This is an automatically translated article.
If your child gets an electric shock, take him or her to the doctor right away as there may be internal damage that you cannot see. The most common way that children are electrocuted is by biting the power cord, putting metal objects in the socket that is not covered, this is very dangerous.1. What is electric shock?
When the human body is directly exposed to an electrical source, the current passing through the body produces a so-called electric shock. Depending on the voltage of the current and the duration of contact, this shock can cause anything from mild discomfort to serious injury, even death.Young children, especially toddlers, are often susceptible to electric shock, especially when they bite into an electrical cord or hold a metal object plugged into an outlet, and the current flows through their body. This can burn both internal and external tissues, possibly even damaging your baby's internal organs.
Some factors that can cause electric shock include:
Power lines Lightning Electrical machinery Electric weapons Home appliances Electrical outlets Although shocks from household appliances are usually less severe, but they can quickly become more serious if a child chews on a power cord we're plugged into a live outlet.
In addition to the source of the electric shock, several other factors affect the severity of the electric shock, including:
The amount of current passing through the body Duration of exposure to the power source Child's health Path electricity through the body Type of current: alternating current usually causes more damage than direct current because it causes muscle spasms making it difficult for children to remove electricity from the body

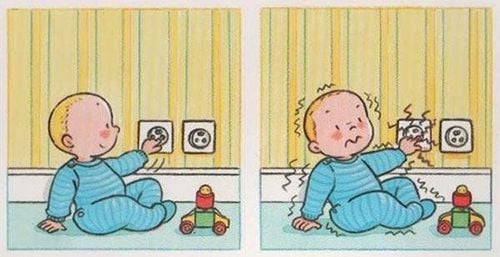
Ổ cắm điện là một trong những tác nhân gây giật điện ở trẻ
2. Symptoms of electric shock in children
Electrical injuries can range from temporary discomfort to permanent organ damage, and can even be fatal. The extent of damage depends on the source, voltage and magnitude of the current, as well as the length of time the child is exposed to the current. Symptoms of electric shock may include:The child loses consciousness Child has muscle spasms Child may experience numbness or tingling Child may find it difficult to breathe Child may have a headache Child may have problems vision or hearing The child may have a burn The child may have a seizure The child's heart rate may be irregular. A child can go into cardiac arrest when the electrical current interferes with the heart's work. Internal damage: organs can be damaged such as the heart, kidneys, brain, muscles, tissues, bones and nerves due to electric current passing through the body. Electric shock can also cause compartment syndrome. This happens when the body is injured causing the limbs to swell. This can also impact the arteries, leading to more serious health problems.
Compartment syndrome may not manifest immediately after the shock, so you need to watch out for your child's arms and legs after an electric shock.

Nếu con bạn bị điện giật, bạn hãy đưa bé đi khám ngay lập tức vì có thể có những tổn thương bên trong mà bạn không thể nhìn thấy được
3. Is there any long-term effects on children receiving electric shock?
Some cases of electric shock can have long-term effects on the baby's health, such as:Severe burns can leave permanent scars. Electricity passing through a child's eyes can cause cataracts. Some shocks can cause ongoing pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness from internal trauma. Injuries from electric shock are very serious, so it is important to seek help as soon as possible.
4. What to do when a child is electrocuted?
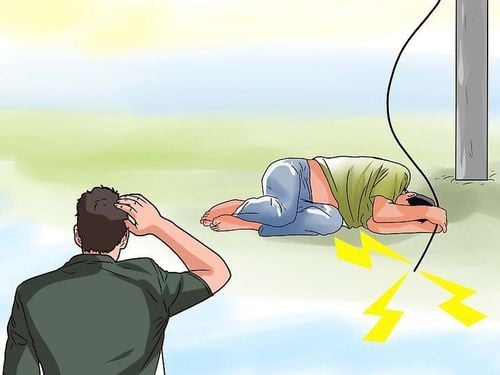
As soon as you detect that your child has received an electric shock, you need to quickly remove the child from the power source. However, you need to pay attention to the following, if you do not want yourself to be electrocuted:Do not touch your baby if he is still exposed to electricity. Disconnect the power by unplugging the power cord or turning off the main switch. If you cannot turn off the power, move an electrical source, such as an electrical cord, using a non-conductive object to remove the cord from the young person. Do not touch electrical cords or puddles of water with currents. If you cannot remove the power source and you need to move your baby, use insulating materials such as rubber gloves to pull your child out. In addition, stand on something dry that does not conduct electricity, such as a rubber mat, wooden chair, etc. Once the child has been separated from the power source, you need to quickly check the breathing, pulse, skin color and alertness of the child. If the baby is not breathing or has no heartbeat, you need to give him CPR immediately, while having someone get medical help. Only medical professionals can determine the severity of any electrical injury. Although your child may look fine on the outside, with only minor injuries, there may be more serious internal injuries. Therefore, after removing the power source from the young person, you need to quickly call an ambulance or take the child to the nearest medical facility.
Ngay khi phát hiện trẻ bị điện giật, bạn cần nhanh chóng tách bé ra khỏi nguồn điện
If the child has a burn, the doctor will clean and bandage the burn on the surface of the skin and order tests to look for signs of internal organ damage, if any.
If a child bites an electrical cord, the child can get burned inside his or her mouth, the burn is often much deeper than it appears. Your child may need surgery after initial treatment. You need to be on the lookout for the possibility of bleeding from a mouth burn within hours or possibly days after the burn. If you notice your child is bleeding, put a clean gauze pad on it and take the child to the hospital right away.
5. Measures to prevent electric shock in children
To protect your child from electric shock, you need to do the following:Cover outlets with covers and place heavy objects in front of electrical outlets if possible. Throw away items with old or frayed cords. Keep the power cord out of the reach of children. Double check that the outlets in the bathroom, kitchen, and yard have a grounding circuit breaker (GFCI). GFCIs are fast acting circuit breakers designed to prevent accidental electric shock by disconnecting power if current is interrupted. Unplug appliances when not in use, especially electrical appliances in the kitchen and bathroom. When outdoors with your children, watch out for broken poles and downed power lines, especially after a storm. Always keep an eye on your child when playing in areas with potential electric shock hazards. Inspect electronic toys and throw away anything that sparks, smells strange, or feels hot to you. Place TVs and audio devices against the wall so that your child cannot reach the cords of these devices. For children over 12 years of age, most electric shock injuries are caused by children exploring or playing around high-powered electrical appliances and systems. You need to explain to minors that they shouldn't climb power poles, don't play near transformers, etc.

Che các ổ cắm bằng nắp đậy và đặt đồ đạc nặng trước ổ điện nếu có thể
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to sources: babycenter.com, healthychildren.org, webmd.com, healthline.com, hopkinsmedicine.org