This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi An - Pediatrician - Neonatologist - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Hand, foot and mouth disease is a contagious disease that spreads very quickly and can become an epidemic if not recognized early and well controlled.
1. What is hand, foot and mouth disease?
Hand, foot and mouth disease is an acute infectious disease caused by coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71. The disease is common in children under 5 years old, because at this time the child's immune system has not been fully developed, so the ability to resist the invasion of pathogenic viruses is not good, easy to catch infectious diseases.
Bệnh chân tay miệng là một bệnh truyền nhiễm cấp tính do vi-rút gây ra
Encephalitis - meningitis, myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema leading to death. death. Weakness, paralysis; cranial nerve palsies Hypertension, vascular collapse Increased muscle tone,... Hand, foot and mouth disease does not only affect children, there are reports of adult cases of hand, foot and mouth disease transmission. from sick children when taking care and cleaning for children.
2. The spread of hand, foot and mouth disease
This is an infectious disease, the ability to spread very quickly and can become an epidemic if not recognized early and well controlled.So, how is hand, foot and mouth disease transmitted? Accordingly, the virus spreads very quickly and exists in saliva, sneeze, runny nose, feces, broken fluid on the skin, mucous membranes... they cause the body to increase secretion of secretions when sick . Children sneezing, runny nose, sucking on toys together are favorable transmission routes. When released, the virus can still survive for a long time in a room temperature environment, clinging to utensils, toys, floors, cups, towels, clothes,... If a child is healthy Communicating in this environment is very susceptible to infection.
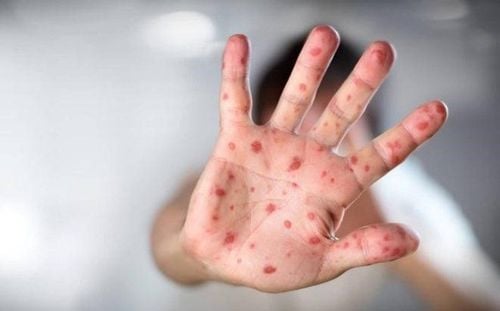
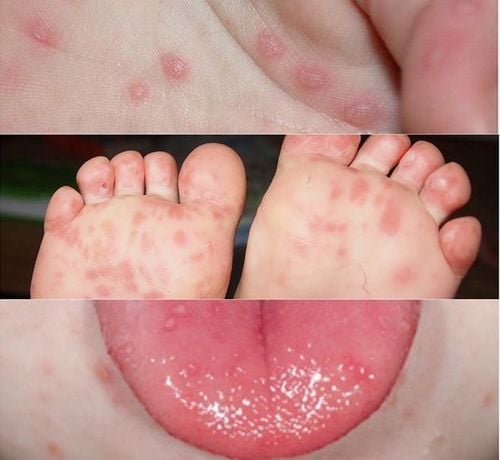
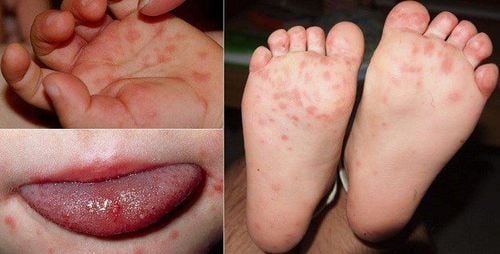
The main manifestation of hand, foot and mouth disease in children is skin and mucosal lesions in the form of blisters in special locations such as oral mucosa, palms, soles, buttocks, knees.
3. Hand, foot and mouth disease incubation period
The incubation period for hand, foot and mouth disease is 3-7 days. This is the time when the symptoms are not typical, the patient has not yet discovered that he has hand, foot and mouth disease and can spread the hand, foot and mouth virus to the community.When symptoms appear, in infants and children there are some typical signs as follows:
The illness usually begins when the child has flu-like symptoms: A low-grade fever lasting 24 to 48 voice, poor appetite, irritability, fatigue, sore throat... After 2 days these symptoms subsided, signs of hand, foot and mouth disease began to appear. Children will have blisters on the skin in the oral cavity (tongue, inner cheeks), palms and soles. Blisters may also appear on the buttocks or around the anus. Blisters are the most obvious symptom of this disease. Because of blisters in the mouth, children will lose their appetite and stop feeding. When they first appear, these rashes appear as small, red, and flat scars. Then they gradually blister up to contain water inside like blisters, erythema, gray color, when healed, do not cause scarring. These nodules are painless and do not itch, unlike chickenpox, which is itchy and painful. The vesicles in the mouth and other places burst open, causing wide open sores. Making children in pain, parents need to keep these open wounds clean for children to avoid infection.
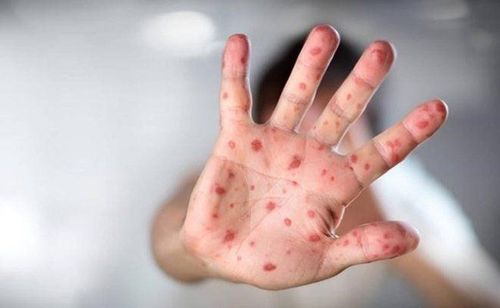
Bệnh tay chân miệng làm xuất hiện mụn nước trên da
4. Hand, foot and mouth prevention
Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease and specific treatment, the treatment of the disease is mainly symptomatic treatment. Therefore, in order to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease in children, parents need to:Practice good eating and drinking hygiene such as: eating clean and safe processed food, drinking cooled boiled water. Teach children not to put their hands in their mouths or suck on toys. Children's items such as towels, clothes, dishes as well as learning tools, children's toys should be soaked with disinfectant solution and dried in the sun. Tables and chairs, floors, handrails, stairs, doorknobs, especially at babysitting points need to be cleaned and disinfected periodically with antiseptic water, similar to toilets and sewers. In addition, parents or caregivers need to actively observe the health status of children every day. When a child becomes ill, it is necessary to quickly report for isolation and disinfection to minimize the spread to other children, forming an outbreak. For suspected cases, children should be taken to medical centers soon for examination and monitoring. When the child is infected, parents need to observe and not let the child scratch or poke the blisters on the body; Clean living environment, avoid exposing children to dirty air and water. Master. Doctor. Nguyen Thi An, former Head of Pediatrics Department, Quang Ninh General Hospital, is a person who is very passionate about health care for children and successfully treats many difficult cases. Currently, he is a Pediatrician - Neonatologist - Neonatology Department of Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Department of Preventive Medicine - Ministry of Health