This is an automatically translated article.
Head trauma in children is one of the most common dangerous events causing disability and death. Children with a minor head injury fall only cause bruises and lacerations on the head, but if it is severe, it can cause brain damage.
1. Types of head trauma in children
Childhood head trauma is any type of injury to the scalp, skull, brain, or other tissues and blood vessels of the head. Head trauma is also commonly known as traumatic brain injury, depending on the extent of the injury. It is one of the most common causes of disability and death in young children.
The risk of falling and having a head injury is common in toddlers or adolescents, occurring twice as often in boys as in girls. Furthermore, head injuries in children are more common in the spring and summer months, when children are very active in physical activities such as running and playing. In addition, children participating in sports such as football, hockey and basketball are also at a higher risk of head injury.
Types of head trauma in children include:
Concussion: This is a head injury that can cause a concussion, causing the brain to stop working properly for a short time. In some cases, a baby's head banging can lead to loss of consciousness or alertness for minutes to hours. Sometimes it is also possible that a child has a minor head injury and the parents are unaware of the unusual symptoms. Hematoma: This is a bruise on the brain after a baby has suffered a head injury. At this point, the injured area will become congested, causing bleeding and swelling inside the surrounding brain. In some cases, a child may have a seizure that occurs on the opposite side of the head due to the brain hitting the skull. Skull fracture: Severe head trauma in children can cause skull fractures. There are 4 main types of skull fracture: Linear skull fracture: This is a fracture where the bone cannot be moved. Children need to be closely monitored in the hospital, but in most cases children can return to normal activities after a few days without treatment. Fracture of the skull: A part of the skull will become indented where the bone was broken when a child falls and sustains a severe head injury. This condition can occur with or without cuts in the scalp. If the inside of the skull presses on the brain, the child needs urgent surgery to help realign it. Pressure fractures: Fractures that occur along the joint lines in the skull, are often seen in infants when the fontanelles have not closed and the skull joints have not yet closed. At this time, the cranial joints will be difficult to heal, but wider. Skull floor fracture: This is a fracture of the bones at the base of the skull, usually when the head trauma in children is severe. Children with this type of skull fracture often have bruises around their eyes and bruises behind their ears. The child may also have clear fluid draining from the nose or ears, because part of the cerebral cortex is torn, causing the cerebrospinal fluid to leak. These cases must be closely monitored in the hospital.

Chấn thương vùng đầu ở trẻ em là bất kỳ loại tổn thương nào đối với da đầu, hộp sọ, não
2. What are the symptoms of a head injury in children?
Symptoms of head injury in children can vary widely, depending on the severity of the injury.
When a child has a minor head injury, the following symptoms may occur:
Swollen or bruised skin; Shallow abrasions on the scalp; Headache; Sensitive to noise and light; Irritability or unusual behavior; Indifference, bewilderment; Dizziness or problems with balance; Nausea, change in taste; Abnormalities in memory or concentration; Sleep changes; Blurry or double vision; Tinnitus . Symptoms of moderate to severe head injury may include any of the above plus:
Loss of consciousness; Severe headache that does not go away; persistent nausea and vomiting; Short-term memory loss; Stutter; Difficulty walking; Weakness on one side or area of the body; Sweat; pale skin color; Seizures or convulsions; Bleeding or discharge from the ear or nose; Pupil dilation; Deep cuts on the scalp; Loss of consciousness and coma.
3. How to approach the diagnosis of head injury in children?
When it is found that a child has suffered a head injury, it is best for parents to take the child to a doctor. The doctor examines and discusses the child's symptoms, health history, and recent injuries.
After that, the child also needs to have the following imaging tests and tools:
Blood tests; X-ray: X-rays will help evaluate the overall skull; Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging: Compared with X-rays, these methods allow better assessment of the internal structures of the skull, investigation of vascular lesions or brain contusion, if present.

Các triệu chứng của chấn thương đầu ở trẻ em có thể rất đa dạng
4. How are head injuries in children treated?
Treatment will depend on the symptoms, severity of the injury, and the child's age and general health. The principles of treatment of head trauma in children include:
Follow-up alone; Bandage and stop bleeding wounds; Suture the scalp to close the open wound; Reducing agitation, by giving a sedative to help the child relax or sleep; Surgery if traumatic brain injury is severe.
5. What are the possible complications of a head injury in children?
Children with severe head trauma may lose some function in muscle strength, speech, sight, hearing or taste. This depends on the area of the brain that is damaged. Long-term or short-term changes in personality or behavior may also be affected. Accordingly, these children require lifelong medical treatment and rehabilitation, which may include physical therapy, occupational orientation or language assistance.
The extent to which a child recovers from a head injury depends on the type of brain injury and other possible medical problems. It is important for early detection, minimal brain damage as well as active rehabilitation, focusing on maximizing the potential of children in the family and community.
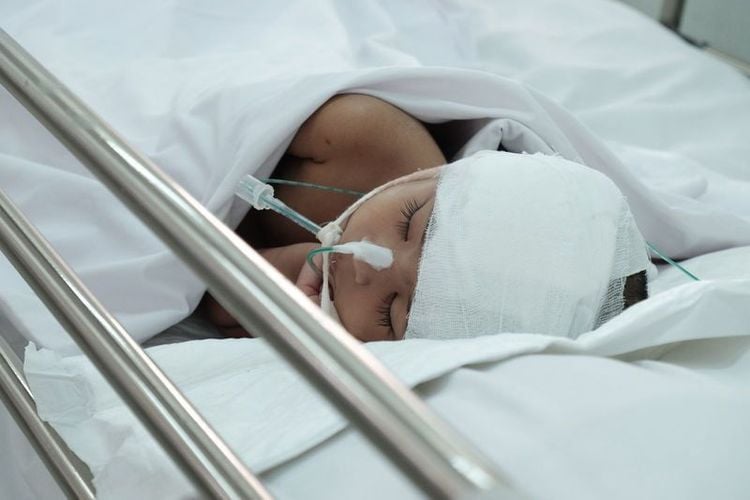
Việc điều trị chấn thương đầu ở trẻ em sẽ tùy thuộc vào các triệu chứng, mức độ nghiêm trọng của chấn thương
6. How can parents help prevent head injuries in children?
Head injuries in children can be prevented in ways such as:
Closely monitoring children as they learn to walk Design an appropriate environment to play safely for children Fully equipped provide children with protective equipment such as wearing helmets when playing sports, cycling, rollerblading, skateboarding In summary, head injury in children is an event that can happen at any time during childhood and adolescence. Most baby head hits are mild and don't cause traumatic brain injury or long-term complications. However, when detecting that their child has fallen on the head, parents should take the child to a doctor to be evaluated and carefully monitored by a doctor, to minimize the risk of unfortunate brain damage in the future.
Currently, the Pediatrics Department at Vinmec International General Hospital is trusted by many parents to examine the diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to. Vinmec brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts by:
Gathering a team of leading pediatricians: including leading experts with high professional qualifications ( professor, associate professor, doctorate, master), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. The doctors are well-trained, professional, have a heart - a vision. Understanding young psychology. Besides domestic pediatricians, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. upon reaching adulthood. Advanced techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to play comfortably and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.