This is an automatically translated article.
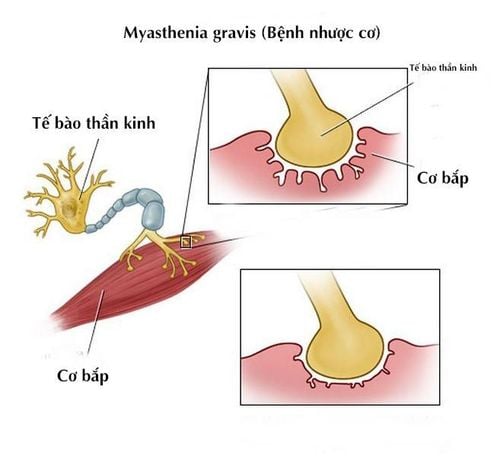
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disease that leaves extremely dangerous complications. Therefore, early recognition of signs will make treatment methods easier, minimizing complications to the human body.
1. Is myasthenia gravis dangerous?
Myasthenia gravis is a dangerous disease characterized by reduced muscle mobility. Weak muscles in myasthenia gravis are worse with activity and will improve and recover with proper rest. Accordingly, muscle weakness in the affected muscle areas can cause symptoms such as:
Shortness of breath because of weakened chest wall muscles; Difficulty chewing or swallowing makes it difficult for a person with myasthenia gravis to close their mouth, bottle, or drool; Moving up stairs, rolling objects, or making a difficult sitting position in a chair; Hard to say; Drop your head or bow your head down; Facial paralysis or weakness of facial muscles; Asthenia ; Change the voice; In addition, weak muscles around the eyes also cause double vision, difficulty maintaining gaze, drooping eyelids.

Nhược cơ khiến người bệnh mệt mỏi, suy nhược cơ thể
2. Complications of myasthenia gravis
In clinical studies, myasthenia gravis has 4 specific stages as follows:
Group I (weakness of the oculomotor muscles), paralysis only restricts movement in the extraocular muscles such as the levator fascia. A small number of cases in this group present with peripheral muscle paralysis but are at risk of severe disease progression. Symptoms often subside very quickly due to a good response to anticholinesterase drugs, the mortality rate in this group is low. Group IIa (mild generalized myasthenia gravis) involves the muscles of the skull, extremities and trunk, and respiratory muscles. Group IIb (patients with moderate generalized myasthenia gravis) with symptoms: double vision, drooping eyelids, slurred speech, swallowing or choking, difficulty eating, weak limbs, inability to exercise. Group III (acute sudden onset of myasthenia gravis), the disease progresses rapidly with full symptoms and reaches the most severe degree in 6 months. Injury to the respiratory muscles occurs early, accompanied by weakness of the oculomotor muscles, trunk and extremities, often with thymoma. In contrast to class I myasthenia gravis, people with myasthenia gravis are in this group, whose symptoms respond very poorly to anticholinesterase drugs. Severe episodes of myasthenia gravis are common and have a high mortality rate. Group IV (late myasthenia gravis), severe clinical picture but slowly progressing, appearing after patients had symptoms of mild myasthenia gravis for two years or more, the proportion of patients with adenoma The inhibition of this group was higher than that of groups I and II. The most dangerous complication of myasthenia gravis is acute respiratory failure due to paralysis of the respiratory muscles, if the chest collapses when breathing in, but the diaphragm still moves normally. If the epigastrium does not swell during inspiration, but the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles contract, the diaphragm is paralyzed, while the loss of swallowing reflex and sputum stagnation is paralysis of the pharynx. Respiratory depression is also caused by aspiration and as a side effect of anticholinesterase drugs, which cause bronchoconstriction and increased expectoration of phlegm. In addition, poor swallowing and coughing is also a cause of myasthenic complications such as aspiration and pneumonia, listening to the lungs has many moist crackles that contribute to worsening respiratory failure. .
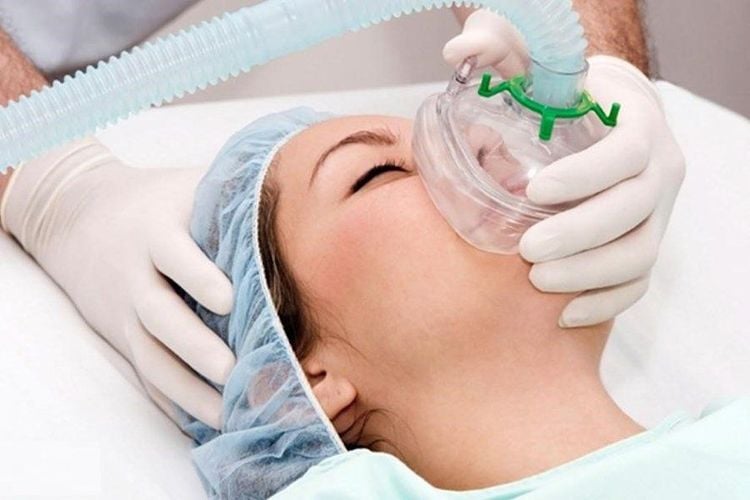
Một trong những biến chứng nguy hiểm của nhược cơ là bệnh suy hô hấp cấp
In addition, another complication of myasthenia gravis is severe myasthenia gravis. This is a condition in which the muscles are not paralyzed but in a very easy state of fatigue. When people with myasthenia gravis are asked to alternate movements such as opening and closing their eyes, or extending and flexing their fingers, after some movements it becomes more difficult and then impossible to perform. present, is no longer able to keep the upper eyelids in a normal state, but is at risk of ptosis. This condition makes sufferers always feel tired, exhausted, eat poorly, reduce or lose the ability to concentrate, affect relationships, and find it difficult to integrate into the community.
3. Treatment of complications of myasthenia gravis
Complications of myasthenia gravis have great effects on organs in the body, so early recognition of symptoms will minimize complications. In order for myasthenia gravis not to become a great obsession for people, the disease is treated as follows:
Myasthenia gravis: Myasthenia gravis is likely to progress rapidly or suddenly, muscle weakness increases rapidly, struggling, especially with respiratory disorders. At this point, you need to be treated with immediate injection of prostigmin 1mg intramuscular or 0.5mg intravenous. Then, in cases of myasthenia gravis, who still have respiratory impairment, they must open the trachea, insert a tube into the trachea, give artificial respiration, and bring the patient to an anesthetic facility for timely resuscitation. Choline crisis: In case of overdose of anti-myasthenic drugs, the patient may experience sweating, salivation, fatigue, vomiting, intestinal spasms, loose stools, burning sensation in the bladder, pupillary constriction, increased bronchial secretions, dyspnoea, pulmonary edema, muscle weakness, myoclonus, stiff jaw, cramps, slurred speech, swallowing disorders, respiratory disorders, indifference, expressionless face. Even many sufferers experience agitation, anxiety, fear, dizziness, headache, convulsions, confusion, dull consciousness, coma. In this case, atropinum should be injected immediately; discontinue use of the cholinesterase inhibitor immediately. If the disease progression does not improve significantly, doctors will have to apply intensive resuscitation measures and indications as in myasthenia gravis. In order for the complication of myasthenia gravis not to become too dangerous, the patient should pay attention to the factors that may contribute to the increase of myasthenia gravis. First, ensure nutritional factors, supplement foods containing high potassium, secondly, it is necessary to avoid bacterial infections of the mouth, pharynx, ... while using immunosuppressive drugs, do not arbitrarily use the drug without consulting a qualified doctor.
Vinmec International General Hospital currently has modern methods of diagnosing myasthenia gravis, performed by a team of highly qualified and experienced medical doctors, with a complete and advanced medical equipment system that will for accurate diagnosis of myasthenia gravis.
For detailed advice on methods of diagnosing myasthenia gravis at Vinmec, please come directly to the Vinmec health system or register for an online examination HERE.
MORE:
Mechanism of formation of myasthenia gravis (myasthenia gravis) How dangerous is myasthenia gravis in children? How is myasthenia gravis diagnosed?