This is an automatically translated article.
Cancer biopsy test is an important test that is very valuable in effective cancer diagnosis and screening. This is a simple method but gives highly accurate results to prevent life-threatening risks.1. What is a biopsy test?
Tumor biopsy test performed by conducting surgery, procedure with the aim of taking a sample of cells or tissue at a suspected site such as tumor, lymph node to evaluate the presence of cancer cells. This is the gold standard in cancer diagnosis and staging. Once removed from the body, the tissues are examined under a microscope and can be chemically analyzed to determine whether the cells are malignant or due to other causes.
Cancer cell biopsies are highly accurate for diagnosing most cancers, and have advantages over other types of imaging tests such as: CT scans and X-rays because these tests can only help identify areas to be examined, but cannot distinguish between normal cells and cancer cells.
Biopsy is usually indicated in cases where abnormalities in the body are suspected due to cancer or other problems.
2. Types of biopsy tests
Types of biopsy tests may include:
Needle biopsy : Using a special long needle to pierce the skin into the kidney, liver, bone marrow, thyroid,... to take a tissue sample.
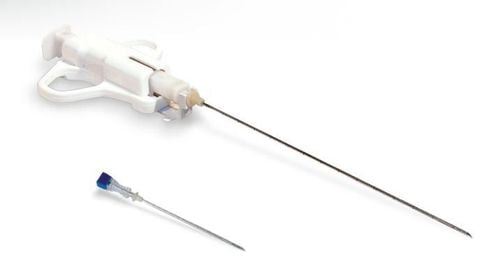
Kim sử dụng trong sinh thiết
Transmural Biopsy: Use specialized instruments to punch a small hole through the top layers of skin to obtain the necessary sample. Endoscopic biopsy: This method uses a flexible tube with a camera to go into parts such as the mouth, nose, urinary tract, and anus, allowing the internal organs to be viewed by the images projected on the screen. can be seen clearly. Excisional biopsy: Part or all of the tumor is removed to remove it. Intraoperative biopsy: During surgery, the doctor will take a small sample for examination and the results will be available in a few minutes.
3. Meaning of biopsy test
Biopsy tests are widely used in cancer diagnosis. By using specialized instruments to take tissue samples and check if the disease has spread beyond the biopsy area. If the results are positive, excision may be required, depending on the direction of the doctor's treatment. Histopathological examination is then performed to determine whether the lesion is benign or malignant. Above all, biopsy test to accurately distinguish the type of cancer, the nature, severity and spread of the disease for further treatment. Biopsy test not only helps you accurately diagnose the disease, but also supports the treatment of the disease in assessing the effectiveness of the treatment regimen. It is important that you observe abnormal signs in the body, because any subjectivity can potentially lead to cancer.
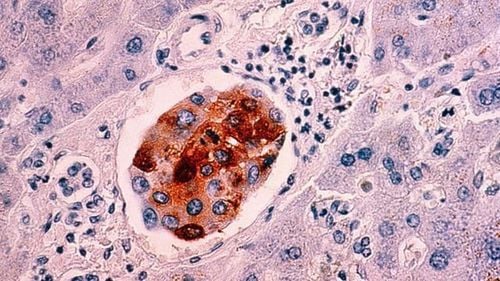
Xét nghiệm sinh thiết giúp chẩn đoán chính xác tình trạng bệnh
4. The process of performing a biopsy
To be able to perform a biopsy test, you need to pay attention to the following stages:
4.1. Before performing the biopsy The biopsy procedure may require some preparation on the part of the patient such as: Avoid eating or drinking for several hours before the test, it may be necessary to stop taking certain medications before the test, such as aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Depending on the type of biopsy, the patient will give you more specific instructions on what to do before the procedure.
4.2. During the biopsy After the specimen is obtained, the biopsy tissue samples will be sent to the laboratory. Specimens can be chemically processed, cut into very thin sections, and studied under a microscope. These slices are attached to a slide, and the remaining tissue is usually saved for later studies.
In the case of cancer, the examiner will need to determine if the sample is malignant or benign. If the case is malignant, they will assess how invasive or advanced the cancer is. As for benign cases, depending on the size of the tumor and whether there is a risk of becoming malignant or not, the doctor will offer an appropriate solution.
Finally, the examiner will prepare a report including any unusual or significant findings to send to the physician who ordered the biopsy. The results of the biopsy will depend on the type of biopsy. A simple case can be within 2-3 days, but a more complex case can take 7-10 days.
Mẫu sinh thiết
4.3. After the biopsy In most cases the patient can go home immediately after the procedure is completed. If a tissue sample is taken from an internal organ, the patient may need hospital monitoring. This specimen collection area may feel sore for a while.
5. Is biopsies of cancer cells dangerous?
Biopsy is generally safe, it is considered a very low risk procedure with the possibility of:
Having a small infection, the risk of infection requiring antibiotic treatment is usually very low. May affect nearby organs, eg: Injury to the intestines such as performing an abdominal biopsy. In addition, this test can also lead to bleeding, test at the wrong place, not get enough samples, leading to misdiagnosis and having to re-sampling which is frustrating and time consuming for the patient. According to the study, the cases of complications only accounted for more than 5% after the test. So this is still a safe technique.
6. Biopsy of cancer cells can be done in which organs?
6.1 Bones Bone samples are taken to see if cancer, infection, or abnormal cells are present. Often the outer layer of bone is sampled, unlike a bone marrow biopsy that involves the innermost core of the bone. A bone biopsy should be done after all imaging methods have been taken.
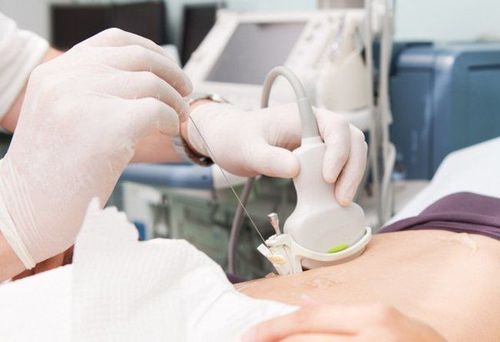
6.2 Bone Marrow Because blood cells form from bone marrow, a bone marrow biopsy is used in the diagnosis of blood cell abnormalities when the diagnosis cannot be made on blood. The method is used especially in the analysis of hematologic malignancies, such as leukemia and lymphoma.
Sinh thiết tủy xương
6.3 Lungs Common is pleural biopsy.
6.4 Gastrointestinal Endoscopy is the best approach to the upper and lower digestive organs. For example, biopsies of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum through the mouth; and biopsies of the rectum and colon through the anus. At present, most of the small intestine is still very difficult to biopsies because of its complex shape.
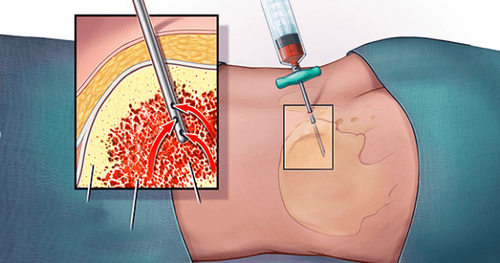
6.5 Liver Performed to detect cancer or diseases that cause liver enzyme disorders. For hepatitis, biopsies are not usually used for diagnosis, but merely to assess the body's response to therapy, or to assess the degree of cirrhosis. For Wilson's disease, liver biopsy is used to quantitatively assess copper levels in the liver.
Sinh thiết gan
6.6 Prostate Includes biopsies in the direction of the rectum, perineum, and urinary tract.
6.7 Nervous System Includes biopsies of the brain, meninges, and nerves.
6.8 Genitourinary system Includes biopsy of kidney, endometrium, and cervix.
Other organs: Including biopsies of breast, lymph nodes, muscles and skin
To perform biopsy tests at Vinmec International General Hospital, customers can go directly to the Health system Vinmec nationwide to visit or contact the hotline HERE for support.
MORE:
Role of biopsy in diagnosing skin cancer What is the role of bone marrow biopsy What is a tumor biopsy?