This is an automatically translated article.
Gonorrhea is a very common infectious disease. The CDC estimates that about 1.41 million new gonorrhea infections occur in the United States each year, and up to half of them are young people (ages 15-24). In 2018, there were 583,405 cases of gonorrhea reported. Gonorrhea can easily be cured with antibiotics, but if left untreated, you run the risk of serious problems like infertility.1. What is gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by infection with the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This bacteria is commonly found in the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes in women, and the urethra in men. Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria can also cause infections of the lining of the mouth, throat, eyes, and rectum.
2. What are the signs of gonorrhea?
The rate of men getting gonorrhea in one sex with infected women is 20% while the rate for women is 60-80%.
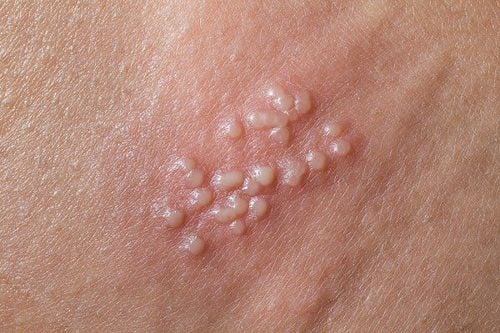
Many men have gonorrhea without any symptoms of the disease. Typically, signs of gonorrhea in men include difficulty urinating, and the urethra appears white, yellow, or green. These symptoms usually appear 1-14 days after infection. In the case of a urethral infection caused by epididymitis, men may also experience testicular or scrotal pain.
For women, about 50-80% of gonorrhea cases have no symptoms or obvious symptoms. Some infections often have symptoms, including a mild cough, and nonspecific signs that can easily be confused with a vaginal infection.
Common signs when women have gonorrhea include difficulty urinating, increased vaginal discharge or vaginal bleeding. Women with gonorrhea are at risk for serious complications from the infection, even though the symptoms may not be obvious.
Symptoms of rectal infection in both men and women can include discharge, anal itching, pain, bleeding... Rectal infections are also asymptomatic. Throat infections can cause a sore throat, but there are often no symptoms.
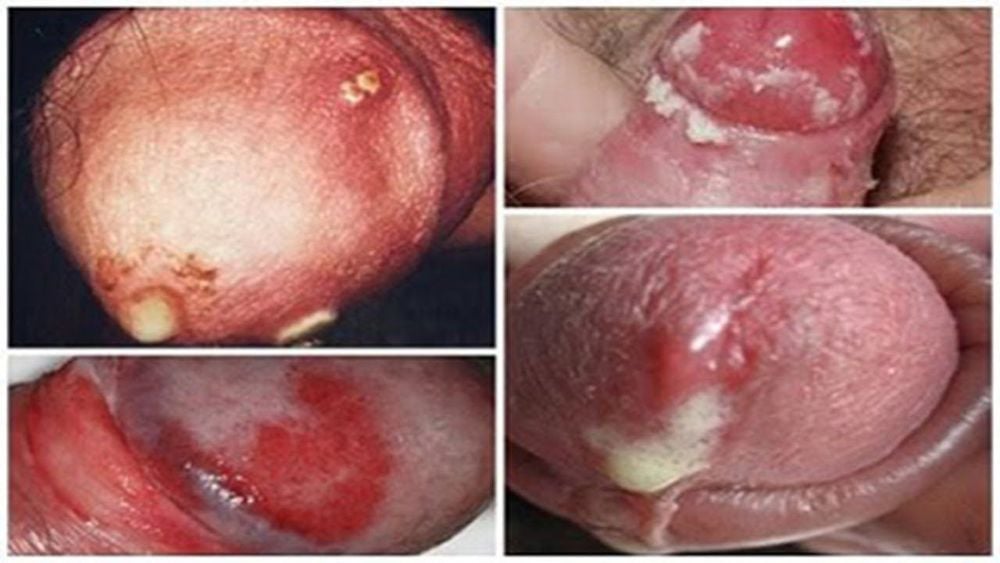
Hình ảnh bệnh lậu ở nam giới
3. Is gonorrhea dangerous?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria cause disease so silently that many people do not know they are carrying the disease, through sexual contact.
Gonorrhea, if not treated promptly, can be life-threatening, including serious health problems in both men and women.
In women, gonorrhea can spread into the uterus or fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Symptoms can be mild or severe, including fever and abdominal pain. PID damages the fallopian tubes, causing infertility or increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy in women. Pregnant women with gonorrhea, if left untreated, can put their babies at risk of miscarriage or infection. This can cause blood infections, sores in the baby. Treating gonorrhea when detected in a pregnant woman will reduce the risk of these complications.
In men, gonorrhea can be complicated by epididymitis. This can lead to infertility in men.
If not treated promptly, gonorrhea can also spread into the bloodstream and cause systemic opportunistic infections (DGI). Gonorrhea infection can spread to other parts of the body. Bacteria can enter the bloodstream. Inflammation of the joints, skin, and other organs can occur if you have gonorrhea but don't get it treated.
Untreated gonorrhea can increase your risk of getting or transmitting HIV.
Bệnh lậu do vi khuẩn Neisseria gonorrhoeae gây ra
4. Treatment of gonorrhea
To avoid getting gonorrhea, you can protect yourself by not having sex with someone who has gonorrhea or by using safe sex methods like using condoms...
Gonorrhea can be cured cured if treated properly. Currently, the CDC is promoting dual therapy (i.e., the use of two drugs simultaneously) for the treatment of gonorrhea. The most important thing is to take the drugs prescribed by your doctor to treat gonorrhea. Medicines for gonorrhea should not be shared with anyone. Although the drug will stop the infection, it cannot cure the damage caused by the disease.
It is becoming more and more difficult to treat gonorrhea with antibiotics because the bacteria that cause gonorrhea are becoming too resistant to common drugs like penicillin...
After being treated, the symptoms persist continue to occur, you should immediately go to medical facilities to be re-checked. Sex should be avoided for at least a week after completing treatment for gonorrhea.
Gonorrhea is a very contagious disease and nowadays it is becoming more and more difficult to treat. Even if you are cured, but if not prevented properly, gonorrhea can still come back. Therefore, when you see any signs of the disease, you should immediately go to a medical facility for timely treatment, and at the same time you need to know how to protect yourself by using safe sex methods. entirely when the health status of the sexual partner is unknown.
Package of Social Diseases Examination and Screening of Vinmec International General Hospital helps customers to screen for social diseases in order to detect diseases early for effective treatment and avoid complications. Screening package for social diseases for all ages, for both men and women. For advice and to book an appointment, you can contact HERE
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Webmd.com; Cdc.gov