This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Van Quan - Department of General Surgery & Anesthesia, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Gallstones are common in women. The "silent" stones do not cause any symptoms and are often discovered incidentally during examination and diagnosis by abdominal ultrasound. To detect and promptly treat gallstone disease below is the advice of doctor Vu Van Quan, specializing in Gastroenterology, Vinmec Hai Phong General Hospital
1. What are gallstones?
Gallstones are crystals that crystallize into solid crystals of components present in bile in the gallbladder. Pebbles range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as big as a golf ball, from a single pebble to several pebbles at once to help digest fat.
2. Symptoms of Gallbladder Stones
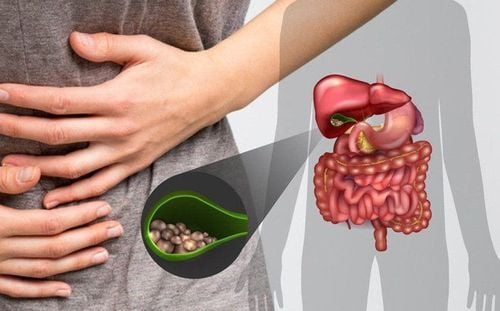
Cramping pain in the right lower quadrant or epigastrium. Usually the onset is sudden and stops within a few minutes to a few hours, the pain is severe at the onset, then the pain persists for a while and then gradually subsides. - Pain often occurs after meals, especially a large meal in the afternoon, fatty foods often cause pain, however, any food can trigger biliary colic. The pain often recurs many times. Nausea or vomiting. Non-specific symptoms include belching, indigestion, flatulence...
3. Who is prone to gallstones?
In Vietnam, gallstones are very common, especially in women before the age of 40, because at this time, the amount of estrogen (female hormone) produced more will affect the process of making bile.
In addition, people who are obese or lose weight quickly are also more likely to get disease

4. Treatment of gallstones
4.1. Treatment of gallstones without symptomsThe following methods may be considered:
Monitoring, no need for any treatment Avoid high fat diet, be physically active, lose weight Take stone breakers that work for small stones but Long treatment time and high recurrence rate Extracorporeal lithotripsy: is no longer indicated for gallstones, because of the high recurrence rate, and the risk of causing biliary obstruction and causing gallstones. pancreatitis. Cholecystectomy is indicated in a few cases: Children; Glycorrhea patient; Are using corticosteroids, pain relievers, neurological diseases that reduce the sensation of abdominal pain; Gallbladder with many small stones or stones larger than 2 cm; Have combined gallstones 4.2.Treatment of symptomatic gallstones 4.2.1 Medical treatment of biliary colic Patients hospitalized for biliary colic usually have significant pain severity and require appropriate treatment.
Pain relief is the mainstay of treatment for patients hospitalized with biliary colic.
When the patient is pain free, there are 2 options: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy or appointment to hospital for laparoscopic cholecystectomy after 4 weeks
4.2.2 Laparoscopic cholecystectomy Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the treatment of choice for symptomatic gallstones
Before surgery is indicated, the possibility that the patient's pain is symptomatic symptoms of a disease other than gallstones.
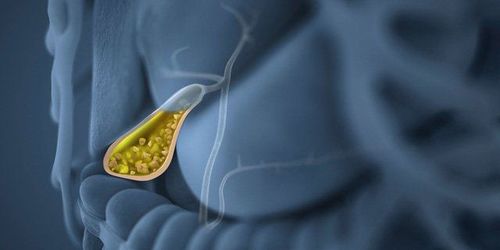
5. Prevention of gallstones
Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a reasonable weight (BMI between 18 - 23) A low-fat, low-cholesterol diet Regular exercise: Should be active for at least 30 minutes a day and at least 5 days /week.

Above is the information you need to know about gallstone disease as well as its treatment. However, to know the patient's condition as well as the appropriate treatment measures, it is necessary to have a specific examination by the doctor to get the best treatment results.
If there is a need for consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the national health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.