This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Resident Doctor Tran Duc Tuan - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of imaging and interventional internal and external blood vessels.Headaches are pain that occurs in the head or neck. The two most common types of headaches are primary headaches and secondary headaches. To determine the cause of your headache, your doctor may recommend a CT scan or an MRI. However, these procedures need to be performed in some cases and special precautions should be taken before proceeding.
1. Things to know about headaches
A headache is pain in the head or upper neck. They can be primary (unrelated to a medical condition) or secondary (caused by an injury or other medical condition).Primary headaches include: Tension, migraine and cluster headaches.
Tension headaches include pressure and tension as a band that begins at the back of the head and upper neck, gradually encircling the head. Cluster headaches are headaches that occur in groups, or clusters, over a period of weeks or months separated by a headache-free period of several months or years. During the headache phase, a person with cluster headaches will experience multiple attacks throughout the day, each lasting 30 to 90 minutes. These pains, which often occur at the same time of day, include sharp, penetrating pain around or behind one eye, watery eyes, and nasal congestion.
2. Headache Diagnosis and Evaluation
To diagnose the cause of the headache and rule out underlying medical conditions, the doctor will take the patient's history and perform a neurological exam. Diagnostic testing may include the following imaging tests:2.1 Head CT Scan Computerized tomography (CT) combines special X-ray equipment with a computer to create pictures of the inside of the body. Doctors also use brain CT scans to detect bleeding from ruptured or leaking aneurysms, strokes, brain tumors, and diseases or deformities of the skull.
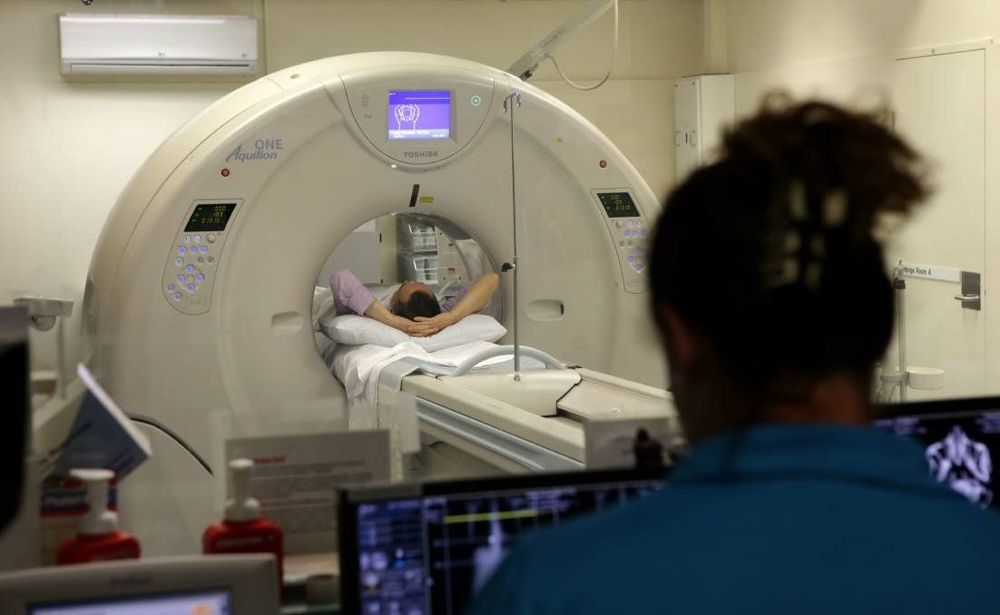
2.2 Head Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a procedure that uses a strong magnetic field, radiofrequency pulses, and a computer to create detailed images of organs, soft tissues, and bones. and virtually all structures inside the body.
Brain MRI results are used to examine the anatomy of the brain and aid in the diagnosis of tumors, abnormal growths, blood vessel problems (such as aneurysms), eye disorders, inner ear, stroke stroke, diseases related to the pituitary gland and some chronic disorders of the nervous system such as multiple sclerosis, Chiari malformation (a congenital condition).
2.3 Lumbar puncture (also called lumbar puncture) This diagnostic test involves obtaining and analyzing a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid, the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, from the lumbar region of the spine. Doctors use lumbar puncture to diagnose infections, including: Meningitis (infection of the membrane that covers the brain) and encephalitis (infection of the brain), inflammatory conditions of the nervous system , including Guillain-Barre syndrome and multiple sclerosis, bleeding around the brain, and cancers involving the brain and spinal cord.
2.4 CT angiogram If the doctor suspects an aneurysm, the patient may perform a CT angiogram.
3. Headache, when to do CT and MRI
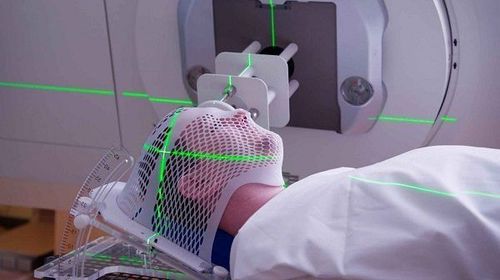
Head CT scan i.e. X-ray scan only to examine the patient's head. The patient lies still and the X-rays move continuously around the head from the chin to the top of the head. Patients are only indicated to have a CT scan of the head when there are signs of suspicion of having a cerebrovascular accident, having a tumor inserted in the brain or having a serious accident that is likely to have a traumatic brain injury.
As recommended by the American Headache Society, patients should not have cranial imaging if the headache has been diagnosed as a migraine headache. Because taking pictures will create the risk of radiation effects and be expensive. In cases where the patient can undergo an MRI to diagnose the cause, the CT scan should not be continued, except in special cases. An MRI scan involves little radiation and can give your doctor a variety of other images of the disease.
Vinmec International General Hospital is proud to be one of the general hospital systems that have invested in modern CT scanners with a team of doctors who are top experts who can conduct imaging, diagnose, detect pathologies of brain damage, and at the same time find out the causes of the disease, thereby directing examination, treatment and rehabilitation for patients.
For detailed information, please contact the hospitals and clinics of Vinmec health system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: adiologyinfo.orgMORE
CT scan of the brain: Everything you need to know What is a CT scan? In which cases need contrast injection? Diagnosis of cerebrovascular abnormalities in headache patients by CT angiography