This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Trinh Thi Phuong Nga - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. The doctor has nearly 20 years of experience in diagnostic imaging.Parathyroid disease occurs mainly in women, aged 50 to 60 years. The disease is diagnosed quickly through testing calcium and PTH hormone levels in the blood.
1. What is parathyroid disease?
Parathyroid disease is a disease that occurs in the pea-sized (usually 4) parathyroid glands, located near the thyroid gland. This is where parathyroid hormone (PTH) is produced, which helps maintain blood calcium levels. The disease affects the function of the parathyroid glands in maintaining the balance of calcium levels in the body.There are three types of parathyroid disease: Hyperparathyroidism, parathyroid cancer, and hypoparathyroidism.
1.1. Hyperparathyroidism Hyperparathyroidism (HPT) is the most common parathyroid disease. It occurs when one (or several) of the parathyroid glands overproduce the hormone PTH, causing hypercalcemia. Usually, the function of the parathyroid gland is affected by a benign tumor on the gland.
Hypercalcemia can cause serious health problems, including:
Osteoporosis Kidney stones Cardiovascular disease High blood pressure Most people with primary hyperparathyroidism have no symptoms. Some patients may experience mild symptoms such as:
Muscle weakness Fatigue Increased need for sleep Body weakness Bone and joint pain In people with more severe hyperthyroidism, the disease can causes symptoms such as:
Loss of appetite Nausea Vomiting Constipation Memory impairment Increased thirst and frequent urination When two or more parathyroid glands are overactive, the disease is called parathyroid hyperplasia. In some cases, patients develop hyperparathyroidism secondary to kidney failure.

1.2. Parathyroid cancer Parathyroid cancer can also cause hyperparathyroidism. This very rare disease usually occurs in people around the age of 50. It is likely to recur at the same site after treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the risk of disease recurrence by keeping blood calcium levels stable.
Detecting parathyroid cancer early will help the treatment process take place more smoothly and effectively. Often, in people with parathyroid cancer, the danger comes not from the cancer but from hypercalcemia and other related complications.
1.3. Hypoparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism is a condition in which the body does not produce enough PTH hormone, causing hypocalcemia. It often occurs after neck surgery, damage to the parathyroid glands, can also be due to autoimmune phenomena in the glands.
Hypoparathyroidism increases the risk of:
Addison's disease: Addison's disease occurs when the adrenal glands do not make enough PTH hormone. The disease is caused by autoimmune hypoparathyroidism. Cataract . Parkinson's disease: Parkinson's disease is a disease that progresses over time, affecting brain function and causing abnormal movements in combination with many other symptoms. Pernicious anemia: Pernicious anemia is a condition in which the body does not produce enough red blood cells due to a lack of vitamin B12. People with this condition are unable to absorb vitamin B12 from foods. It occurs only in autoimmune hypoparathyroidism.
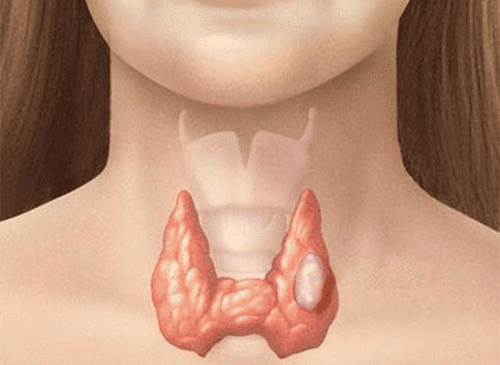
2. How is parathyroid disease diagnosed?
Diagnose parathyroid disease by testing calcium and PTH levels in the blood.After diagnosis, other tests are prescribed to assess severity:
Bone densitometry (DEXA, DXA): Measurement of bone density using a very small amount of ionizing radiation to create an image of the inside of the body (usually the lower spine and bilateral thighbones). This is a simple, quick and non-invasive method. Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It is an easy, safe, non-invasive, and non-radiative examination method. Whole-body CT scan: A CT scanner uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to create three-dimensional (3D) images. CT Scanner may be indicated for contrast injection. This procedure is usually done in the radiology department and the images are analyzed by a radiologist. Whole-body MRI: An MRI uses a strong magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed images of the inside of the body. 25-hydroxy-vitamin D test: People with primary hyperthyroidism are often vitamin D deficient. This test helps monitor vitamin D levels in your blood and determine if you need a vitamin D supplement.
3. How is parathyroid disease treated?
Treatment of parathyroid disease by methods such as surgery (surgery), internal medicine (drugs), dietary supplements and monitoring the progression of the disease.3.1. Surgery Surgery to remove an abnormal parathyroid gland has a high success rate. Surgery can be beneficial for most people with primary, symptomatic hyperthyroidism. Surgical removal of an abnormal parathyroid gland improves bone density, reduces the risk of fractures, and reduces the chance of kidney stone formation. Before surgery, the patient is assigned to perform tests and imaging tests to locate the abnormal parathyroid gland:
Computed tomography (CT-4D): CT-4D provides images. more detailed images than conventional CT. It is performed using contrast medium with a balanced concentration and time ratio. CT-4D is especially useful when other imaging tests fail to detect an abnormal parathyroid gland. Ultrasound: An ultrasound may be used to look for tumors on one or more parathyroid glands. Surgery is then done in one of two ways:
Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy : The abnormal thyroid gland is removed through a small incision in the neck. During surgery, the patient needs local or general anesthesia to relieve pain and relax muscles. This surgery shortens the recovery time compared to more invasive types of surgery. Invasive parathyroidectomy: Surgery is more invasive than minimally invasive surgery. It is used when it is planned to test more than one parathyroid gland. Therefore, a larger incision is needed to examine all 4 parathyroid glands and remove all abnormally functioning glands. Surgery requires a maximum hospital stay of two days and general anesthesia.
Accordingly, surgical complications are very rare. Primarily damage to the nerves that control the vocal cords affects speech and chronic low calcium levels that require lifelong calcium and vitamin D treatment. Complication rates are higher for multiple parathyroid surgery.
People with primary hyperparathyroidism due to hypercalcemia and familial hypocalciuria should not have surgery.
3.2. Monitoring Some people with mild primary hyperparathyroidism may not need surgery, just monitoring the disease instead. This method is applied on the following subjects:
No disease symptoms Only slightly increased blood calcium levels Renal function and bone density are normal The disease monitoring process usually includes:
Physical examination according to time Blood tests to measure calcium levels and kidney function Bone density measurements 3.3. Medications Calimimetic drugs work to reduce the amount of hormone PTH produced by the parathyroid glands. Another medicine called cinacalcet is used to treat secondary hyperparathyroidism in people on dialysis – kidney failure and primary hyperthyroidism caused by parathyroid cancer. Cinacalcet is also approved for the management of hypercalcemia of primary hyperthyroidism.
3.4. Supplements People with low calcium levels due to surgery to remove the parathyroid glands need to take calcium supplements for the rest of their lives. Meanwhile, people with frequent hypocalcaemia or persistent muscle spasms are treated with intravenous calcium infusion.
Some people with primary hyperparathyroidism may be prescribed vitamin D supplements. However, patients need to pay attention to the amount, too much vitamin D and calcium supplements can cause hypercalcemia or urinary calcium. . This can affect kidney function, or even cause kidney failure.
Parathyroid disease is a dangerous condition and increases the risk of many other conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately diagnose the condition of the disease so that the doctor can direct the examination and timely treatment.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to be fully equipped with modern diagnostic facilities such as: CT, MRI, X-ray machine, Ultrasound, Bone density measurement,... . to diagnose parathyroid disease and general thyroid diseases.
After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease and stage, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The treatment process is always closely coordinated with many specialties to bring the highest efficiency and comfort to the patient. After undergoing the treatment phase, the patient will also be monitored and re-examined to determine whether the treatment is effective or not.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org