This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Vu Van Quan - Department of General Surgery & Anesthesia - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.The appendix is an intra-abdominal, worm-shaped component 3 to 13 cm long that opens into the cecum through the appendix orifice covered by a valve. Appendicitis is one of the most common surgical emergencies. If not treated promptly, the inflamed appendix can progress to rupture of fluid, pus into the abdomen causing generalized peritonitis and can be life-threatening.
1. Overview of acute appendicitis
The appendix (Appendix) is a part of the digestive tract, located at the junction connecting the small intestine (Ileum) and large intestine (Cecum). Usually, the appendix is located in the lower right abdomen, but in many cases it is located in other locations nearby, even in the middle and left side of the abdomen.Acute appendicitis is an inflammatory condition of the appendix that causes an acute surgical abdominal pain that requires urgent intervention, mainly emergency surgery.
In Vietnam, the number of surgeries for acute appendicitis always accounts for the highest percentage in surgical abdominal emergencies. Acute appendicitis is common in young people, especially in the age group of 20-40 years, then the frequency decreases gradually. An estimated 70% of patients with acute appendicitis are under the age of 30.
Diagnosis of acute appendicitis cannot be based on a single symptom, sign or test alone, but requires a combination of All of the above factors to increase the accuracy of the diagnosis. When the appendix is in an abnormal position (retrocaecal regurgitation, pelvic appendix, hepatic angle appendix, left abdominal appendix,...) or in the elderly, children, pregnant women, etc. .. sometimes appendicitis symptoms are atypical, making it difficult to diagnose, easy to miss at an early stage (only detected when appendicitis is in the late stage when there are complications).
2. Causes of acute appendicitis
2.1. Appendiceal lumen obstruction
Obstruction of the appendix lumen is considered to be the main cause of acute appendicitis. Foreign bodies such as fecal stones, food (seeds, fibers, etc.), parasites, tumors or enlarged lymph nodes can obstruct the lumen of the appendix. Fluid in the appendix becomes stagnant, increasing the pressure in the appendix lumen. At the same time, bacteria grow and invade the intestinal wall. Eventually leading to necrosis of the appendix (obstructive appendicitis).2.2. Appendiceal mucosal ulcer
Inflammatory lesions start from ulcers on the appendix mucosa, gradually invade the layers below, causing the wall of the appendix to swell and block the blood vessels supplying the appendix. At this time, the appendix is ischemic and necrotic (secretory appendicitis).3. Progression of acute appendicitis
Most obstructive appendicitis will progress to appendiceal perforation/rupture, resulting in peritonitis, a systemic infection with a very poor prognosis, difficult to treat, and life-threatening. seriously threaten the patient's life.Meanwhile, exudative appendicitis has a more diverse progression, depending on the patient's resistance. In addition to perforation/rupture progression, appendicitis can progress to appendiceal masses or abscesses. However, these are conditions that do not require urgent intervention such as perforation/rupture.
If the inflammation of the mucosa is resolved early, the appendix may return to a completely normal state or there is a possibility of fibrosis or mucinous formation of the appendix.
4. Symptoms of acute appendicitis
4.1. Appendiceal abdominal pain
Is the first and always present symptom. Characteristic of the pain: Pain begins in the area around the navel or above the navel. The pain is usually dull and constant, rarely intense or sharp. After 2-12 hours, the pain moves down to the right iliac fossa (above the groin) and gradually increases in intensity. This typical migratory pattern is the most reliable symptom of acute appendicitis. Depending on the location of the patient, depending on the location of the appendix and so the location and nature of the pain can be different for each person.
4.2. Fever
Patients usually have a mild fever, about 37.5 - 38 degrees Celsius.4.3. Digestive disorders
Patients may have other symptoms such as: Anorexia/loss of appetite, vomiting/nausea, diarrhea, rarely constipation.5. Tests used in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis
5.1. Tests for inflammation
Due to the inflammation of the appendix and the risk of intra-abdominal infection from rupture/perforation, the patient will be tested for inflammation.These tests mainly look at peripheral blood, so the patient will usually have blood drawn on admission.
5.2. Imaging tests to examine the condition of the appendix
Abdominal ultrasound: This is the first imaging tool for 1 case of acute appendicitis. In fact, because it is easy to be equipped at all medical levels, now abdominal ultrasound is almost a common imaging method. used in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis, especially in pregnant women and young children.Advantages: Easily available at many medical facilities, mobile, fast, inexpensive, patients are not exposed to rays and can help distinguish other causes of abdominal pain other than acute appendicitis. Cons: Sensitivity >83%, depends on the level of the operator. Computed tomography CT-Scan :
Advantages: Higher accuracy than ultrasound (sensitivity >90%) in diagnosing acute appendicitis, quick results, accurate image of the whole muscle in the belly, regardless of the skill of the performer. Cons: Patients must be exposed to high-intensity radiation and often have to use contrast agents, so it is not suitable for children, pregnant women or patients with kidney failure. When needed, it is recommended to use only low doses and no contrast agent. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
Advantages: As accurate as CT-Scan, the patient is not exposed to radiation. Cons: Expensive, not available, difficult to read, long waiting time not suitable for extreme cases. Therefore, MRI should only be taken when the medical facility has adequate facilities, applicable to difficult-to-diagnose cases where the patient cannot have a CT-Scan.
6. Special types of acute appendicitis need attention
6.1. In pregnant women
The diagnosis of acute appendicitis in pregnant women is challenging because the symptoms of appendicitis are similar to those commonly encountered in normal pregnancies. On the other hand, because the appendix is pushed up and out during pregnancy, the location of the pain will also change.Ultrasound is quite useful and should be the first survey of choice because it has absolutely no effect on the fetus. In contrast, CT-Scan is a means to consider. An alternative MRI may be selected if possible.
When acute appendicitis is diagnosed in pregnant women, early surgical intervention is necessary because acute appendicitis with necrotizing peritonitis increases the risk of miscarriage by 4 times.
6.2. In patients with ascites
In people with liver failure, renal failure with ascites, the symptoms of acute appendicitis are easily confused and are also difficult to examine clinically or to use imaging means. In these cases, a laparoscopy or laparoscopy is required for diagnosis.6.3. In patients already taking antibiotics
Antibiotics may not completely extinguish the inflammatory process, but even mask the symptoms of acute appendicitis, making it very difficult to diagnose and treat. Therefore, patients need to carefully report to medical staff the process of taking medicine when going to the doctor.7. Treatment of acute appendicitis
The principle of treatment of acute appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix.
Surgery should be performed as soon as possible, as soon as the diagnosis is made. This is the natural and undisputed treatment for cases of necrotizing appendicitis or perforation causing peritonitis. Even some suggest that even though the diagnosis of appendicitis is not confirmed, if the patient has appendicitis-like pain and is progressing, surgery is still recommended to avoid ominous complications of enteritis. redundant.
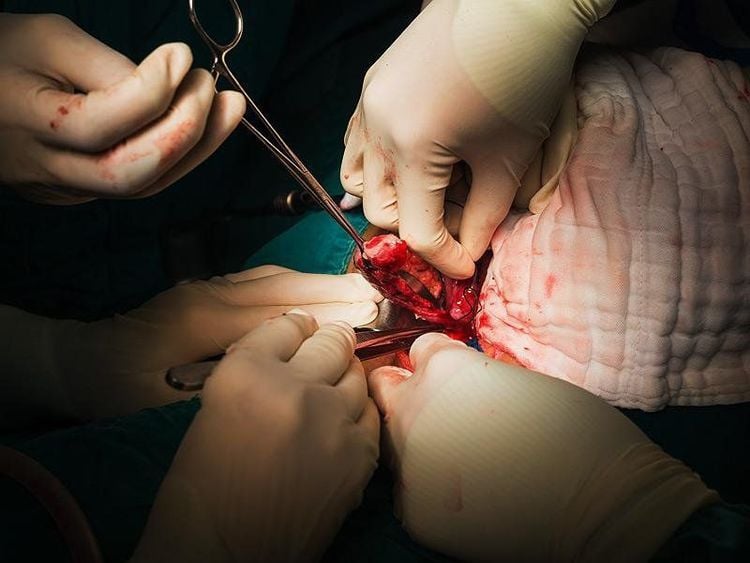
For cases of acute appendicitis progressing to appendicitis or appendicitis:
Appendiceal abscess: Immediate surgery should be avoided because of the high complication rate and risk of small bowel resection. necessary, needs. The current trend is conservative treatment with antibiotics + percutaneous aspiration/drainage first, if there is no response or the abscess is too large, then surgery. Appendiceal clumps: Considered as a mechanical and biological barrier surrounding the inflamed appendix, emergency surgery is not required. The goal of treatment is to control the inflammation of the appendix with antibiotics, then schedule a "cold" operation to remove the appendix, usually after about 6-12 weeks.
8. Prognosis and prevention
Acute appendicitis if diagnosed early and operated early, the prognosis is very good. When there is a complication of perforation/rupture causing peritonitis, the prognosis is very poor and difficult to treat.
Prophylaxis: The cause of acute appendicitis is usually obstruction, with nearly 40% being stuck with fecal stones or foreign objects in the lumen of the appendix. Therefore, it is necessary to have a high-fiber diet and drink lots of water. Enlargement of lymph nodes is also common, so it is necessary to actively treat inflammatory diseases of the pharynx and digestive tract if present.
Acute appendicitis is an acute surgical condition requiring prompt medical intervention. The disease has a dangerous progression, but if detected and treated early, it is very easy. Therefore, patients need to be aware of the prevention of acute appendicitis, and at the same time, they must immediately visit medical facilities when they suspect appendicitis pain for the fastest treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.