This is an automatically translated article.
HIV testing window period is an extremely important step in HIV recognition and treatment. It is considered part of routine health care. So what is a window HIV test and what does it mean?
1. What is a window HIV test?
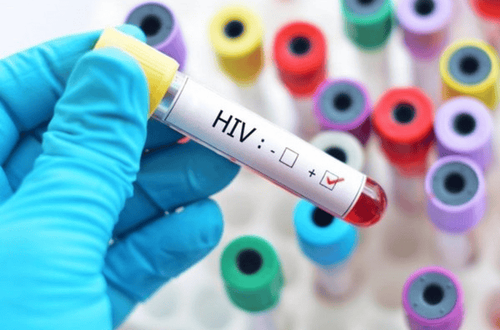
HIV tests are tests of blood or body fluids to determine if you have HIV. Most of the time, it takes the body a while to make enough antibodies or the virus to develop, so it can be difficult to detect HIV infection during the "window" period. It may take about 3-6 months for you to confirm an HIV-positive result. If you test early, you're more likely to get a false negative even though you've actually been infected.
As recommended by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), people aged 13-64 should have an HIV test at least once as part of their health care. periodic health. If you happen to be infected with HIV, testing and early detection will help prepare you for better treatment and prevent transmission of the disease to others.
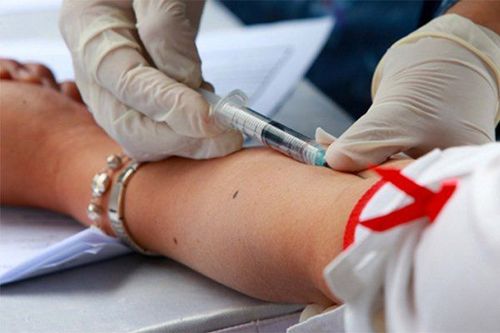
Xét nghiệm HIV là các xét nghiệm máu hoặc dịch trong cơ thể để xác định bạn có bị nhiễm HIV hay khônh
2. Warning signs of HIV infection
HIV symptoms appear at different times in each person. Some people may not see any symptoms that affect their health, some people are infected with HIV but still live healthy for many years.
Even if they don't have any symptoms, they can still spread the disease to others. It is difficult to identify someone with HIV by mere observation, because the symptoms of HIV are similar to those of the flu or mononucleosis. Once the immune system is strongly attacked by the virus, the patient will have the following symptoms:
The body is too tired, exhausted. Uncontrolled weight loss. Fever that persists for weeks and has no known cause. Sweat a lot at night. Swollen lymph nodes. Chronic constipation. Mouth/esophagus sores. Infection, rash. Prolonged cough. Confusion.
3. Why should HIV test be done?
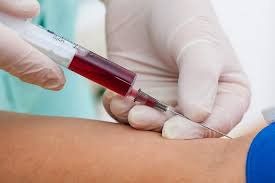
It can be said that an HIV test is the only way to know for sure whether you have HIV or not. People in high-risk groups for HIV infection should get tested and tested for HIV more often.
If you tested and received HIV negative more than a year ago, but are still involved in the following activities, you should get tested as soon as possible because of the risk of infection. your HIV virus is still very high:
Have sex without using a condom. Having vaginal or anal sex with someone who has HIV. Having had unprotected sex with many different people since the last HIV test. Injecting drugs, sharing needles and other personal items with others. Have been diagnosed or are being treated for another sexually transmitted disease. Get diagnosed and treated for hepatitis or tuberculosis. You should get tested for HIV at least once a year if you're still doing any of these activities. In case you are pregnant, you should tell your doctor when taking the test to receive advice and measures to help you and your baby not get HIV.

Xét nghiệm HIV là cách duy nhất giúp xác định chắc chắn rằng bạn đã bị nhiễm HIV hay chưa
4. Types of HIV Tests
HIV testing includes 3 main types of tests, including:
Nucleic acid test (NAT). Antigen/antibody test. Antigen test. HIV testing is usually done on a blood or oral fluid sample, sometimes a urine sample.
Nucleic acid test (NAT): A NAT test helps to determine if the HIV virus is actually in the blood. The test may give a positive/negative result or a viral load in the blood (called an HIV viral load test). In general, this type of test is quite expensive, and it is not used routinely for personal screening, unless you are at high risk for HIV exposure or are experiencing early HIV symptoms.
NAT testing is usually quite accurate in the early stages of infection. However, to help your doctor understand a negative test result, it's best to do an additional antigen/antibody test. In addition, the accuracy of this test may be reduced if you take pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) or post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP).
Antigen/antibody test: This test allows to look for both HIV antigens and antibodies. Antibodies are produced by the immune system when the body is exposed to bacteria or viruses such as HIV. Antigens are foreign substances that enter your body and activate your natural immune system. If you have HIV, an antigen called P24 is made even before antibodies develop.
Antibody test: An antibody test is a quick HIV test and can be done at home. The test looks for HIV antibodies in the blood or body fluids.
To detect HIV earlier, you can do an antibody test using blood from a vein instead of doing tests with blood or body fluids.
Laboratory tests are mostly HIV antigen/antibody tests. However, we can still conduct antibody screening tests in a laboratory at a medical facility. When performing the test, the doctor will draw blood from a vein, then put it in a sample tube and send it to a lab for analysis. It will take a few days for you to receive your test results; With a rapid antibody screening test, results are usually available sooner (in about 30 minutes, even less). The test is performed in a routine clinical setting, taking a blood sample from a finger or oral fluid; Self-testing for antibodies in oral fluids is also a quick way to test for HIV. You just need to take a sample of your own body secretions and test it with a medical kit. After about 20 minutes, you will get the results. The advantage of this test is that it can be done at home or at HIV screening programs in the community or in clinics. If you take any type of antibody test and get a positive result, you will need to do a follow-up test to confirm the results. To find out what type of test is right for you, you should see your doctor for advice and answers to your questions.
Once your final results are available, if you already have HIV, talk to your doctor about treatment options. In the event that the test is negative, you should continue to take HIV prevention measures, such as using condoms correctly, having healthy sex, and taking HIV prevention medications if: you are at high risk.
5. Do pregnant women need to be tested for HIV?
All pregnant women should be tested for HIV to initiate treatment as soon as possible in case of infection, which helps to reduce the rate of fetal HIV infection transmitted by the mother.
During pregnancy, treatment should be started as soon as possible to minimize HIV transmission to the baby. In particular, even during labor or after the birth of the baby, prophylactic treatment should be started to bring about a positive outcome.

Xét nghiệm HIV để điều trị sớm, giúp giảm tỷ lệ thai nhi bị nhiễm HIV do mẹ truyền sang
6. How long does it take to get HIV test results?
Depending on the test method to determine the time to receive the results. For lab tests it will take longer, about 2 weeks for you to get the results. For the type of test done at home, it will only take about 20 minutes to get results, but its specificity is not as high as those of laboratory methods.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Web MD