This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Nguyen Chi Quang, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. Dr. Quang has many years of deep professional experience and strength in the treatment of obstetric and gynecological diseases.Ovarian cysts account for about 80% of ovarian tumors in general, are a very common tumor in women, especially women of childbearing age. Ovarian cysts come in many forms with many different complications, most of which are dangerous and life-threatening to patients of all ages.
1. What is an ovarian cyst?
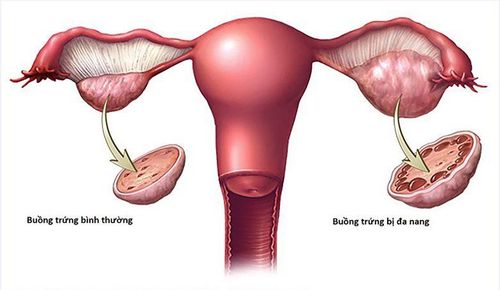
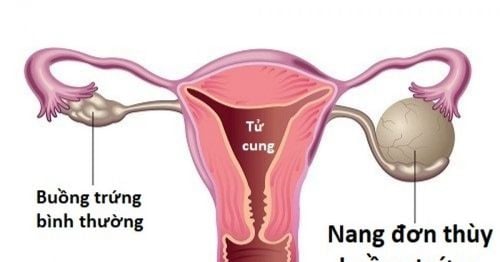
An ovarian cyst is an abnormal growth on the ovary. Ovarian cysts can develop from the tissues of the ovaries or from the tissues of other organs in the body. Ovarian cysts exist in many different forms with many different complications, in which, ovarian cyst torsion is a dangerous and life-threatening complication.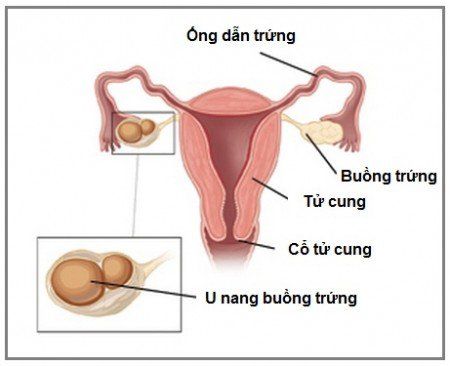
2. Common types of ovarian cysts
Functional cysts: Tumors arising from endocrine dysfunction of the ovary, anatomically, the ovarian organization has not changed. Functional ovarian cysts are usually benign, can go away on their own and are not dangerous. Organic cysts: There are changes in ovarian histology in these tumors, so these are tumors with a high risk of carcinogenesis. In which: Ovarian cyst is the most common form, accounting for about 40% of ovarian cysts. If on the surface of the tumor there are comb-shaped proliferative blood vessels, or there are papillae on the surface or inside the tumor, which are signs of cancer. Ovarian mucinous cysts: make up about 20% of ovarian tumors. Ovarian dermoid cysts: make up about 25% of ovarian tumors. Cystic endometriosis: The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus, consisting of 2 parts, the base part is almost unchanged with the menstrual cycle, during pregnancy and childbirth. However, when the endometrial tissue grows right on the surface of the ovary, it destroys the healthy ovarian tissue. Tumors often cause pain, many adhesions block the fallopian tubes, causing infertility.3. Diagnosis of ovarian cysts
Can ultrasound detect ovarian cysts? Usually, to diagnose ovarian cysts, your doctor will perform a pelvic exam. In addition, to accurately detect cystic tumors, the doctor may prescribe ultrasound for the patient. After 6 to 8 weeks, the patient may be asked to come back to monitor the tumor.Other methods that may be used for diagnosis include CT or MRI. Patients may have blood tests for certain types of cysts. In cases where the cyst is large or persistent, or where cancer is suspected, a biopsy may be required (a biopsy is a procedure where a small sample of tissue is removed and examined under a microscope).
4. Are ovarian cysts dangerous?
For each patient, complications may appear sooner or later. When symptoms are obvious, the tumor has grown and pressed on the surrounding organs, causing many dangerous complications, even affecting life. Some dangerous complications include:4.1. Twist the cyst
Occurs with any type of tumor, the small, long-stemmed, non-adherent tumors are susceptible to torsion.4.2. Cyst rupture
Cyst rupture occurs when the fluid pressure in the tumor is too great, causing the cyst to rupture. The patient presented with sudden abdominal pain, continuous pain, lower stomach and two painful, responsive pelvic fossa. In some cases, the rupture of the cyst causes internal bleeding, the patient can be shocked and lose blood. On vaginal examination, the tumor is difficult to identify, and the uterus is painful when moving. If not treated in time, it can be life-threatening.4.3. Compressing the surrounding organs
This complication usually occurs quite late, when the tumor has grown for a long time and is large in size. As a result, the tumor presses on the bladder causing urinary incontinence, compresses the rectum causes constipation, sometimes compresses the ureter causing pyelonephritis, even very large ovarian tumors compress the inferior vena cava causing collateral circulation, edema of the lower extremities, ascites,...Ovarian cyst is a common disease in women, if not detected and treated promptly, it will cause dangerous complications. Therefore, women should have regular gynecological examination every 4-6 months to detect early abnormal signs of ovarian cysts as well as other gynecological diseases.
Currently, Vinmec is implementing a basic gynecological examination and screening package to help customers:
Early detection of inflammatory diseases makes treatment easy and inexpensive. Screening for early detection of gynecological cancers (such as cervical cancer). When registering for the Basic Gynecological Examination and Screening Package, customers will receive:
Gynecological examination. Transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries. Bilateral breast ultrasound. Tests such as: Treponema pallidum rapid test, Chlamydia rapid test, taking samples for cervical-vaginal cytology, bacterial staining (female vaginal fluid), HPV genotype PCR automated system, .. Total urinalysis by automatic machine.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.