This is an automatically translated article.
Pulmonary valve angioplasty is a technique indicated for the treatment of pulmonary valve stenosis. This method is highly effective and successful, reducing the risk of unwanted complications.
1. A brief overview of the pulmonary valve angioplasty technique
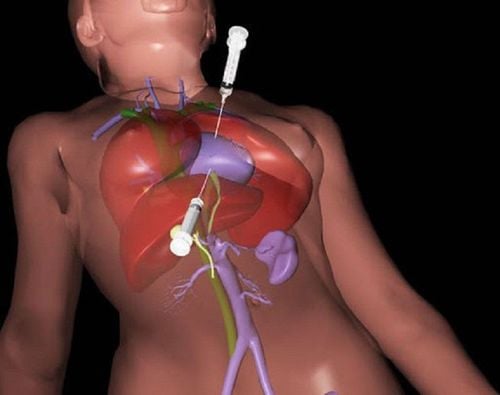
Pulmonary valve is a bird's nest valve located in the position between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle. Pulmonary valve stenosis is a common pulmonary valve disease, when severe stenosis can cause right heart failure. This is the fourth most common congenital heart disease (8-12%). Pulmonary valve stenosis is caused by sticking to the edges of the pulmonary valve, preventing the leaflets of the pulmonary valve from opening during systole, obstructing the flow of blood from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery during systole.
The main treatment for cases of pulmonary stenosis is pulmonary angioplasty. This technique has a high success rate, positive results and up to 75% reduction in transvalvular differential pressure. This is considered the first choice of treatment for patients with isolated pulmonary valve stenosis.
2. Technical procedure of pulmonary valve angioplasty
2.1 Preparation of Implementation Personnel: 2 doctors proficient in interventional cardiology, 1 nurse and 1 experienced technician; Patient: The procedure is explained, consents to the procedure, and the consent is signed. Patients and their families need to prepare a complete medical record according to the regulations of the Ministry of Health. Patients were also evaluated by ultrasound prior to the procedure; Technical tools: Table of tools (including sterile bowls, sterile gloves, surgical gowns and sterile acidimeter), three-prong tools, sterile gauze bandages, pumps of 5ml - 10ml - 20ml capacity - 50ml, arterial access kit (includes 1 puncture needle, 1 sheath kit and local anesthetic), right heart catheterization device, pulmonary valve dilatation device (includes balloon, balloon tensioner) and loop wire), needle for suturing the site of the inlet vein.
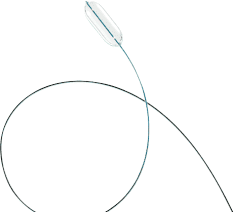
Hình ảnh bóng nong van động mạch phổi
2.2 Carrying out a large-scale disinfection technique in the area of the blood vessel entrance; Access to the right femoral vein; Inject Heparin 50 units/kg or 5000 units for adults; Cardiac catheterization must measure right ventricular pressure, pulmonary artery pressure, evaluate pressure gradient across the pulmonary valve; Photograph of the right ventricle in AP position and 90° left tilt. The doctor evaluates the pulmonary valve, the right ventricular outflow tract and the location of the pulmonary valve stenosis; Measure the size of the pulmonary valve annulus; Drive the MP catheter with guidewire 0.018 - 0.035 up the pulmonary artery. It is best to avoid the left pulmonary artery to ensure the best fixation of the guidewire. In infants, if the child has a ductus arteriosus, the doctor will push the guidewire through the ductus arteriosus, down the descending aorta; Mix contrast agent with physiological saline to inflate the balloon; Bring the balloon to the patient's right atrium with a loop wire. Insert the balloon through the orifice of the pulmonary valve and then gradually inflate the balloon to separate the pulmonary valve. The doctor usually inflates the balloon about 3-4 times, each time inflating the balloon for no more than 10 seconds; In adults, if the diameter of the pulmonary valve annulus is more than 20mm, the technique of 2 balloon dilation can be used, using 2 balloons to expand the valve at the same time. At that time, it is necessary to bring both guidewires to the pulmonary artery and slide the 2 balloons at the same time; Inoue balloon technique: In adults, the doctor can drive the Inoue balloon directly up through the pulmonary valve if the valve is not too narrow, or use a wire loop to bring up the pulmonary artery and then slide the Inoue balloon up to dilate the valve. pulmonary artery; After angioplasty, the doctor pulls out the balloon, keeping the guidewire inside the pulmonary artery; Take right ventricular angiogram, evaluate the pressure gradient across the pulmonary valve, pulmonary artery pressure, and pressure gradient across the valve after dilation; Remove the instruments and suture the venous access site. 2.3 Post-procedure monitoring Monitor vital functions such as pulse, blood pressure, SpO2 ; Monitoring patients, early detection of complications after pulmonary valve angioplasty such as pericardial effusion or contrast agent allergy; Monitor the position of the venous access to see if there is a hematoma, bleeding, infection, arteriovenous catheterization,... or not.
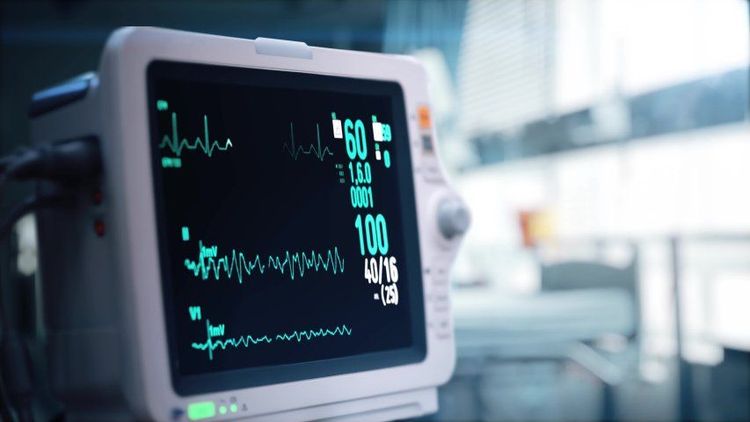
Sau nong van động mạch phổi, người bệnh cần được theo dõi các chỉ số chức năng sống
2.4 Risk of complications and intervention methods Pulmonary valvular angioplasty can cause some risks of complications, so it is necessary to have timely intervention methods:
Rupture of the right ventricular outflow tract causing pericardial effusion: Need manage acute pericardial effusion with drainage and prompt surgery; Pulmonary regurgitation after angioplasty: Usually does not cause significant effects, should be monitored and intervened if necessary; Right ventricular outflow tract spasm causes hypotension and hypoxia: It should be managed by intravenous fluids and use of beta-blockers; Other complications: Tricuspid valve regurgitation caused by manipulation of ligaments, bleeding or thrombosis of the femoral vein, transient arrhythmias, etc., should be handled according to the standard protocol. Pulmonary valve angioplasty is a safe and effective procedure in the treatment of pulmonary stenosis alone. However, in order to ensure a faster, safer procedure and less risk of complications, patients need to choose a reputable medical facility with good doctors and good equipment. equally necessary.
Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading centers in the country for examination, diagnosis, screening and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Vinmec not only has the convergence of a team of experienced and reputable leading experts in the field of surgical treatment, internal medicine, interventional cardiac catheterization, but also has a system of modern equipment, on par with The most prestigious hospitals in the world such as: MRI 3 Tesla (Siemens), CT 640 (Toshiba), high-end endoscopy equipment EVIS EXERA III (Olympus Japan), high anesthesia system Avace level, Hybrid operating room according to international standards... Especially, with the space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring patients the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.