This is an automatically translated article.
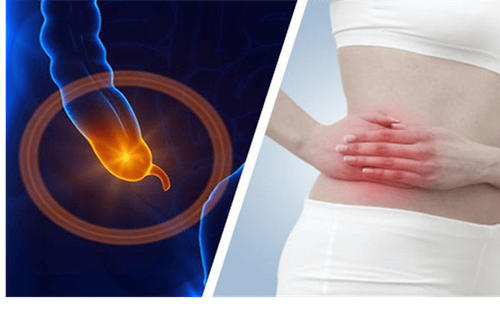
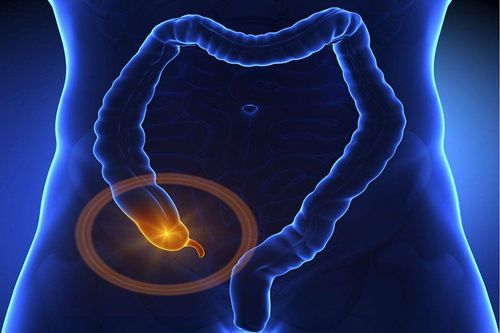
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital. Doctor has nearly 20 years of experience in the field of gastroenterology - Hepatobiliary tract.The appendix is a small, finger-shaped tube-shaped structure that arises from the first part of the large intestine called the cecum. Appendicitis is when the appendix becomes infected and inflamed. When the appendix becomes inflamed, it swells and in some cases ruptures and even dies. Anyone can get appendicitis, but it's most common between the ages of 10 and 30. The standard treatment is resection of the inflamed appendix.
1. Symptoms of appendicitis
1.1 Abdominal pain is the first and always present symptom. Abdominal pain in appendicitis due to inflammation typically has the following characteristics: The pain begins around the umbilicus or epigastrium accompanied by nausea or vomiting. After about 2-12 hours, the pain gradually increases and moves down to the right iliac fossa region, continuous dull pain, increases when coughing or when changing position,... This is the most reliable symptom to recognize. 1 case of acute appendicitis.Depending on the location of the appendix, the patient will have a very different feeling about the location of abdominal pain in appendicitis: hip pain (postcecal appendix), hypogastric pain (pelvic appendix) , pain under the right flank (appendix under the liver), ...
In addition, the nature of abdominal pain in appendicitis depends on many other factors: Medication being used, patient's tolerance , the patient's resistance, the patient's medical condition.
1.2 Fever Usually no fever or mild fever ~38 degrees Celsius due to inflammation of the appendix. If there is a complication of peritonitis, the infection is severe, causing high fever.
1.3 Anorexia Anorexia, though not constant, is nearly always present in acute appendicitis, so much so that many experts consider the absence of this symptom to warrant reconsideration of the diagnosis of appendicitis.
1.4 Nausea, vomiting Nausea, vomiting are signs of acute appendicitis. It always comes after abdominal pain. However, this symptom can deceive patients as well as doctors with other diseases such as gastritis or food poisoning.
1.5 Diarrhea Diarrhea is only seen in some special cases such as appendicitis of the pelvis or appendix that has been complicated by rupture, creating inflammation in the sac of Douglas (the lowest area of the abdomen when standing) causing irritation. likes to have a bowel movement
It should be noted that there are many diseases of the abdomen and pelvis that mimic appendicitis. For that reason, in order to diagnose appendicitis, a patient should be fully evaluated with laboratory tests, imaging studies, and a thorough examination by a gastroenterologist.

2. Complications of appendicitis
If appendicitis is not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can lead to the following complications:Perforated appendix: when the appendix ruptures, bacteria will spread throughout the abdomen and can be dangerous to the body. live. Surgery to remove the appendix and clean the abdomen is required immediately. Abdominal abscess: When the appendix is left for a long time or improperly treated, the abdominal organs such as the great omentum, small intestine,... come to cover the pus-filled cavity, forming a localized pus-filled pocket. in the abdomen is called an abscess. Treatment for this case is to prioritize drainage under the guidance of ultrasound in combination with antibiotic treatment according to the protocol. Then an appointment for appendectomy after 6 months. The diagnosis of appendicitis should be made by an experienced gastroenterologist after a thorough examination and examination with laboratory and imaging studies.
Diagnosis is based on:
Physical examination: including a thorough history, careful abdominal examination is necessary for a definitive diagnosis. Blood tests: Helps assess inflammation and infection to aid in diagnosis and treatment. Imaging: Patients can have X-ray, ultrasound, or CT scan of the abdomen to help confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis as well as differentiate it from other causes of pain other than appendicitis. .
3. Treatment of appendicitis
From 2004 to now, there have been a number of studies on non-operative treatment of uncomplicated appendicitis with antibiotics. Results from these studies showed that the success rate of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis was 90%, 10% were unresponsive and had complications requiring surgical intervention. Follow-up of patients who successfully treated for uncomplicated appendicitis within 1 year had 30% recurrent appendicitis.
So treatment of uncomplicated appendicitis with antibiotics cannot completely treat appendicitis and the disease will have a very high risk of recurrence in a short time. Therefore, the gold standard of treatment for appendicitis remains surgical resection of the inflamed appendix. This is an effective method to help definitively treat appendicitis.
Currently, emergency non-operative treatment is considered in special cases when the appendix ruptures and creates an abscess. Treatment for this case is to prioritize drainage under the guidance of ultrasound in combination with antibiotic treatment according to the protocol. Then an appointment for appendectomy after 6 months.
Inflammatory appendectomy can be performed in 2 ways: laparoscopic or open surgery. However, laparoscopic surgery is the method of first choice for appendectomy in all cases unless there are contraindications to laparoscopic surgery such as patients with severe cardiovascular or respiratory disease who cannot tolerate surgery. laparoscopic surgery, or patients with a history of previous laparotomy,...
Laparoscopic surgery is most commonly used in the treatment of appendicitis because of its many outstanding advantages. These include faster recovery time, less pain, very small incisions and no scars, especially good for people with obesity and the elderly. In cases where the appendix has ruptured and the infection is inside the abdomen, or the patient with ruptured abscess cannot perform well and safely with laparoscopic surgery, it will be converted to open surgery. It's not a failure with laparoscopic surgery but for safety reasons.
Appendicitis without complications, mainly treated by laparoscopic transabdominal surgery. In case there are complications, depending on the complication, the doctor will prescribe different surgical methods, incisions and treatment methods. After surgery, it is necessary to gently exercise as soon as possible to improve blood circulation, stimulate bowel movements to work again to avoid blockage or adhesions. If there are no complications, the patient can return to normal physical activity after 4 weeks.
Appendicitis can cause complications such as: generalized peritonitis, appendicitis abscess, bowel rupture, and even death. Therefore, when you see any abnormal signs, it is necessary to immediately go to a medical facility for examination and timely intervention.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination, consulting and service services. comprehensive and professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.