This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Tran Van Trong - Specialist in Pediatric Surgery, Plastic Surgery - Aesthetics - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.Electrical burns are caused by an electric current passing through the body, an arc flash, or clothing catching fire. The body converts electricity into heat, resulting in thermal burns. External signs of electrical burns do not accurately predict the actual extent of damage because tissues or internal organs can burn much more severely than the skin.
1. What is an electrical burn?
An electrical burn is a skin burn that occurs when an electric current comes into contact with the body. When electricity comes into contact with your body, it can pass through your body. When this happens, electricity can damage tissues and organs.Electrical burns can be mild or serious, and can even be fatal. Organs damaged by electrical burns:
Heart: the heart rhythm becomes irregular, can also stop beating Kidneys: the kidneys may stop working Bones and muscles: If the muscles are severely damaged, substances from inside damaged muscle cells can cause bleeding. This condition is called rhabdomyolysis. In some cases, electrical burns can cause injury to other organs. Some subjects may have an abnormal build-up of pressure in a muscle group, known as acute compartment syndrome Nervous system: people with electrical burns may experience unconsciousness, muscle weakness, or eye or ear damage. .
2. Causes of electric burns
Electrical burns occur when the human body is exposed to an electrical source, either directly or through a material that is conductive. For example, an employee could fall from a dump truck and instinctively grab a power line to catch himself, causing electrical injury; alternatively, the worker may be holding a pole in contact with the power line, causing him to be injured by the electric current. Or, for example, when a person becomes the victim of an electrical burn at home, such as when an electrical cord on an appliance is exposed and comes into contact with the human body, or when the power source is exposed to a stream of water to which an individual is also exposed. , for example, the hair dryer falls into the bathtub.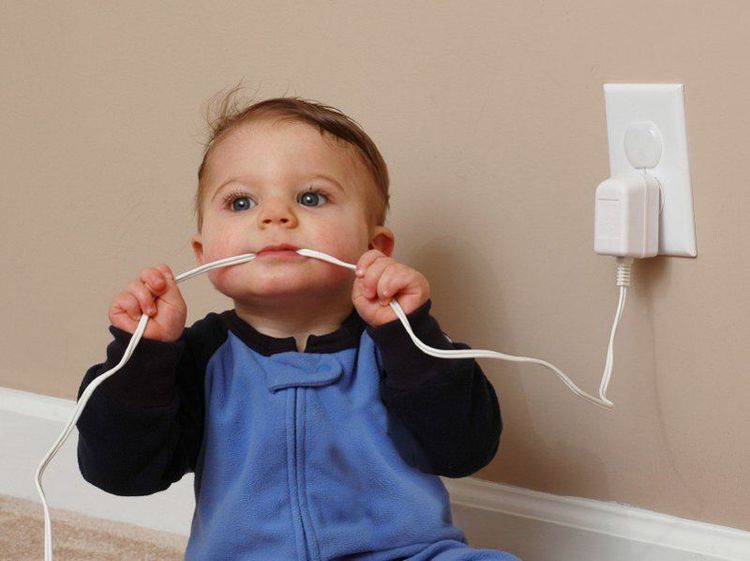
3. Symptoms of electrical burns
Symptoms of electrical burns depend on how much electricity is in contact with your body and how long the exposure lasts. Electricity can cause different types of skin burns, depending on which layer of skin is affected. The terms doctors use to describe different types of burns are:Superficial - A superficial burn affects only the top layer of skin. Red, dry and painful skin. When you press on the burn, it will turn white. Partial thickness - Partial thickness burns affect the top 2 layers of skin. The skin is red and may leak fluid or form blisters. Full Thickness - A full thickness burn affects all layers of the skin. Burns are usually painless, as the burned skin does not feel anything. The skin can be white, gray or black.
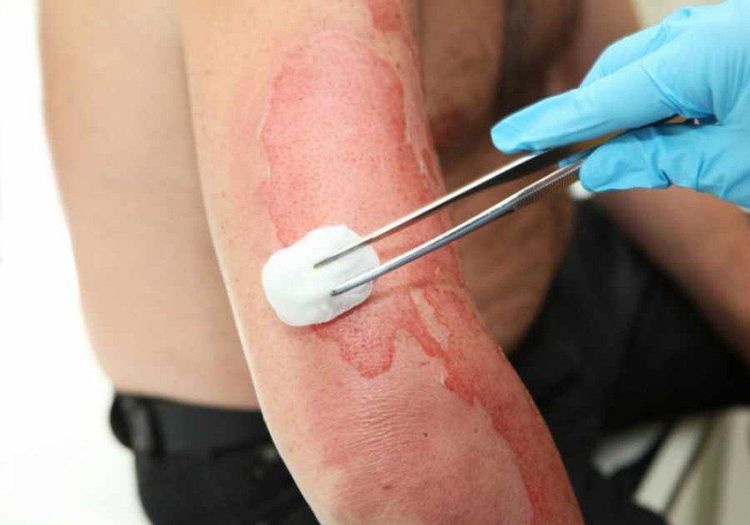
4. Complications of electric burns
Complications from electrical burns are similar to those of other thermal burns, such as infection (which can progress to sepsis), compartment syndrome, and rhabdomyolysis (due to extensive muscle damage from internal burns). In addition, people can be injured from being thrown from a power source or falling from a height (roofs, bucket trucks, ladders) due to electric shock and these injuries (fractures of long bones, fractures of the spine, tears, pneumothorax, etc.) requires appropriate examination and treatment.Possible cardiac complications. One can experience an arrhythmia, possibly even a fatal arrhythmia, at the time of the injury. Anyone with an arrhythmia or any chest pain or other typical heart-related symptoms is also at risk for an arrhythmia 24 to 48 hours after injury. Therefore, these patients should be under cardiac monitoring at all times. Any high voltage injury requires continuous cardiac monitoring for a minimum of 8 hours.
Especially children's electrical burns occur because a child puts a wire in his mouth and bites, causing a burn wound at the corner of his mouth. These patients can be treated at home with no other associated injuries. However, the most likely complication in this case is the delay in bleeding from the artery, which can occur about 7 days after the date of injury.
Due to the complex nature of the trauma organ with electric burns, it is necessary to accurately examine the state of the injury, not only looking at the external injury because the internal damage is really dangerous.
5. Treatment of electrical burns
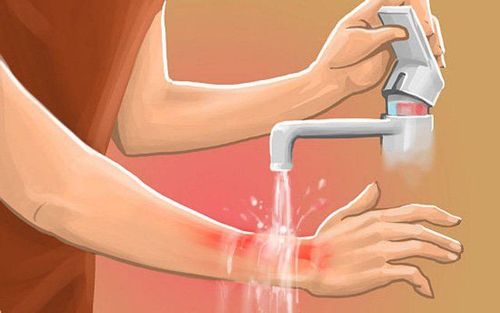
Treatment depends on the type of skin burn you have and its severity. First aid for minor electrical burns may include:Cooling the burn - You can place a cool cloth over the burn or soak it in cool water. Do not put the bandage on the burn. Cover the burn with a clean bandage - Your doctor may also recommend or prescribe a cream or ointment to soothe the skin or prevent infection. Treating Pain - To ease your pain, you can elevate the burned part of your body. For example, you can prop your foot or foot on a pillow. You can also take an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as acetaminophen (sample brand name: Tylenol) or ibuprofen (sample brand name: Advil, Motrin). Get a tetanus shot, if it's been too many years since you were last vaccinated.
Strong pain relievers Special bandages Antibiotics and other creams or ointments Surgery on the burned area Your doctor will also treat damage to your internal organs if it has any problem.
6. Prevention of electric burns
To help prevent you or a family member from getting electrical burns, you can:
Place child safety caps on all electrical outlets. Keep power cord out of reach of children. Follow the instructions when using electrical appliances. Avoid using electrical appliances in the bathroom or bathtub. Turn off the breaker when you are working on the power source.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Uptodate.com and Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov