This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.During the development and pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus, it will attack and destroy liver cells. If not detected and treated promptly, the disease can lead to cirrhosis, even liver cancer.
1. What is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B, also known as hepatitis B, is caused by a small DNA-carrying virus that belongs to the family Hepadnaviridae. This virus enters the human body in the form of Dance particles, these particles will move from the blood into the liver to enter the nucleus of liver cells. In the nucleus of hepatocytes, these particles will borrow the cell's material to encode and copy a series of newly released viruses, and continue to infect other liver cells.
The hepatitis B virus itself does not directly damage liver cells, but because the human body's immune system recognizes infected liver cells, and attacks and destroys the cells. This causes liver damage. When this process is continued over a long period of time, damaged liver tissue becomes scar tissue and can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and even an increased rate of liver cancer.
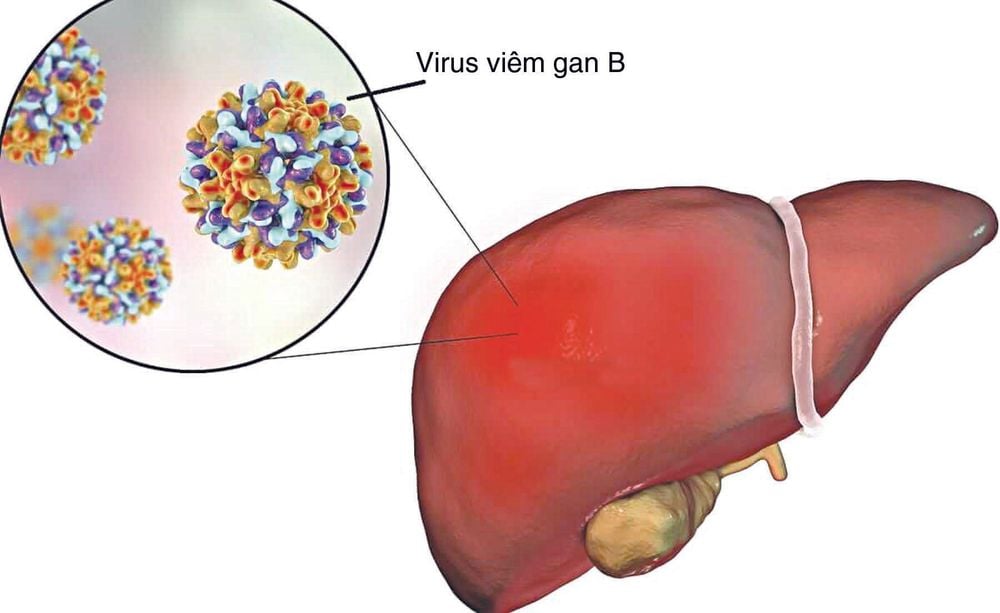
However, not everyone infected with the hepatitis B virus will be infected with the active virus for life. In some cases, a healthy immune system can clear the virus before it turns into chronic hepatitis B. This situation is known as acute hepatitis, occurring within the first 6 months of infection sometimes causing severe hepatitis symptoms such as fatigue, jaundice, fever, etc. but most often there are no symptoms during this period.
People with a healthy, healthy immune system recover from an acute viral infection in about 90%. Meanwhile, only 10% turn into chronic hepatitis B virus. However, if you are infected if you are infected with hepatitis B from mother to baby at birth, there is a 90% chance that you will become a chronic carrier of the virus.
2. Hepatitis B virus transmission route
Hepatitis B virus circulates in the blood and can be transmitted in the following ways:
Mother to baby : Transmission during labor, this is the most important route of transmission. Sexuality: The hepatitis B virus can be spread through heterosexual or same-sex sexual activity. Blood: Hepatitis B virus is transmitted through transfusion of blood or blood products contaminated with the virus. Or when coming into contact with secretions of a hepatitis B patient, sharing contaminated needles, ear piercing, acupuncture tattooing if the equipment used is not properly disinfected.

3. Why is hepatitis B infection at risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer?
When the body's immune system is attacked and destroyed by the virus massively, it will lead to hepatitis B. If prolonged, liver cells will be damaged much leading to elevated liver enzymes. If the liver cells are damaged too much, it will lead to severe hepatocellular failure, also known as fulminant hepatitis. Patients will have flu-like symptoms, sometimes with nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, weight loss, and itching all over. More severe symptoms such as: fever, yellow eyes, yellow skin, abdominal pain, joint pain, muscle pain, dark yellow urine, and if it falls into fulminant hepatitis can be fatal...
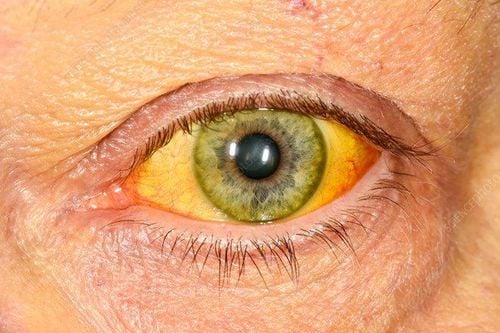
To diagnose hepatitis B virus infection, it is necessary to have a blood test to screen for hepatitis B virus at medical facilities with HBsAg test. If the HBsAg test is positive, the doctor will advise the patient to perform quantitative HBV DNA (indicating viral load), HBeAg (indicating viral replication), and liver function tests such as AST. , ALT to have a basis for indications of antiviral treatment. If the HBsAg test is negative, it means that the patient is not infected with the hepatitis B virus, and should be tested for more quantitative HBsAb to see if the body has enough antibodies to the hepatitis B virus, if this is negative. If you are HIV positive or have weak antibodies, you should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
In summary, when you have hepatitis B virus, you need to be examined and treated in combination with lifestyle changes, can reduce the risk of leading to hepatitis B. cirrhosis and liver cancer. Therefore, screening for hepatitis B in regular health check-ups, taking measures to prevent infection and when infected with hepatitis B requires lifestyle changes and appropriate therapeutic interventions to prevent complications. symptoms occur.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is implementing a hepatobiliary screening package that fully includes all of the above tests, bringing peace of mind and accurate results to customers. When there are signs of liver disorders or even when there are no symptoms, proactive liver function tests are necessary to protect your health. In addition, Vimec also has a Vaccine Center in the hospital ready to serve the needs of vaccination against hepatitis B virus.

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.