases such as salivary gland inflammation, salivary gland tumor,... Therefore, each person needs to actively learn and protect the body. body, especially in eating and oral hygiene to avoid pathogens.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.