This is an automatically translated article.
Coughing up blood is one of many signs related to many diseases in the lungs such as: Tuberculosis, lung abscess, lung fungus... You should see your doctor as soon as possible if you are coughing up blood.1. What is hemoptysis?
Coughing up blood is a common symptom of respiratory problems and is a sign of a serious medical condition.Coughing up blood is often foamy with sputum, bright red, then slowly turning dark. Before the onset of the cough, the patient often feels a burning sensation behind the breastbone, chest pain, and itchy neck.
Coughing up blood is divided into several types based on the amount of blood coughed up in 24 hours and depending on the medical condition. It is necessary to distinguish between hemoptysis due to lung diseases and hemoptysis in diseases of the digestive system, ear, nose and throat, ...
2. Mechanism of coughing up blood
2.1 Due to rupture of overdeveloped bronchial vessels (systemic arteries) This mechanism is most common and common in bronchial neoplasms, fibrous inflammatory lesions of the lung, bronchiectasis, due to vascular proliferation. in tumors, in necrotizing inflammatory lesions, in fibrous lesions, especially in post-TB bronchiectasis. This increased perfusion originates from the bronchial artery.2.2 Due to rupture of pulmonary blood vessels, lung abscess destroys parenchyma or erosive lung tumor, ruptures blood vessel, venous aneurysm, rasmussen aneurysm in the tuberculous cavernous wall burst, causing severe hemoptysis.
2.3 Due to increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation at the junction (Von-Hayek pause) Between the pulmonary blood vessels and the bronchial vessels rupture, causing hemoptysis, common in hemodynamic pulmonary edema; pulmonary infarction. Coughing up blood is more severe if the pulmonary circulation pressure increases.
2.4 Alveolar bleeding due to damage to the alveolar capillary membrane Seen in Goodpasture syndrome, disseminated lupus erythematosus.
2.5 Hemoptysis in patients with bleeding syndrome Hemorrhagic coagulopathy syndrome, acute leukemia, myelosuppression, prolonged use of anticoagulants. Especially when the patient has associated lung disease.

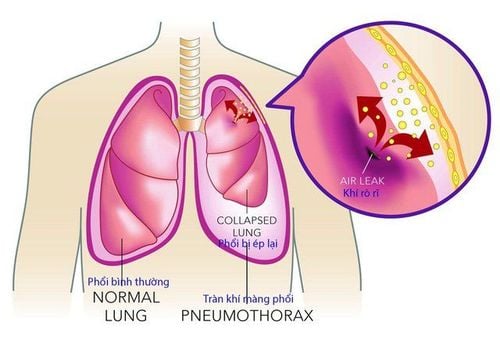
Cơ chế ho ra máu do dập vỡ các mạch máu phế quản quá phát triển hay gặp nhất và thường gặp trong u phế quản
3. Causes of coughing up blood
Causes of hemoptysis, but clinically common causes are some of the following:3.1 Bronchoalveolar trauma At most, the prevalence is from 30% to over 50% according to foreign authors and from 15% to 35% according to some Vietnamese authors. Hemoptysis due to tuberculosis is often mixed with foam and hemoptysis. Bronchiectasis: Occurs in 15% to 30% of causes of hemoptysis, hemoptysis, or recurrent hemoptysis. Hemoptysis of bronchiectasis is common in Vietnam, easy to misdiagnose with pulmonary tuberculosis. especially hemoptysis due to sequelae of bronchiectasis after tuberculosis is very important to distinguish it from recurrent tuberculosis. Bronchial cancer: From 20% to 38%, tumor growth, vascular proliferation, tumor necrosis damage blood vessels and cause hemoptysis; usually coughs up little blood, which can be bright red or dark or ripe plum color. Radiation therapy for lung tumors can cause tumor necrosis and hemoptysis. Bronchopulmonary infections: Lung abscess, necrotizing pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae are the causes of hemoptysis. Bacterial hemorrhagic tracheobronchitis can also cough up small amounts of blood. Less common causes of hemoptysis: Residual cavernous Aspergillus neoplasms; endobronchial foreign body, silicosis, lung fluke and pulmonary amoebiasis.
3.2 Cardiovascular causes Hemoptysis in cardiovascular causes is often caused by diseases: mitral stenosis, left ventricular failure, acute pulmonary edema, pulmonary infarction, primary pulmonary hypertension.
3.3 Other, rarer causes Hemoptysis in patients with blood diseases (acute and chronic leukemias, hemophilia, thrombocytopenic purpura), dengue hemoptysis when present bleeding in the lungs. Coughing up blood due to thoracic trauma, broken ribs or crushed lungs, pressure from blast waves. Hemoptysis of unknown cause occurs in up to 5% or more.
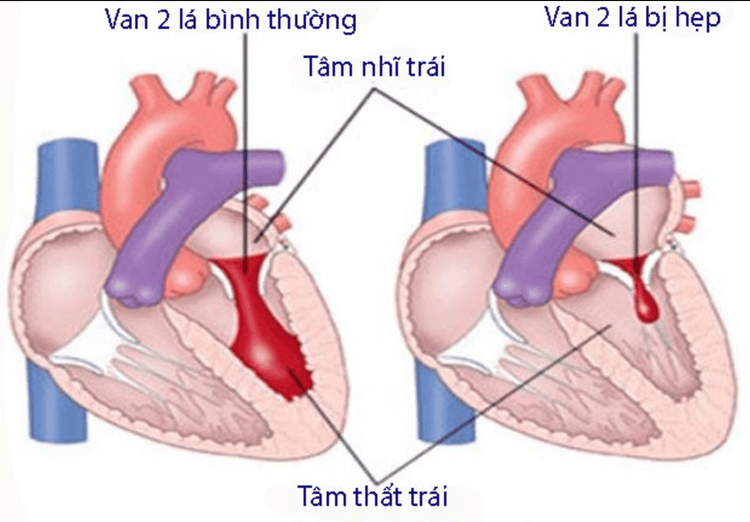
Ho ra máu trong nguyên nhân tim mạch thường do các bệnh: Bệnh hẹp van 2 lá, suy thất trái...
4. Classification of hemoptysis
Currently, there are several classifications of hemoptysis by different authors.Mild hemoptysis: When the total amount of blood out is less than 50 ml within 24 hours. Moderate hemoptysis: when the total amount of coughing up blood is from 50 ml to less than 200ml/24 hours Severe hemoptysis: The total amount of blood coughed up is 200ml or more in 24 hours. Severe hemoptysis (lightning hemoptysis): This is when blood rushes to fill the 2 lungs, causing suffocation and rapid death.
5. Diagnose the cause of coughing up blood
It is necessary to combine a comprehensive clinical examination with chest X-ray to guide the diagnosis; it is necessary to take chest X-ray right at the hospital bed. Examine the ear, nose, and throat to rule out bleeding in the nose and pharynx. Preliminary flexible bronchoscopy detects the bleeding site in the bronchial lumen, which can be combined with endoscopic hemostasis when necessary. High-resolution computed tomography helps diagnose the location of bronchiectasis, lung tumor, and cavernous tuberculosis that are the causes of hemoptysis. Bronchial angiography detects pathological bronchial arteries and is indicated for bronchial artery occlusion to treat hemoptysis. Sputum testing for tuberculosis, Aspergillus, and lung flukes are common causes of hemoptysis.6. Treatment of hemoptysis
6.1 General principles Immobilization and good nursing regimen Use antitussive sedatives Use hemostatic drugs, blood transfusion Treat cause of hemoptysis Administer anti-infective antibiotics Treat symptoms and signs Dear. 6.2 Specific treatment 6.2.1 Good immobilization Keep the patient immobile in a quiet, airy room in the summer, warm and protected from drafts in the winter. If the patient is hemoptysis and hemoptysis is severe, the patient should be placed with the head low and tilted to the side for suspected injury (based on available documents such as radiographs or asking the patient or patient's home if the patient cannot be contacted). Placing the patient in a supine position to spit out blood helps prevent blood from flowing from the damaged lung to the healthy lung, blocking the bronchi and causing acute respiratory failure and death. When the patient improves or stops coughing up blood, the patient can be placed in the Fowler position. At the same time, urgently measure pulse, temperature, blood pressure and take blood for emergency test of blood group, complete blood count: red blood cells, hemoglobin, white blood cells, white blood cell formula, hematocrit. Closely monitor the number of times of hemoptysis in 24 hours, the amount of blood coughed up once and the total amount of blood coughed up in 24 hours to promptly assess the degree of hemoptysis and take appropriate action. Closely monitor respiratory, cardiovascular and systemic status, if there is respiratory failure due to blood pooling in the bronchial lumen, it is necessary to remove promptly, it is necessary to intubate to suck blood or treat in the intensive care unit. positive.
Bệnh nhân ho ra máu nên nằm bất động trong phòng yên tĩnh, thoáng về mùa hạ, ấm và tránh gió lùa về mùa đông
6.2.5 Using antibiotics to fight infections In hemoptysis, there is often blood pooling in the bronchial-alveolar lumen, then chemically and is a very good environment for bacteria to grow, so antibiotics must be used to treat ( oral or injectable (depending on the case) to prevent superinfection.

Ho ra máu do nhiều nguyên nhân gây nên, do vậy ngoài điều trị cầm máu cần tùy thuộc vào nguyên nhân mà điều trị
6.3 Some other treatment measures 6.3.1 Endoscopic treatment The airway must be circulated to prevent blood clots in the lungs causing complications of atelectasis or suffocation. Use a rigid or flexible bronchoscope or an endotracheal tube to aspirate blood and release blood clots if there is a complication of atelectasis in one lung.
6.3.2 Accompanying bronchial artery occlusion In hemoptysis, up to 90% of cases are due to bleeding from the bronchial artery (Pneumothorax). People carry out occlusion of the pulmonary artery, which will stop the bleeding, at the same time remove the pathological pulmonary artery from the general circulation and prevent recurrent hemoptysis. The pulmonary artery supplies blood to the lung parenchyma, but occlusion will not affect the feeding function because then the pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein will supply compensatory blood through the aortopulmonary anastomosis. Concomitant pulmonary embolism is indicated in cases of moderate and severe hemoptysis, recurrent hemoptysis. Coughing up blood is mild, but recurs many times a year, affecting the patient's life. Relative contraindications: Patients with coagulopathy, bleeding. Respiratory failure, severe heart failure, acute or chronic renal failure stage III, IV. This method is performed under the guidance of selective bronchial angiography to determine the source of bleeding.
Điều trị ho ra máu phải lưu thông đường thở để đề phòng máu cục ứ đọng trong phổi gây biến chứng xẹp phổi hoặc ngạt thở
6.4 Treatment of severe hemoptysis Absolute immobilization, quiet chamber, do not move the patient. When bleeding is happening, place the patient on the side of the bleeding lesion, with the head lower than the chest. When the bleeding stops, lie down in the Fowler position (half lying half sitting); a completely liquid diet (milk, porridge but let it cool; ice can be applied to the chest). Administer oxygen at a flow rate of 2-3 l/min if necessary for continuous breathing through the nostrils. Morphine (if there is no respiratory failure) subcutaneously 1 ampoule 0.01 g or 1/2 ampoule diluted with 30% hypertonic glucose solution 20 ml by slow intravenous injection. Gardenal 0.10g or seduxen 10mg intramuscularly 1 ampoule x 2 times/24 hours. It is possible to put the patient to sleep lightly with Lytic Cocktail (gardenal+aminazine + pipolphen) but give small doses sporadically several times a day. For hemostatic drugs (intravenous drip of post-pituitary essence and anti-fibrinolytic drugs. If the red blood cells are less than 2 million, the hematocrit is less than 30% or the patient has shock or hypotension, then give blood of the same group or Transfuse fresh blood directly from 1-2 units (250 ml-500 ml) once every few days until bleeding stops; do not transfuse too much blood at one time because it can increase blood pressure causing hemoptysis Continue Anti-cardiovascular collapse: IV drip isuprene, (isoprenalin) tube 5 ml = 1 mg ouabain 1/4 mg; Dopamine tube 5ml = 50mg Cardiac support: Spactein, coramin Give antibiotics to prevent superinfection: Use a cephalosporin group in combination with an aminoglycoside group, or another group according to the case.If there is a risk of respiratory failure, cardiovascular collapse, it should be treated in the intensive care unit. Coughing up blood is a sign of many dangerous diseases, it is necessary If there are signs of coughing up blood, the patient should go to the hospital to have a doctor diagnose and evaluate the disease, thereby deciding the method of treatment. specific treatment. Vinmec International General Hospital System is a prestigious hospital for many years in the examination, diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases. Here, full convergence of a team of leading medical doctors, leading modern equipment and machinery in the country, comprehensive medical services. Since then, effective support for the process of examination, diagnosis and treatment of difficult cases, patients can completely rest assured when examining and treating here.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.