This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Man - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec International Hospital Da Nang.
Every month, the reproductive organs in a healthy woman prepare eggs in preparation for conception. The complex interaction between the pituitary gland, the ovaries and the uterus creates the perfect environment for ovulation for sperm and egg to meet, then the egg is fertilized, moves into the uterus and forms a fetus. . If the egg does not meet the sperm, then menstruation occurs.
1. What is fertilization?
Fertilization is the union of a male cell (sperm) and a female cell (ovum) to form a new cell, a fertilized egg or zygote. A zygote is a newly formed individual and develops at the earliest stage. In humans, fertilization normally occurs in the outer third of the fallopian tube. Conception is fertilization followed by implantation of an egg. After implantation, the egg develops into the fetus and its appendages (placenta, placenta, placenta and amniotic fluid).Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có hiểu đúng về dấu hiệu mang thai sớm?
Các dấu hiệu mang thai sớm không phải chỉ mỗi trễ kinh mà còn có rất nhiều dấu hiệu khác như xuất huyết âm đạo, ngực căng tức,… Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu dấu hiệu mang thai sớm thông qua bài trắc nghiệm này nhé!
2. The process of forming an embryo
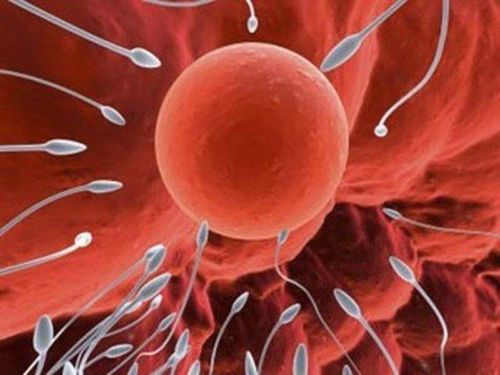
There are about 200 million sperm in each ejaculation.The cervix was previously sealed by a thick mucus plug, under the influence of estradiol produced by the follicle during development, it becomes thinner in the pre-ovulatory phase to allow sperm to migrate. The fastest and strongest movement passes through, the rest stays in the cervical area and sac and vagina.
In general, several million sperms reach the ovum in the appropriate time because sperm can live up to 1 week after release and ovum only 2 days after ovulation. When the sperm crosses the transparent membrane of the ovum, a fusion of the ovule and the spermatozoon occurs, the sperm nucleus is completely inserted into the oocyte cytoplasm, the tail leaving the head is retained outside the membrane. transparent, a cortical reaction prevents any other sperm from entering the ovum. Appears in the ovum one male and one female pronucleus. These two progenitors continued to develop separately, then came together and merged into one after the complete removal of the nuclear envelope. As a result, a new cell is formed to develop into the fetus and its appendages, which have a complete set of chromosomes (46) called an egg. Eggs develop and divide immediately.
The sex of the fetus is determined at the time of fertilization. If the sperm has a Y chromosome, it will develop into a boy (46XY). Conversely, if the sperm carries an X sex chromosome, it will develop into a female fetus (46 XX).
3. Egg movement
The embryo moves from the extra-fallopian third to the uterus for implantation. Embryo migration time: 3-4 days. After entering the uterus, the embryos are still alive for 2-3 days and then implant. Mechanism of movement: Due to the peristalsis of the fallopian tubes, the activity of the oviduct mucosal villi and the flow of fluid moving in the abdominal cavity is directed from the speaker of the fallopian tube to the uterine cavity.4. How do embryos nest?

The implantation process of the embryo takes place as follows:
The embryo begins to nest from 6 - 8 days after fertilization, the implantation time lasts 7-10 days, the implantation process ends on day 13 - 14 after fertilization. The implantation site of the embryo is usually at the fundus of the uterus. If the embryo implants in low positions, especially near the isthmus of the uterus, it will become placenta previa. The lining of the uterus when the embryo moves into the uterine cavity is at the most fully developed stage to prepare for the implantation of the egg (the fetal stage). Implantation process: The blastocyst adheres to the uterine lining, the pseudopods of the trophoblast adhere to the mucosa, called rooting. The cells of the trophoblast destroy the epithelial lining of the uterus, and the blastocyst penetrates deep into the epithelium. Days 9 - 10 blastocysts penetrate the columnar epithelium but are not deep in the stroma, the surface is not covered. Days 11-12 blastocysts are completely in the stroma. Days 13 - 14 epithelium develops and covers the egg nesting site.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article reference source: Webmd.com; Ucsfhealth.org; Medicalnewstoday.com