This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital.Acute pancreatitis is an acute inflammation of the pancreas, the disease has many levels from mild to severe and can cause many dangerous complications, one of which is pleural effusion.
1. Acute pancreatitis
1.1. What is acute pancreatitis? Acute pancreatitis is acute diffuse inflammation of the pancreatic parenchyma. Acute pancreatitis ranges from mild to severe and can cause many dangerous complications leading to death.There are many causes of acute pancreatitis, in which gallstones and worms enter the biliary tract, the pancreatic tract is the most common cause, accounting for 40-50%, the next most common cause is alcohol, accounting for 20-30 %. Other less common causes such as:
Hypertriglyceridemia, hyperlipoproteinemia Hypercalcemia (as in Hyperparathyroidism) Pancreatic tumor Acute pancreatitis after surgery, after trauma Acute pancreatitis due to the use of certain drugs such as: : Azathioprine, Thiazid, Methydopa, Tetracycline, Cimetidine,... Acute pancreatitis due to infection, virus (mumps virus, CMV, EBV) Acute pancreatitis due to chronic diseases such as: allergic capillary inflammation, enteritis Chronic pancreatitis,... Acute pancreatitis usually has a sudden onset, usually after a full meal, with a lot of meat and a lot of alcohol. Other predisposing factors such as hepatic colic are seen in patients with gallstones, patients after surgical interventions, and patients after taking certain medications.
Abdominal pain is the most common symptom in acute pancreatitis, 95% of patients with acute pancreatitis have pain symptoms. The location of pain is usually in the epigastrium, the pain is often sudden, intense, and progressive. Depending on the cause of acute pancreatitis, the pain will vary. If the cause is a stone, the nature of the pain is sudden, epigastric abdominal pain, stabbing pain, and pain radiating to the back. If the cause of acute pancreatitis is calculus, the pain is usually not sudden and not as intense as is the case with stones. Other symptoms are:
Vomiting, nausea, pain after vomiting Tachycardia, low blood pressure Fever, jaundice, anemia.

Collection of fluid, necrosis, infection of the pancreas Pancreatic pseudocyst, pancreatic abscess, fistula of the pancreatic duct into the abdomen Blood vessel damage, bleeding Global complications Body as:
Respiratory failure, pleural effusion, renal failure, cardiovascular collapse Gastrointestinal bleeding Acute respiratory failure (ARDS) Disseminated intravascular coagulation
2. What is pleural effusion?
Pleural effusion is a phenomenon in which the amount of fluid in the pleural space increases more than the normal physiological level. If the amount of fluid increases slightly, it may cause no symptoms or only mild shortness of breath, when the volume increases if it is not treated promptly, it can cause many dangerous complications. Common symptoms of pleural effusion are shortness of breath, dry cough, fever, chest tightness,...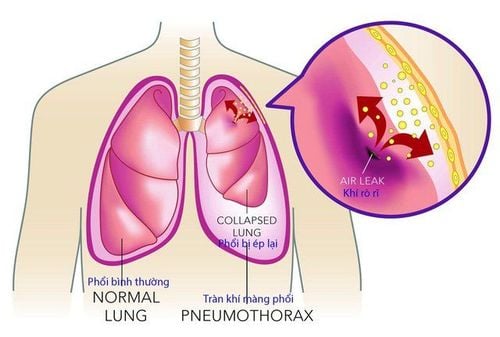
3. Why does acute pancreatitis cause pleural effusion?
Pleural effusion is a possible complication in patients with acute pancreatitis. Effusion can occur in both lungs or only one side, but unilateral effusion is more common. Pleural effusion due to acute pancreatitis is usually mild or moderate.In acute pancreatitis, the normal digestive enzymes secreted by the pancreas to digest food such as amylase, lipase, trypsin,... come back to destroy pancreatic tissue. Normally, these enzymes are in the form of inactive pro-enzymes, they are only activated in the duodenum or in the presence of trypsin.
When there are favorable factors for the onset of acute nephritis such as after a full meal with a lot of meat, drinking a lot of alcohol, roundworms, stones, trauma,... these triggering factors will damage cells and induce the release of cell enzymes. These cellular enzymes will activate trypsinogen to trypsin, which in turn activates the remaining enzymes that cause pancreatic damage.
The first lesion of acute pancreatitis is interstitial edema, about 85-95% of cases will be completely cured. However, 10-15% will have severe changes with pancreatic tissue destruction, hemorrhagic necrosis, and fat necrosis.
In severe cases of the disease, pancreatic enzymes will enter the abdomen causing damage to the abdomen, pancreatic enzymes also enter the circulatory system to distant organs such as lungs, kidneys, causing damage and functional failure. capacity in these institutions. Complications may occur such as shock, acute respiratory failure, acute renal failure, peritonitis, pancreatic pseudocyst... Acute pancreatitis also releases intermediate chemicals such as Prostaglandin E1, Prostaglandin E2, interleukin 1,... causes increased vascular permeability, increased fluid secretion leading to effusion in organ systems, including pleural effusion.
With nearly 20 years of working at Da Nang General Hospital in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy - hepatobiliary disease, every year, Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang participates in endoscopy more than 1500 cases including: endoscopic diagnosis of diseases stomach, colon such as: detecting inflammation, ulcers, polyps, cancer, finding HP bacteria, detecting cancer early in the digestive tract...; Endoscopic treatment such as: Hemostasis in gastrointestinal bleeding, esophageal varices ligation in cirrhosis, endoscopic gastrointestinal polypectomy...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.