This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Phan Ngoc Hai - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang. Dr. Hai used to work at the Neonatology Department of Da Nang Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital and Hoan My Da Nang Hospital. His strength is in general pediatric examination and treatment, neonatal examination and treatment, pediatric resuscitation.Because of their immature immune systems, children are often more susceptible to infectious diseases than adults. Most illnesses in children are caused by viruses. Viral fever can also progress to dengue fever, respiratory infection or flu or typhus, hand, foot and mouth disease. Some children exposed to a special source of transmission of viruses (viruses) H1N1, H5N1, H7N9 can show severe pneumonia progressing to severe respiratory failure, death if not detected early and treated promptly.
1. What is a virus?
A virus is the name for a very small organism called a virus. Viruses have a simple structure and are much smaller in size than bacteria. They cannot live outside for long, but must enter the body of animals or humans, using the materials of these hosts to grow, multiply and cause disease. There are hundreds of viruses in which many different viruses can cause illness with similar symptoms.2. How are children infected with the virus?
There are very few viruses that are transmitted through blood, injection, blood transfusion, sex, or mother-to-child transmission at birth. Most viruses are transmitted from person to person through secretions that are released when talking, coughing, sneezing, or runny nose.In this way the virus is very contagious and breaks out into an epidemic quickly. Children often get the virus when they come into contact with people around them, friends, sick babysitters, or holding toys or objects in public places such as doorknobs and stair rails. Contamination of secretions containing pathogenic viruses.

3. Common symptoms
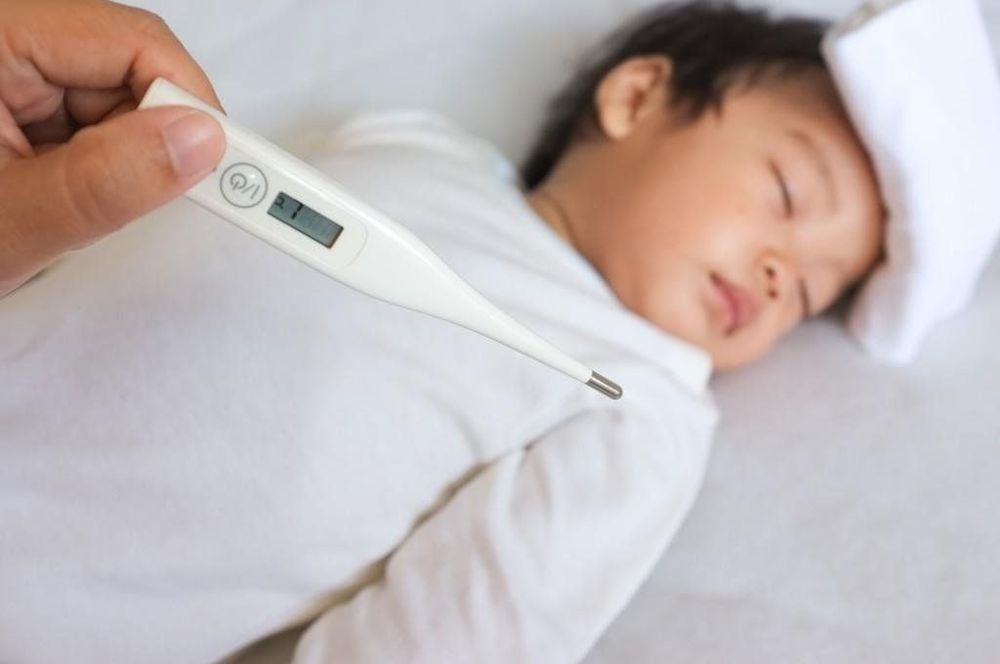
Besides the general manifestations of viral infection such as fever (fever can be mild or very high), cough, sneezing, runny nose, fatigue, loss of appetite, irritability, body aches... Depending on the agent The baby will have some other characteristic signs such as watery eyes, red eyes, eyes with discharge and sensitivity to light, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, nosebleeds, bleeding gums. purpura on the skin, rash or blisters...Some serious complications are rare such as pneumonia causing progressive respiratory failure or encephalitis, Guillain Barre.
4. Care and treatment
Take off some blankets, don't wear too many clothes so that the child's body heats up to reduce the fever. Use fever-reducing medicine (paracetamol) in children with a temperature of > 38.5 degrees Celsius or when fever makes them irritable and fussy a lot. This is a fast-acting drug, usually works 30 minutes and lasts 4-6 hours, with few side effects. It is necessary to give children the correct dose of 10-15 mg/kg/time. Although aspirin is very effective in reducing pain and fever, it is absolutely not recommended for children to use this medicine when infected with a virus because it will make the condition worse due to liver and brain damage. Wipe cool with warm water when the child's fever is over 39-40 degrees Celsius or when the fever has not been reduced. Fever-reducing wipes are usually applied to children from 6 months to 5 years old, not to infants because they easily cause heat loss and hypothermia. Warm water helps blood vessels under the skin dilate well to help remove heat. Avoid using cold or ice water, which will cause the blood vessels to constrict and not give off heat. Use 4 towels dipped in warm water, wring a little wet, cover 2 armpits, 2 groins, another towel to wipe all over the young body. Check the child's temperature every 15 - 30 minutes, stop wiping when the temperature is below 38 degrees Celsius.Treatment when the child has a high fever, convulsions Put the child on his side to let the mucus flow out easily, avoid breathing in the mucus. lungs Analgesic acetaminophen Cooling the child with warm water Take the child to a medical facility for further treatment. Take your child to the doctor right away if: Drowsiness, sleep a lot, difficult to wake up Vomiting a lot, vomiting everything Unable to eat or drink or stop nursing Convulsions or startling movements, or tremors Unusual breathing, breathing fatigue, cyanosis Hands and feet are cool, skin is puffy Irritated stomach pain Nosebleeds, bleeding gums, black stools. The child should be taken to the hospital immediately if the child has a high fever for 3 consecutive days; children under 2 months old; children with chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, asthma; increasing abdominal pain; excessive vomiting, diarrhea; severe headache, stiff neck; confuse; fussy, lethargic difficult to wake up; shortness of breath, cyanosis; nosebleeds, bleeding teeth, vomiting blood or bloody stools...
Most viral infections go well and the child recovers in a few days with rest, care and treatment. A healthy diet rich in energy.
To avoid dehydration with fever, encourage your child to drink water, but don't give him too much at one time. Let your child drink small sips of filtered water, oresol solution, fruit juice to provide adequate water, moisten and soothe the burning pain in the oropharynx to make it easier for the child to swallow and less likely to vomit. It is not necessary to abstain excessively. Babies need to be provided with adequate nutrients to make up for the lack of energy when sick. So let your baby eat many meals a day with foods rich in energy, easy to digest, soft, liquid, cold. Some vitamins and minerals can be added to children through food or supplements. Use physiological saline 0.9% NaCl to clean the eye gel and stagnant fluid in the nose. Using salt water in the refrigerator compartment, nasal drops are a method to help children reduce stuffy nose safely and effectively. If the child's resistance is low, the child can become infected during or after the virus infection, with symptoms that do not go away after a week or become worse. At this point, take your child to the doctor for appropriate treatment. Antibiotics will be needed in this case.

5. Prevention of viral fever
Give your baby a nutritious diet to help him have a good resistance to diseases. Have your baby fully vaccinated according to the Expanded Immunization Program as well as consult a doctor to vaccinate your baby against some other diseases. Wash your hands often and encourage your child to do the same, especially when coming home from a public place. Teach children how to use tissue and cover their mouth with their hands when sneezing, runny nose, or cough. To prevent viral fever and other diseases in children, parents should add some supportive foods containing lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, B vitamins, ... helps to fully meet the needs of nutrients while supporting the immune system, enhancing resistance, reducing the risk of upper respiratory tract infections, bronchitis, flu.Lysine is very necessary for the development of children, Lysine promotes the production of digestive enzymes to stimulate children to eat better and digest easily and effectively, increase food metabolism, maximize absorption of nutrients. Nutrition from food. Fortifying lysine for babies also helps the body create antibodies, develop resistance to help reduce cough, thin phlegm in children.
Parents can learn more:
Why do you need to supplement Lysine for your baby?
Please regularly visit Vinmec.com website and update useful information to take care of your baby and family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.