This is an automatically translated article.
The Hargraves cytology test, also known as the LE cell test, is a laboratory test used in people with symptoms of suspected systemic lupus erythematosus to accurately diagnose this disease.
1. Systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus is defined as a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder. Lupus' inherent role is to protect the human body from infection and create an inappropriate immune response to organ tissues. Lupus usually affects certain skin, joints, blood vessels, internal organs such as kidneys, heart, lungs, brain. There are many types of lupus, but the most common is systemic lupus erythematosus or for short, lupus erythematosus, which affects many parts of the human body.Lupus erythematosus is more common in women than in men, and is common in Africa, Asia, Hispanic regions, and Native American populations. The disease is more likely to occur in people between the ages of 15 and 45 years, but there are still cases of children or adults with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Up to the present time, the cause of systemic lupus erythematosus has not been found clearly and completely studied. Some have suggested that lupus erythematosus is hereditary and that the trigger is related to the surrounding environment. Other studies have found that systemic lupus erythematosus is caused by medications or infections, viruses, or hormones. Systemic lupus erythematosus is often associated with other autoimmune disorders such as hemolytic anemia Sjogren's syndrome, thyroiditis, or idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Lupus erythematosus cells or LE cells were first described by Hargraves and are therefore also called Hargraves cells. Lupus erythematosus cells are found in the bone marrow of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. The scientists then studied the biology of these LE cells, creating them by exposing the blood of people with lupus directly to their own plasma for the right time and temperature. . Since then, it has been found that a type of test called Hargraves cell test or LE cell test has an important role in diagnosing systemic lupus erythematosus.
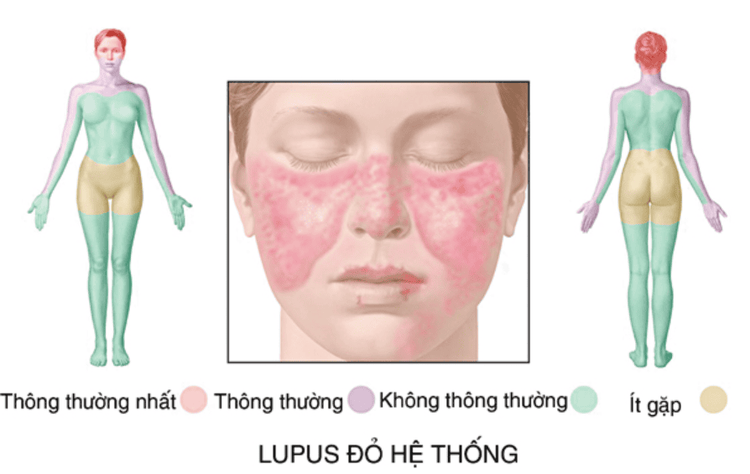
Nguyên nhân bệnh Lupus ban đỏ hệ thống vẫn chưa được tìm thấy rõ ràng
2. Hargraves . cytology
People who develop the following symptoms will be included in the group suspected of having systemic lupus erythematosus and are assigned to have a Hargraves cytology test to confirm the diagnosis:Muscle and joint pain Arthritis, mono or inflammation Multiple joints Red, butterfly-shaped rash on the nose, cheeks Fever Prolonged fatigue Swelling of glands in the body Increased sensitivity to sunlight Symptoms of Raynaud's phenomenon Hair loss Chest tightness Symptoms of anemia such as blurred vision, dizziness, pale mucous membranes... Oral ulcers Inflammation of organs such as kidneys, lungs, heart, pericardium, central nervous system, blood vessels... LE cell test will be performed on patients with the above symptoms and is done by taking the following specimens:
Bone marrow anticoagulation with Heparin Venous blood anticoagulating with Heparin Venous blood Oxalate anticoagulating Blood vein splits Fibrin Venous blood clots LE Factor and other cells in the patient's body. When doing the Hargraves cytology test, taking a bone marrow sample causes a lot of pain to the patient, so now, venous blood sampling is often the more popular option for testing. Venous blood of patients not used for treatment will be clotted and serum removed, transferred to wire mesh and centrifuged for 5 minutes to create a Buffy layer and finally spread on glass slides for LE cytology. diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus.
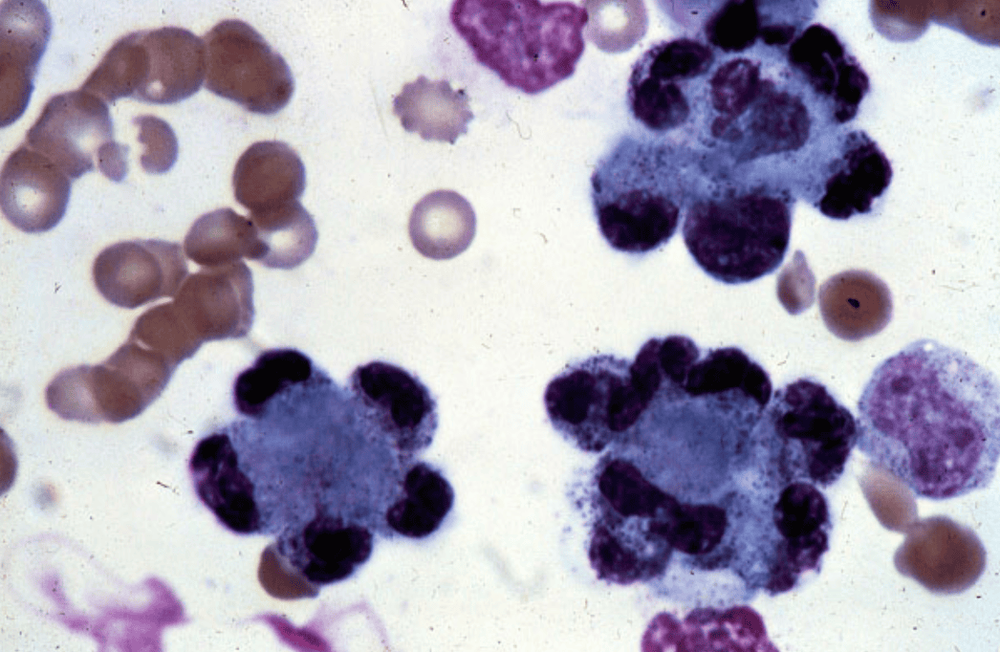
Xét nghiệm tế bào LE chẩn đoán bệnh Lupus ban đỏ hệ thống
If the result is the opposite of the above, it is negative and the doctor can conclude that the patient does not have systemic lupus erythematosus. Hargraves cytology is positive when 2% to 30% of LE cells are seen on a white blood cell microfield. However, for the test to be accurate, it also depends on a number of factors such as technique, technician's observation. In the process of performing LE cell testing, it is necessary to avoid confusion with Tart cells, which are mononuclear cells, have nuclei and are not as large as LE cells.
LE cell test is positive not only in systemic lupus erythematosus, but also in other conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, chronic hepatitis, scleroderma, dermatitis, acquired hemolytic anemia, disease Hodgkin... and people using some drugs such as Phenylbutazone, Hydralazine... so the possibility of testing positive LE cells for lupus is only about 50% to 75%.
Hargraves cytology is a laboratory technique used to diagnose systemic lupus erythematosus. However, not all cases that are positive for LE cytology have the disease, so it is necessary to rely on other factors as well as other laboratory results to support the definitive diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. system.
MORE:
Should lupus patients get pregnant and give birth? What disease is lupus? Dangers and complications of the disease Should patients with lupus erythematosus get pregnant and give birth?