This is an automatically translated article.
Of the 5 hepatitis viruses identified so far, the hepatitis C virus discovered in 1989 is considered particularly dangerous, due to its ability to easily turn into a chronic form of hepatitis, and then progress to cirrhosis. liver and liver cancer.
1. Characteristics of hepatitis C . virus
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) belongs to the family Flaviviridae, is an RNA core virus, 50 - 60 nanometers in size, with a single RNA chain and a lipoprotein envelope. Currently, hepatitis C virus is classified into types I, II, III, IV, V and VI. These types differ in their epidemiological distribution and pathogenicity. In particular, type II of hepatitis C virus has the highest frequency of converting to cirrhosis. Hepatitis caused by HCV has an incubation period of 30 - 120 days, with an average of 2 months.
Hepatitis C can be found anywhere in the world. The highest rates of HCV infection are among injecting drug users and those with bleeding, transfusion-related diseases. There is currently no vaccine against hepatitis C.
2. How is hepatitis C transmitted?
Hepatitis C is usually transmitted when the blood of a person infected with the hepatitis C virus enters the body of an uninfected person. Today, most people get this infection by sharing needles or other items to inject drugs.
Medical worker stabbed with a needle while working The child was born to a mother who was positive for hepatitis C. Sharing certain items with someone who has the hepatitis C virus (such as razors, toothbrushes, etc.) Have sex with someone who has the hepatitis C virus.
3. Pathogenicity of hepatitis C . virus

Virus viêm gan C (HCV)
HCV causes acute hepatitis and tends to become chronic in most patients with infection. In an experimental infection model in apes, it was shown that in acute hepatitis C there is little necrosis in hepatocytes in the early stages, viral RNA is found in the liver tissue and persists for several weeks.
Acute HCV hepatitis does not lead to acute liver failure, unless it occurs in individuals with a pre-existing chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). About 50-70% of acute hepatitis C will progress to chronic.
Mechanism of liver damage in chronic hepatitis C is not only viral but also linked to other autoimmune diseases of the body. Complications of chronic hepatitis C eventually lead to cirrhosis in 20-25% of cases and hepatocellular carcinoma.
4. How long does the hepatitis C virus live in the natural environment?
Hepatitis C virus can live outside the body, at room temperature for at least 16 hours but no longer than 4 days.
5. Is the hepatitis C virus transmitted when bitten by a mosquito or insect?
Currently there is no evidence of hepatitis C virus infection from mosquito bites or other insect bites from infected person to healthy person.
6. Hepatitis C virus is sexually transmitted
The risk of sexually transmitting hepatitis C is possible but is thought to be low. The risk of transmission is increased for people who have sex with many people, who have sexually transmitted diseases, who have rough sex, or who have HIV. However, more research is needed to better understand how and when the hepatitis C virus can be transmitted through sex.
7. Hepatitis C virus spreads through household contact
This is still possible, but quite rare, unless there is direct contact of the damaged skin with the blood of someone living with the hepatitis C virus living in the house.
8. Long-term consequences of hepatitis C
It is estimated that for every 100 people infected with hepatitis C virus, 75-85 people are chronically infected with hepatitis C virus. Among them:
There are 60 - 70 people with chronic liver disease There are 5 - 20 people with cirrhosis after a period of 20 - 30 years There are 1 - 5 people who die from cirrhosis or liver cancer.
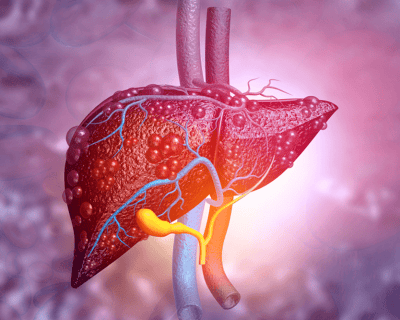
Viêm gan C mạn tính có thể chuyển thành xơ gan, thậm chí là ung thư gan
9. Does hepatitis C go away on its own?
About 15 - 25% of patients infected with hepatitis C virus can recover on their own (the hepatitis C virus is gone in the body) without treatment. For the remaining 75 - 85% of cases, the disease does not go away on its own, it is necessary to treat to avoid long-term complications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.