This is an automatically translated article.
Article by a doctor from the Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital."Decade of Nine Hemorrhoids" - that's common, but in fact many patients silently suffer from this "difficult to say" disease. With answers from Dr. Ngo Viet Thang - a doctor of Gastroenterology at Vinmec Times City Hospital below, you will understand the causes and symptoms of hemorrhoids and especially help you realize that modern hemorrhoid treatment is not effective. "terrible" as in the imagination.
1. What is hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids are not just a disease of the veins. These are diseases of a vascular system from arterioles, veins, and arteriovenous anastomoses to smooth muscle and connective tissue lined by the normal epithelium of the anal canal. The venous plexus is located in the submucosa supported by an elastic fibrous structure. The constant increase in pressure such as straining to have a bowel movement, accompanied by constant blood stasis, will lead to dilatation and the creation of hemorrhoids into the lumen of the anal canal. At the same time, as we age, the supporting connective tissue structures are increasingly weakened, the hemorrhoids gradually fall out of the anal opening, leading to internal hemorrhoids.
2. Classification of hemorrhoids There are mainly 2 types, including internal hemorrhoids and external hemorrhoids.
External hemorrhoids: When hemorrhoids originate below the dentate line (also known as the anal-rectal line), it is called an external hemorrhoid. The hemorrhoid is now covered with squamous epithelium and lies beneath the skin surrounding the anus. Internal hemorrhoids: If the hemorrhoid originates above the dentate line, it is called an internal hemorrhoid, and the hemorrhoid is covered with mucosa and transitional epithelium. Hemorrhoid grading: based on the progression of hemorrhoids that are still inside or have prolapsed from the anus.
1st degree hemorrhoids: hemorrhoids are completely located in the anal canal. Grade 2 hemorrhoids: Normally, hemorrhoids lie neatly in the anal canal, when pushing to defecate, the hemorrhoids protrude or protrude a little. After going to the toilet, get up and the hemorrhoids will retract inward on their own. Grade 3 hemorrhoids: every time you go to the toilet or walk a lot, squat, do heavy work, the hemorrhoids prolapse again. At this time, you have to lie down for a while before the hemorrhoids recede or gently push in with your hands. Grade 4 hemorrhoids: hemorrhoids are almost always located outside the anal canal.
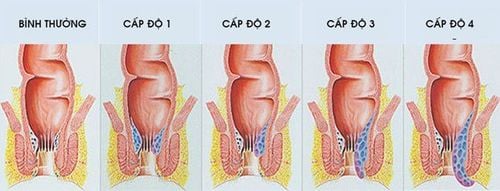
Các cấp độ thường gặp ở bệnh trĩ
4. Causes of Hemorrhoids The veins around the anus tend to stretch under pressure and can bulge or become congested. Hemorrhoids can develop due to increased pressure in the lower rectum due to:
Straining to have a bowel movement Prolonged sitting on the toilet Diarrhea or chronic constipation Obesity Pregnancy Anal intercourse Low-quality diet Fibroids Hemorrhoids increase with age because the tissue structure that supports the veins in the rectum and anus becomes loose and flabby.

Ngồi lâu trên bồn cầu cũng là một nguyên nhân của bệnh trĩ
Painless bleeding during bowel movements. Initially, a discreet amount of bright red blood may be seen on the toilet paper or in the toilet bowl. Bleeding is the earliest and most common symptom. Later, after pushing a lot, the blood flows in drops or rays. It is worse when squatting also bleeds. Itching or irritation in the anal area due to mucus secretion from the mucosa of the anal canal. Pain or discomfort, which ranges from painless, mild pain to very painful anal fissures, obstruction, or strangulation. Perianal swelling A raised, burning, or painful mass near the anus (possibly a blood clot in the hemorrhoid) Hemorrhoid symptoms usually depend on the location:
External hemorrhoids are the most uncomfortable, because the skin over the hemorrhoid is most bothersome. hemorrhoids are irritated and ulcerated. If a blood clot forms inside an external hemorrhoid, the pain can come on suddenly and be severe. The patient may feel or see a mass around the anus. Blood clots can be absorbed leaving the skin wrinkled, causing itching and burning. Internal hemorrhoids usually don't cause pain, even when they bleed (bleed). The sick person may, for example, see bright red blood on the toilet paper or drip into the toilet bowl. Hemorrhoids usually cannot be seen or felt, and they rarely cause discomfort. During defecation, stool passing through the anus can scratch the surface of the hemorrhoid and cause bleeding. Internal hemorrhoids can also prolapse outside the anus, creating internal hemorrhoids. When hemorrhoids are prolapsed, it can absorb small amounts of mucus and stools that can cause irritation causing itching, pain, and burning. Constant wiping to try to relieve the itch can aggravate the problem.

Khi bị trĩ, bạn sẽ cảm thấy ngứa hoặc kích thích ở vùng hậu môn do dịch nhầy từ sự bài tiết của niêm mạc ống hậu môn
6. Complications of hemorrhoids Complications of hemorrhoids are very rare but can still occur including:
Anemia due to chronic blood loss through hemorrhoids, at this time the body will not have enough red blood cells needed required to carry out oxygen exchange for the cell. This case rarely happens. If the hemorrhoid prolapses and becomes trapped, the blood vessel supplying the hemorrhoid is blocked. At this point, the pain will be very obvious. When pressed lightly, there will be a bumpy feeling due to a blood clot. Thromboembolism: A condition in which a blood clot forms inside the blood vessel of the hemorrhoid. When blood vessels are dilated and congested due to straining, carrying heavy loads, pregnancy, and playing heavy sports, the pressure in the abdominal cavity will increase, creating favorable conditions for the formation of blood clots, causing embolism. If the external hemorrhoid is occluded, the anal margin will see a small blue bulge, accompanied by a burning sensation when touched and stretched. Embolism in internal hemorrhoids is painful and painful in the deep and the symptoms are not as intense as external hemorrhoids. Perianal dermatitis, papillary inflammation and slit inflammation when the skin between the hemorrhoids is ulcerated, causing itching and burning symptoms. 7. Treatment of hemorrhoids Apply to symptomatic hemorrhoids
7.1 Medical treatment Conservative treatment and lifestyle
Diet high in fiber is an effective treatment for hemorrhoids, limited processing stimulants such as alcohol, chili. Avoid strenuous activity, avoid sitting or standing for too long. Change bowel habits to avoid constipation. Soaking the anus in warm water helps improve symptoms. Using drugs: Can use topical drugs or injections, drugs to support venous circulation
7.2 Surgical treatment For hemorrhoids with thrombotic complications: thrombosed hemorrhoids should be intervened early. by performing excision according to classical methods or combining thrombectomy with hemorrhoidectomy by other methods. The procedure of ligation of hemorrhoids with elastic band or sclerotherapy to feed the hemorrhoids, is usually applied for mild cases of hemorrhoids. Sclerotherapy is indicated in grade 1 and 2 hemorrhoids, not indicated for external hemorrhoids, hemorrhoids with thrombosed, ulcerated or necrotic internal hemorrhoids. For sclerotherapy, 1-2 ml of a sclerosing agent (usually sodium tetradecyl sulfate or 5% phenol, quinine, urea hydrochloride, polidocanol) is injected with a 25-gauge needle into the submucosa of the hemorrhoid. Rubber band ligation - A rubber band is placed around the hemorrhoid, ligation causes ischemia, the hemorrhoid becomes fibrous, atrophy and falls off on its own. Advantages are easy to perform, simple, inexpensive, can be treated as an outpatient for grade 2 and 3 hemorrhoids Longo method (stapled hemorrhoidectomy-PPH, 1998) is recognized in many European and Asian countries. . This method has become a widely accepted option in hemorrhoidectomy for the treatment of grade 3 and 4 internal hemorrhoids. In China in recent decades, it even tends to replace excision. get rid of traditional hemorrhoids. This is a method without cutting hemorrhoids, the principle is to interrupt the upper and middle hemorrhoid blood vessels, then suture the prolapsed anal-rectal mucosa, bringing the hemorrhoids back to the position in the anal canal. shrink hemorrhoidal tissue. The advantage is less discomfort because the anal skin is not removed. THD angioplasty is performed under ultrasound guidance to block the blood supply to the anus, thereby reducing the hemorrhoid aneurysm. Cutting hemorrhoids by classic methods: Miligan Morgan, Ferguson, White Head, these methods directly interfere with hemorrhoids, so they often cause pain. Note when treating hemorrhoids
There is no indication for surgery in immunocompromised patients or those with active colitis. Emergency hemorrhoid surgery is associated with a higher complication rate. Acute complications associated with hemorrhoid treatment include pain, infection, recurrent bleeding, and urinary retention. Late complications include incontinence due to damage to the anal sphincter during dissection.
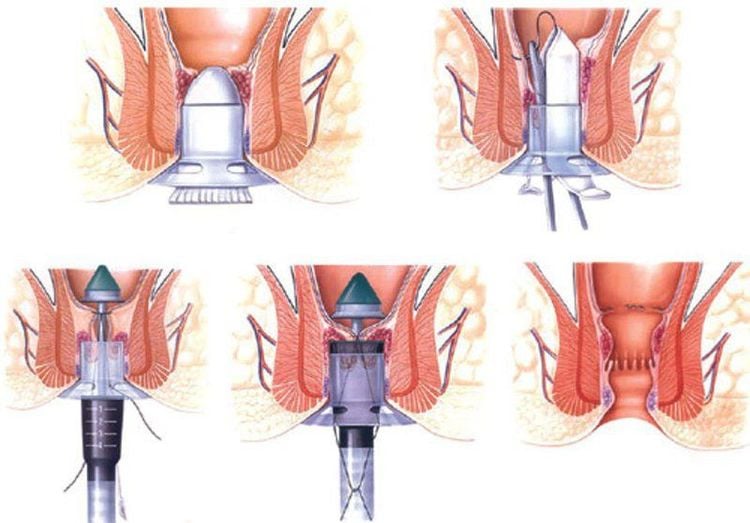
Các phương pháp phổ biến điều trị bệnh trĩ
Eat foods high in fiber. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables and whole grains eg wheat, oats, barley, corn, brown rice, rye, millet, etc. helps soften stools and increase stool volume. Add fiber to your diet slowly to avoid excessive farting. Drink a lot of water. Drink six to eight glasses of water and other liquids (not alcohol) each day to help soften stools. Consider fiber supplements. Most people don't get the recommended amount of fiber 25 grams per day for women and 38 grams per day for men in their diet. Studies have shown that over-the-counter fiber supplements, such as Metamucil and Citrucel, help improve symptoms and reduce bleeding from hemorrhoids. These products help keep stools soft and regular bowel movements each day. When taking a fiber supplement, be sure to drink at least eight glasses of water or other fluids each day. Otherwise, supplements may cause constipation or make it worse. Do not push hard when having a bowel movement because trying to push will put more pressure on the veins in the lower rectum, causing hemorrhoids to enlarge and bleed easily. Go to the toilet as soon as you feel the urge. If you miss the feeling of having a bowel movement, the rectal mucosa gradually absorbs water in the stagnant stools, the stools will become dry, hard and harder to pass. Do exercise. Stay active every day to help prevent constipation and reduce pressure on your veins, which can occur with prolonged standing or sitting. Exercise can also help with weight loss. Avoid sitting for long periods of time. Sitting for too long, especially on the toilet, can increase pressure on the veins in the anus.

The best way to prevent hemorrhoids is to keep stools soft, eat lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains and drink lots of water
In short, most patients think they can treat themselves without going to the doctor. directed by Doctor. However, do not be too confident in your own self-diagnosis, especially for people over 40 years old. Bleeding from the anus in addition to hemorrhoids has many other diseases from benign to malignant such as colorectal cancer, anal canal cancer, colorectal polyps, besides hemorrhoids can also be a symptom of other diseases. caused by other diseases. If you change your bowel habits, change the color of your stools, consult your doctor.
You can also seek medical help if bleeding is accompanied by pain, bleeding is frequent or heavy, or does not improve with home remedies. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience heavy bleeding from the anus, dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Health System Hospitals nationwide, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.