This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Dr. Pham Quoc Thanh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalMagnetic resonance imaging is an imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create images, so how does an upper abdominal magnetic resonance imaging scan the pulse?
1. What is upper abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with visceral vasculature?
Upper-abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with visceral angiography is a method of magnetic resonance imaging to evaluate intra-abdominal blood vessels such as the abdominal aorta, the visceral artery, the superior mesenteric artery, etc. In addition, evaluate the morphology and abnormal lesions of the viscera. In addition to assessing the perfusion status, the lesions originate from the vascular system supplying blood to the organs.2. Indications and contraindications for upper abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with visceral vascular examination
Upper-abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with visceral vasculature is indicated and contraindicated in the following cases:
Indicated for patients with localized and diffuse pathologies of the visceral organs upper abdominal cavity. In cases where it is necessary to differentiate between tumor lesions and inflammatory lesions, benign lesions from malignant lesions. Absolute contraindications for patients during the scan are not allowed to wear electronic devices such as pacemakers, anti-vibration machines, hearing aids, cochlear implants, metal jewelry, pumping equipment. automatic subcutaneous drug, Neurostimulator... Metal clamps used in intracranial, orbital, vascular surgery under 6 months. If the patient's condition is severe, resuscitation equipment is needed next to the person. In addition, upper abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with visceral vasculature is relatively contraindicated for metal surgical clamps over 6 months. Patients' psychology such as: Fear of the dark, fear of narrow spaces, fear of being alone,...
Khi chụp cộng hưởng từ không được mang các thiết bị điện tử như: máy trợ thính
3. Need to prepare the patient before taking the scan?
It is necessary to prepare enough drugs to be used during the magnetic resonance imaging process, specifically:
Sedatives, Contrast drugs, Antiseptics for skin and mucous membranes. Accordingly, patients should also note the following:
Perform magnetic resonance imaging without fasting. You should only fast for 6-8 hours when performing cholangiography (MR cholangiography) Need to listen and follow the instructions of the medical staff in charge of the scan to make the working process go smoothly. Contraindications mentioned in section 2 Use specialized clothes for magnetic resonance imaging room Have a copy of the request for a scan from a doctor performing clinical diagnosis, complete medical records (if necessary)
4. Steps to conduct upper-abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with visceral vascular examination
In order for magnetic resonance imaging to bring high results, the patient needs to follow the exact steps required by the doctors and nurses:
Patient's lying position
The doctor instructs the supine position magnetic resonance imaging table. Select the position and position the receiver coil. Move the table into the machine's magnetic field and position the scan area. Before injecting magnetic contrast,
Pulse sequence 1: TruFISP is horizontal (without holding your breath), number of layers 19-24, thickness of layers: 5- 6mm. Pulse sequence 2: T2 Haste FS cross-sectional or vertical (holding breath), number of layers 24-29, layer thickness 5-6mm Pulse sequence 3: T2 Haste cross-sectional (breathing), from right diaphragmatic arch to place bisected aorta, number of layers 24-29, thickness of cut 5-6mm. Pulse sequence 4: T1 in phase transverse (breathing), from right diaphragmatic arch to bifurcation of the aorta, number of layers 24-29, layer thickness 5-6mm Pulse sequence 5: T1W out of phase transverse (holding breath), from right diaphragm to bifurcation of the aorta, number of layers 24-29, layer thickness 5-6mm Pulse sequence 6: T2W TSE 3D trigger: number of layers 40-72, layer thickness cut 1.5-1.75mm. Pulse sequence 7: Transverse T1 VIBE FS before contrast injection (holding breath), number of layers 64-72, thickness 2.7-3.3mm
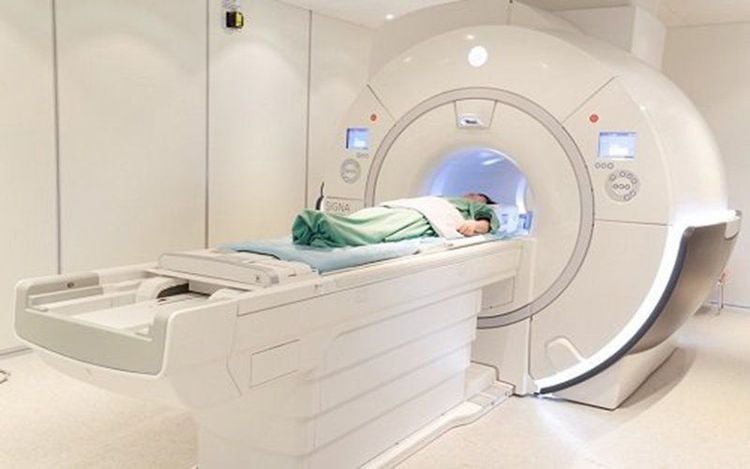
Khi chụp cộng hưởng từ tầng trên ổ bụng cần làm theo hướng dẫn của bác sĩ
5. Kinetic imaging technique after injection of magnetic contrast agent
Insert an intravenous line with an 18G needle, connected to a double-bore electric injection pump in which one contains the contrast agent and the other contains physiological saline. The usual amount of contrast agent used is 0.2ml/kg body weight. Pulse sequence 8: T1 VIBE FS, taken at 30 seconds, 60 seconds cross section (copy pulse sequence number 5) Pulse sequence 9: T1 VIBE FS (breath hold), shot at 90 seconds, cross section, number of layers 52-60, thickness of cut 2.7-3.3mm Pulse sequence 10: T1 VIBE FS, cross section, taken at 120 s (copy pulse sequence no. 5) Sequence pulse 11: T1 VIBE FS, cross section, taken at 180 seconds, number of layers 72-80, layer thickness 2.7-3.3mm Late capture: T1 VIBE FS at time points 5, 10, 15 min, cross section - applied to hemangioma or cholangiocarcinoma. After taking the scan, the technician prints the film and then transfers the image to the doctor's workplace for image analysis, perfusion parameters and diagnosis.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the upper abdomen with visceral vascular examination shows clearly the anatomical structures of the viscera in the upper abdomen. Through imaging, the perfusion status of the upper abdominal organs can be assessed and damage is determined.
6. Complications during the shooting process and how to handle it
When performing magnetic resonance imaging technique, if an accident occurs, the doctor should quickly handle the accident as follows:
Patient's state of fear, agitation, psychological panic. At this time, the doctor performing the scan needs to encourage, comfort and reassure the patient's spirit. In case of anxiety and fear, sedation can be used under the supervision of an anesthesiologist. Complications related to contrast agents are handled according to the issued regulations and guidelines of the Ministry of Health. Upper-abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with visceral angiography is an important technique in imaging, so you should visit as soon as possible to assess the lesion as well as perform this technique at the hospital. prestigious hospitals, supporting modern MRI machines and owning a standard examination room of the Ministry of Health and a team of qualified doctors.
Usually, the patient will receive the MRI results after 15-30 minutes, depending on the abnormalities in the body of the scanner, then the specialist will give the most accurate diagnosis. for patients. Upper abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with visceral vasculature will yield more accurate results than many other imaging techniques. From there, it helps doctors come up with the most effective treatment methods and regimens for patients, as well as detect many other diseases early. That's why it's so important to get an early diagnosis.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is the first unit to put into use a 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging machine with Silent technology, bringing outstanding advantages. Besides, the combination with a team of qualified and experienced doctors will help customers get accurate results in the shortest amount of time.
To schedule an MRI scan at Vinmec with today's most modern magnetic resonance machine system, you can immediately contact the nearest Vinmec International General Hospital facility system, or register for a medical examination. online HERE.