This is an automatically translated article.
The metastatic cancer is named after the primary cancer. For example, when a patient has liver cancer and liver cancer cells spread and grow to the lungs, the part of the cancer that is in the lungs is called liver cancer that has spread to the lungs.1. Why does cancer metastasize? How does metastatic cancer happen?
Cancer cells grow on their own in the midst of normal cells and they move from one area to another. Sooner or later, cancer cells will spread from the original site via the bloodstream or lymphatic route to other parts of the body and form new cancerous masses.When cancer cells are not detected and treated in time, they can grow and spread to other parts of the body. All cancer cells have the ability to metastasize and the places they most often go are:
Bones Lungs Liver Brain In addition, cancer cells can also migrate to the pleura or peritoneum and cause dangerous symptoms such as:
Shortness of breath Pleural effusion Respiratory bleeding. After getting rid of the main tumor, the cancer cells will find their way into the blood, lymphatic system, and surrounding tissues. After successfully infiltrating, the cancer cells will create new tumors along with new circulating blood vessels to nourish it. They can persist and develop for several years, after which the patient discovers the condition.
2. Signs of metastatic cancer
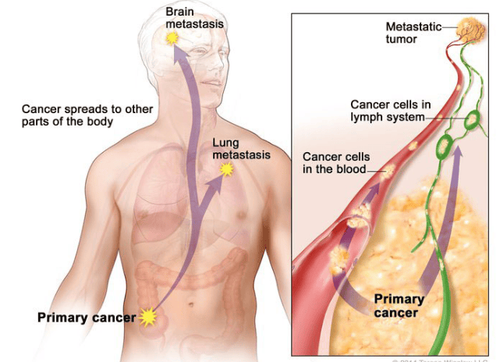
Các tế bào ung thư sẽ đi theo đường máu hoặc đường bạch huyết để di căn tới các cơ quan khác trong cơ thể
Some common signs make it easy for patients recognize metastatic cancer such as:
Pain. Fracture when the cancer metastasizes to the bone. Headache, dizziness, convulsions when metastases in the brain. Jaundice, swelling in the abdomen when metastases in the liver. Shortness of breath, coughing up blood when metastases in the lungs. Although all cancers can cause pain, pain is not necessarily the first symptom of cancer. However, there are patients without any manifestation of metastatic condition. Because when an organ metastasizes, it begins to shrink until its lymph nodes burst or undergo lysis.
3. What stage is metastatic cancer?

Ung thư di căn cần được điều trị phù hợp
T (Tumour) - primary tumor: is an indicator of the size of the cancer and how far it has spread into nearby tissue. T is numbered from 1 to 4, the larger the number, the larger the tumor size. N (Node) - lymph nodes: assesses how far the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. N is numbered 0 - 3, N0 means no lymph nodes have spread, N3 means there are many lymph nodes containing cancer cells. M (Metastasis) - Metastasis: This index is used to assess the extent to which cancer cells have spread to other organs and parts of the body. M is numbered as follows: M0 is cancer that has not spread; M1: The cancer has metastasized. Based on the combination of the above indicators, it will be assigned to each overall stage of the disease, designated I, II, III, IV according to each specific cancer type. Sometimes, these stages are further subdivided, more specifically by letters such as stage IIIa, IIIb,...
Stage I: usually only relatively small cancers and only present in the organ where it started (not yet metastasized). Stage II: usually when the tumor has grown but has not yet begun to spread into surrounding tissues. Stage III: Usually only when the cancer is larger and has begun to spread into surrounding tissues, cancer cells are already present in nearby lymph nodes. Stage IV: The cancer has spread to other organs in the body. This is a relative staging, but for each cancer there will be a specific and exact division. However, often when the cancer has metastasized, it is the final stage of the disease. At this point, the treatment will be more difficult.
Thus, if cancer is not detected and treated in time, cancer cells can move from the original location to other locations, other organs and start to multiply. form a new tumor that has the same characteristics as the original cancer. The treatment of late-stage metastatic cancer faces many difficulties and the effectiveness of vision is also significantly reduced. Therefore, when cancer is detected, it is necessary to conduct treatment immediately, to prevent the metastasis of cancer cells.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.