This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Truong Thanh Tam - Pediatrician - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.1. Overview of hand, foot and mouth disease in children
Hand, foot and mouth disease in children is a disease caused by coxsackie virus and enterovirus 71 (EV71). The disease is common in children younger than 5 years old, especially from 6 months to 3 years old, which is the age to go to kindergarten and is easily contagious.Newborns under 6 months of age are less likely to get the disease because of protection from the mother's antibodies. The main route of transmission of hand, foot and mouth disease is the gastrointestinal tract. The virus enters the sick child's body through the lining of the digestive system such as the mouth, intestines and spreads to other organs in the body through the bloodstream. The virus infects organs such as the central nervous system, skin, mucous membranes, heart, and lungs.
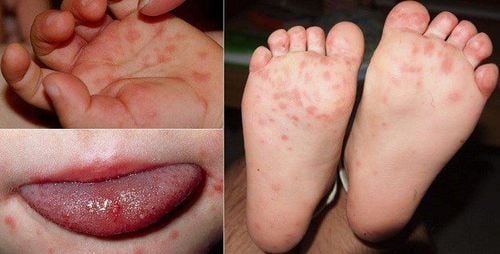
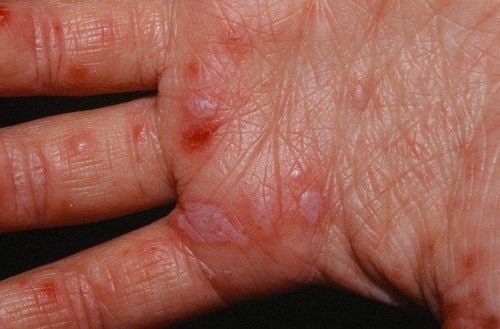
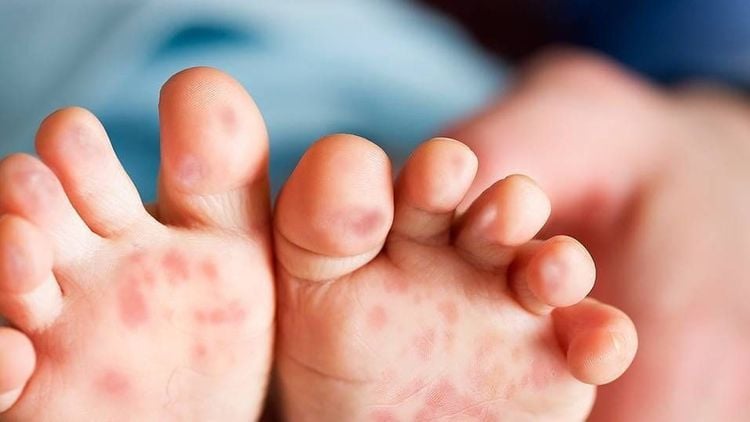
Children with hand-foot-and-mouth disease have characteristic features with bullous lesions on the oral mucosa, the skin of the palms and soles, the knees on the sides, and the buttocks.
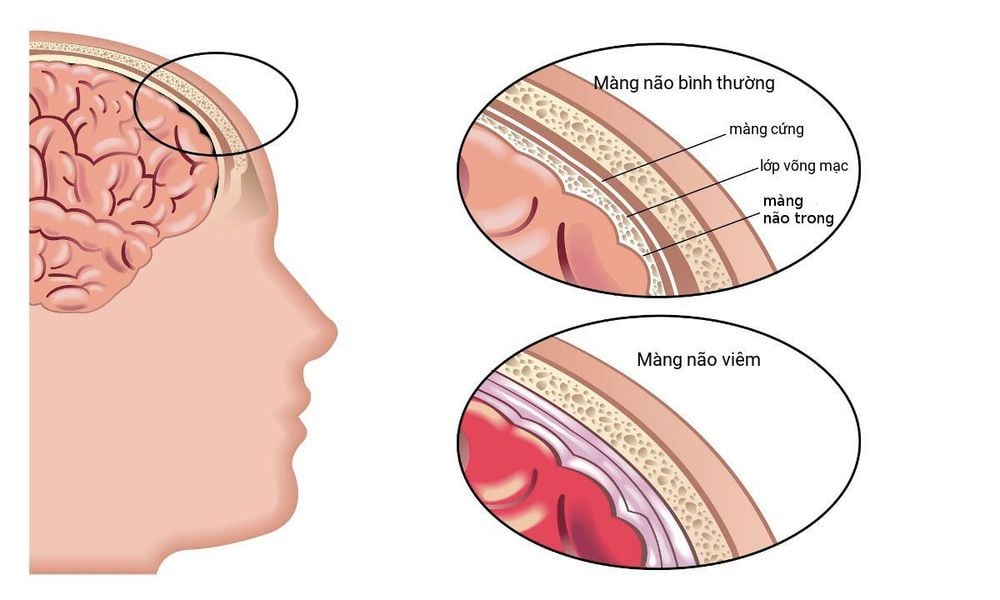
Hand, foot and mouth disease in children can also lead to many serious complications such as: meningitis, acute pulmonary edema and myocarditis causing acute respiratory and circulatory failure. These complications are the cause of death in children with hand, foot and mouth disease if not treated promptly.
2. Diagnosis of hand, foot and mouth disease
A child with HFMD is usually detected for follow-up and treatment based on epidemiological information, clinical symptoms, and results of laboratory tests.2.1 Epidemiological characteristics The characteristics related to age, time of disease and number of children infected in an area during the same time are important clues regarding cases of hand, foot and mouth disease in children.
2.2 Clinical A typical case of hand, foot and mouth disease will go through 4 stages
2.2.1 Incubation period Counted from the moment the virus enters the human body until the first clinical symptoms appear ready. Hand, foot and mouth disease in children has an incubation period of 3 to 7 days on average.
2.2.2 Stage of onset Clinical manifestations are transient and atypical. Children with the disease may have mild fever, loss of appetite, sore throat, body fatigue, fussiness and digestive disorders.
2.2.3 The full-blown phase This is the time when the clinical symptoms become so intense that the child must appear. Typical symptoms of the disease appear include:
Blisters and red sores on the lining of the oral cavity, gums and tongue. Red blisters on the skin of the palms, soles, knees, and buttocks. They usually disappear after a week and leave hyperpigmented dark spots on the skin. High fever Vomiting a lot. Cardiovascular, respiratory and neurological disorders begin to appear in the early days of the disease.
2.3 Laboratory tests When hand, foot and mouth disease is suspected, the child will be ordered to perform the following laboratory tests:
Blood count Bilan inflammation with C-reactive protein (CRP) Bilan water electrolytes Blood sugar test Chest X-ray Cardiac enzyme quantification Echocardiogram Echocardiogram Aspiration of cerebrospinal fluid MRI Cranial MRI Test to detect virus in body: Samples are taken from mucosal skin areas with lesions such as mucous membranes pharyngeal mucosa, rectal mucosa, vesicular nodules on the skin and virus isolation tests were performed.
3. Treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease
Currently, there is no specific treatment for this virus, so the principles of treatment focus on:Adequate nutrition for the child, improving the child's general condition. mild symptoms Coordinate use of antibiotics when detecting infectious complications Monitor and detect cardiovascular, respiratory and neurological complications early for timely treatment.

4. Prevention of hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease is an infectious disease caused by a virus and is spread mainly through the gastrointestinal tract. The disease can be prevented by the following measures:Concentrated isolation according to disease groups Wash hands with antiseptic solutions thoroughly before and after caring for or contacting sick people, before eating and after going. toilet. Disinfect and clean surfaces and beds. Patient waste should be handled in accordance with regulations. Eat with safe food and use clean water. Sanitize children's items, especially toys.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.