This is an automatically translated article.
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops inside a woman's ovaries. Today, the incidence of cysts and fibroids tends to increase, especially among women of childbearing age. So do cysts need surgery?1. What is an ovarian cyst?
The ovary is a female reproductive organ about the size of an almond. Each woman will have 2 ovaries, located symmetrically on either side of the uterus.Ovaries have 2 main functions which are:
Exocrine function: Starting from puberty, the ovaries will release eggs with a cycle of about 28-35 days/time.
Endocrine function: Release of female sex hormones including estrogen and progesterone, which play an important role in female reproduction. Ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled mass inside or above the ovary. This cyst can appear on one ovary or present on both sides at the same time. Most ovarian cysts are benign, only about 10% of cysts have the risk of causing dangerous complications affecting the ability to conceive and a woman's health.
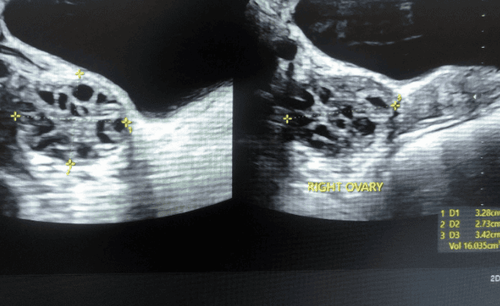
U nang buồng trứng là một khối chứa dịch lỏng nằm bên trong hoặc ở trên buồng trứng
2. Types of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts have many different types, of which there are 3 main types: functional cysts, organic cysts, and endometriosis cysts.2.1. Functional cyst
This is the most common type of cyst. Mainly occurs in people who are still menstruating. These cysts are mostly benign, formed due to physiological disorders during development rather than physical damage to the ovary, so they can disappear quickly after a few months.Functional cysts are divided into 3 subtypes including:
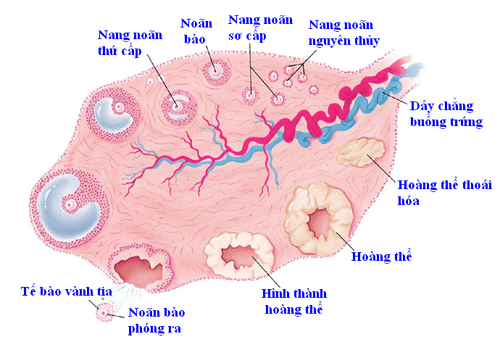
Ovarian cysts: During each menstrual cycle, the ovary releases an egg. This egg develops inside a small sac called a cyst. As the egg matures, these follicles burst to release the egg. However, if the follicle does not open as it should, ovulation will not occur and the follicle will continue to grow in size and form a cyst. Ovarian cysts often cause a delay in menstruation, so many people mistakenly think that they are pregnant. The corpus luteum cyst: Once the ovum capsule opens, the egg is released. The stimulation of the hormone progesterone causes the empty cyst to shrink and degenerate to form the corpus luteum. But if, for some reason, this empty cyst does not atrophy but grows even larger and accumulates fluid inside, it is called a corpus luteum cyst. Luteal cysts are usually larger than ovarian cysts, they can grow to about 10cm in diameter. Most of these cysts will go away on their own after a few weeks. However, they can also cause bleeding complications or painful ovarian torsion. Thyroid cyst: is the rarest type of functional cyst, mainly appearing in women undergoing treatment for infertility, having glioblastoma or multiple pregnancies. Thyroid cysts form when the follicles are overstimulated (due to too high a concentration of HCG) making the egg unable to be released and lutealized.
2.2. Physical cysts
Physical cysts are insidious growths that last for many years. This type of cyst forms as a result of anatomical damage to the normal parenchyma of the ovary. Physical cysts include the following 3 types:Water cyst: is a cyst with a smooth smooth shell that is quite fragile, this cyst has a long stalk, inside is a clear or brown liquid, sometimes on the face On the inside or outside of the capsule shell, small papillae appear. These papillae can be a potential sign of ovarian cancer in the future, especially as more papillae appear. Mucinous cyst: is a cyst with a thicker shell than a water cyst, the outer shell is white, the fluid contained inside the cyst is thick and yellow. Mucinous cysts can grow up to tens of kilograms in weight and easily adhere to nearby organs. However, the risk of malignancy of this type of cyst is not high. Dermoid cyst: dermoid cyst, also known as skin cyst, average size < 10cm but heavy weight, easy to cause torsion. Dermoid cyst has a thick and smooth shell, inside contains hair, teeth, stratum corneum, and residues such as bean residue. This is because these structures form from embryonic cells. Dermoid cysts can affect anyone from children to adult women and menopause. In particular, about 10% of women have this type of cyst during pregnancy.
2.3. Endometrial cyst
During menstruation, the endometrial lining sheds and flows with the blood out of the vagina. However, in some cases, endometrial cells are still left behind, drifting to the ovaries, they will grow thick due to the influence of sex hormones and cause endometrial cysts.3. When do ovarian cysts not need surgery?
After the ultrasound and the necessary tests, your doctor will tell you if the cyst requires surgery and what to do next.Usually the cyst is benign as soon as it is detected without requiring immediate surgery. The tumor will be monitored for an additional 2-3 menstrual cycles, usually 60 days. You need to return to the hospital for regular check-ups as scheduled by your doctor to check the progress of the tumor. If these tumors go away on their own, they're just physiological cysts, which means you won't need any further surgery or treatment.
In addition, the doctor will prescribe hormonal drugs (mostly birth control pills) to prevent new cysts from forming in the future.
4. Ovarian cysts how big should be operated on?
Ovarian cysts will be indicated for surgery in the following cases:If after the follow-up period, the cyst does not show signs of shrinking but continues to grow or has other complicated developments, the doctor will We recommend early surgery to prevent complications. The patient has a large ovarian cyst. Usually, cysts >5cm, especially >8cm, will be considered for surgery, whether they are functional cysts or organic tumors. Some cysts can grow very large, similar to the size of a watermelon. When the cyst is too large, it will press on neighboring organs and affect the function of these organs, so it should be removed immediately. Patient has endometriosis cyst. Through ultrasound, if the patient is found to have a cystic endometriosis, surgery is also needed. Because this type of cyst can be very cancerous and often occurs in young women, if not treated early, the patient will have infertility and many other dangerous complications. Physical cysts, especially mucinous cysts and teratomas, require early removal. Cysts are present on both ovaries. Cysts are cancerous or have signs of cancer. In case, the patient's cyst is suspected to be cancerous, the doctors will also intervene immediately to remove all the malignant cysts, prevent metastasis to preserve the patient's life. In some severe cases where cancer cells are present on both ovaries, the doctor will completely remove the ovaries, fallopian tubes and surrounding supporting tissues. At that time, the patient will no longer be able to reproduce. If women who have reached menopause no longer wish to have children, if a cyst is detected, doctors will recommend surgery and remove the ovaries to prevent recurrence. Cysts show signs of rupture or torsion. These are 2 very dangerous complications. A ruptured or twisted cyst will cause acute blood loss, acute peritonitis. If not treated in time, the patient can lose their life. In pregnant women, if they suddenly have these two complications, they must also intervene immediately, it may not be possible to keep the fetus, but the first rule is still to ensure the mother's life is safe. .
Thông thường, u nang có kích thước >8cm sẽ được xem xét mổ
5. Current surgical methods for ovarian cysts
There are 2 methods of surgery for cysts: laparoscopic surgery and open surgery:5.1. Laparoscopic cyst surgery
It is the most advanced method today, trusted by patients and highly effective. Laparoscopic ovarian surgery is indicated for cases of cystic tumors that are benign, not too large and non-adherent, when there is inflammation of the fallopian tubes and in cases of breast cancer with indications to remove the ovaries. .In some cases, laparoscopic surgery cannot be used, such as patients who are in menstrual period, abnormal bleeding, conjoined masses, abdominal surgery many times, and cancer patients. ovary.
5.2. Open surgery cyst
In cases where the tumor is too large, or suspected that the cysts are malignant, doctors will apply open surgery. The disadvantage of open surgery is that the incision can become infected or stick to the intestines and the recovery time after surgery is often quite long.
Mổ nội soi u nang là phương pháp tiên tiến nhất hiện nay
6. Diet for ovarian cyst surgery
After surgery for cysts, patients need to pay special attention to abstaining and taking proper care to avoid the risk of the incision becoming infected and the tumor having the opportunity to recur.Absolutely stay away from red meats such as beef, buffalo, lamb... because they can increase the amount of estrogen in the blood, increasing the risk of recurrence of cysts and fibroids. Cases of open surgery can leave keloid scars, dark spots, and itching.
Seafood such as shrimp, crab, fish should be limited because it will itch the incision and can protrude the meat.
Fast foods that are not hygienic and nutritious, can also cause poisoning, abdominal pain... so they should not be used.
Banh chung, sticky rice and products from glutinous rice should not be eaten because it will cause festering or infection of the wound.
Water spinach is very easy to bruise and convex scars, so when the wound is newly operated, during the recovery period, it should not be eaten.
Drinks such as tea, coffee, soft drinks are mostly not good for the health of the patient after surgery, so it is necessary to limit their use.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the national health system, please book an appointment on the website to be served