This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Tran Van Trong - Specialist in Pediatric Surgery, Plastic Surgery - Aesthetics - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.Chemical burns are burns that are capable of causing severe burn injuries and causing extreme pain to the victim. If not treated in time, the burn can become more serious, leading to dangerous complications for the burn person.
1. What is a chemical burn?
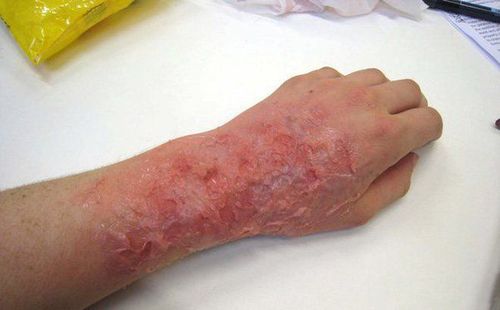
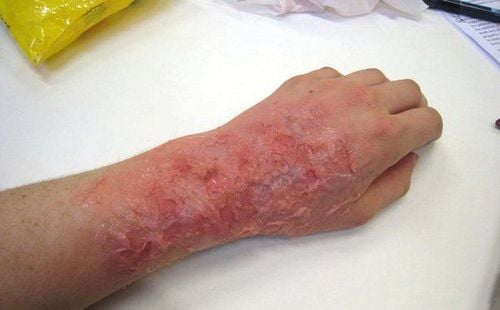
Chemical burns are also known as corrosive burns. Burns occur when the skin or eyes come into contact with chemicals such as acids or bases. Chemical burns can cause reactions on the skin or in the victim's body, damaging internal organs if the chemical is accidentally swallowed.2. Symptoms of chemical burns
Type of chemical inhaled or swallowed Duration of skin contact with chemical Skin condition: open wound, cut or intact when exposed to chemical Location of chemical exposure Chemical What kind of substance? (gas, liquid or solid) Amount and strength of chemical used Here are some common symptoms of chemical burns from acids :
Dead or blackened skin Irritated, red, burned skin burning in the area exposed to the chemical Pain or numbness in the affected area Changes in vision, loss of vision if the chemical comes into contact with the eyes Symptoms that can occur when the victim swallows the chemical, including:
Headache, dizziness Low blood pressure Unstable heart rate Cardiac arrest or heart attack Shortness of breath, cough Muscle twitching
3. Causes of chemical burns
Most chemical burns are from acids and bases. Chemical burns can occur in places such as schools, where chemical substances are handled, or at work. Some of the most common causes of chemical burns include:Ammonia cleaners Car battery acid cleaners Denture cleaners Teeth whiteners Chlorine products for swimming pools
4. Subjects at risk of chemical burns
Infants, the elderly, and the disabled are most at risk of chemical burns. Because these groups of people are not able to handle chemicals properly, it is very easy to get burned in close contact with chemicals.You can also get chemical burns yourself if you handle acids or highly flammable chemicals without help, while your mobility is limited.
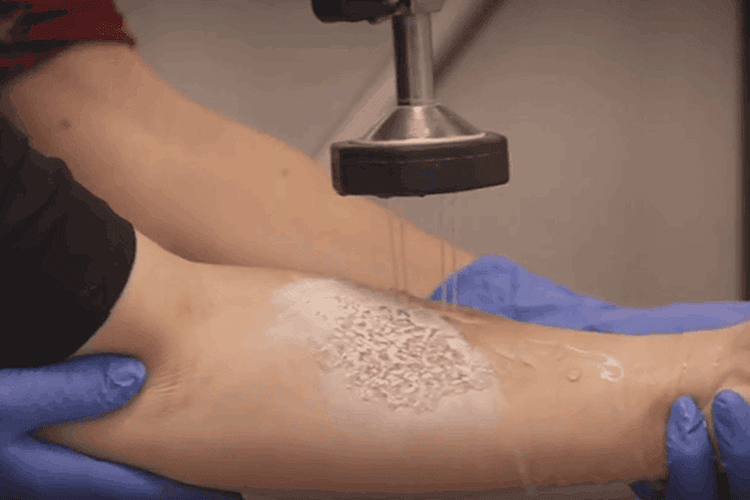
5. First aid methods for chemical burns
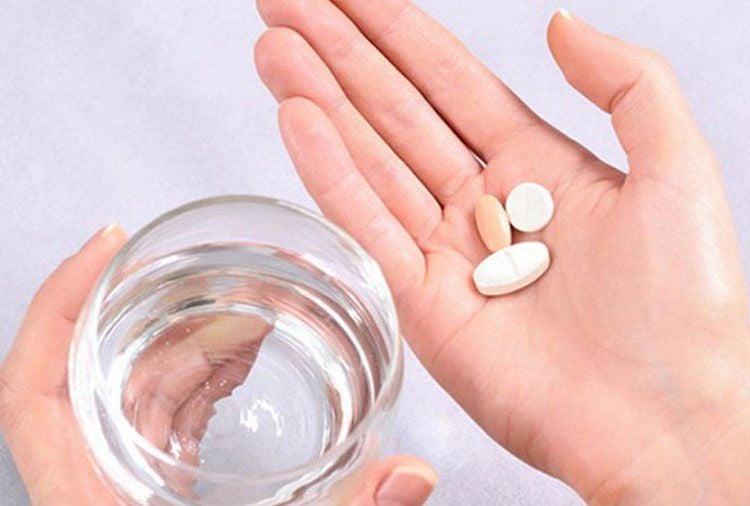

Also, remove contaminated clothing or jewelry. Then cover the injured area with a clean cloth or disinfected dry bandage. If the burn is mild, you can take a pain reliever such as aspirin, then immediately go to the nearest medical facility for emergency care before the burn becomes more serious. In addition, when the following signs occur, you need to go to the hospital immediately:
The diameter of the burn is larger than 7cm Burns to areas such as hands, feet, groin, buttocks or face BURs to major joint area, eg knee Use common pain reliever but no effect Have symptoms of shock such as shallow breathing, low blood pressure, dizziness. Based on the extent of the burn and the severity of the burned area, the doctor may use the following burn treatments:
Antibiotics Removal of infected skin (cleansing, removing dead tissue and dust) dirty) Use anti-itch medication Patch a layer of healthy skin from another part of the body onto the burn Infusion Infusion For severe burns, you will need rehabilitation after the burn. A number of treatments, including: peels, plastic surgery, pain management, occupational therapy help patients recover daily skills, and education that accompanies counseling.
6. Prevention of shock when burned
Burn shock is a state of body-wide response to burn injury with a large degree of tissue damage, causing pathological disorders such as respiratory disorders, circulatory collapse, and disturbances in water and electrolyte balance. To prevent burns, you should note the following:Put the victim in a lying position, and at the same time encourage and comfort the burned person Add water to the victim because they are very thirsty at this time, especially at this time. when having to move the burned person away. Note, only give the victim water to drink when they are awake, without the presence of other injuries or without vomiting. You should give the person with the burn sugar water or oresol. Give the casualty an aspirin. However, if you suspect that the victim has internal trauma, absolutely do not give strong painkillers or sedatives. Then, transfer the victim to a medical facility for treatment as soon as possible. Dr. Trong has more than 10 years of experience in Pediatric and Reconstructive - Aesthetic Surgery, and soon became one of the leading doctors in the field of Children's Surgery, especially Laparoscopic and Plastic Surgery. Plastic Surgery - Aesthetics.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Mayoclimiv.org