This is an automatically translated article.
DiGeorge syndrome, also known as chromosome 22 deletion syndrome, is a common syndrome that causes congenital heart disease and many other birth defects. Genetic testing for DiGeorge syndrome is a prenatal screening and diagnosis method that can help alleviate symptoms and mortality associated with the syndrome.
1. What is DiGeorge Syndrome?
DiGeorge syndrome also known as chromosome 22 deletion syndrome. This is a common syndrome associated with the loss of 30 to 40 haplotype genes.
DiGeorge syndrome causes multiple organ disorders and leads to serious birth defects in children such as:
Heart defects: The syndrome causes congenital heart disease such as tetralogy of Fallot, ventricular septal defect, common artery stem . Thymus gland defects: The syndrome causes impaired immunity, leading to easy infection. Parathyroid gland defects: DiGeorge syndrome reduces the secretion of parathyroid hormone, causing calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood to decrease. Facial deformities: People with the syndrome are characterized by a long face, low and small ears, a long distance between the eyes, drooping eyes, a cleft jaw, a thin upper lip and a cleft lip (also known as a cleft palate). Brain malformations: The syndrome causes behavioral disorders, depression, autism, epilepsy, schizophrenia, attention span, developmental delay, learning inability, language impairment. Other malformations: Poor hearing, vision, underdeveloped body, impaired kidney function. Most cases of DiGeorge Syndrome have no family history. In the fetus, researchers have shown that this syndrome is completely unrelated to the mother's age.
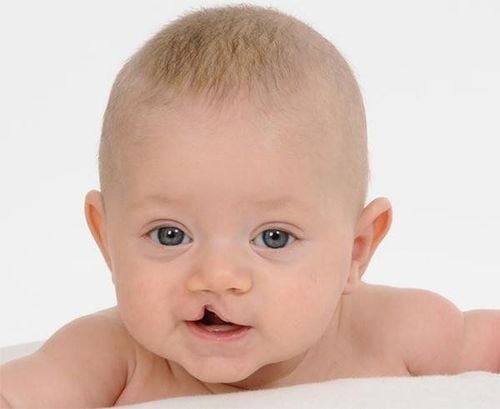
Hội chứng DiGeorge gây hở hàm ếch ở trẻ sơ sinh
2. Genetic Testing for DiGeorge . Syndrome
2.1 Why is genetic testing for DiGeorge Syndrome needed? The symptoms of Digeorge Syndrome are diverse and widely variable, thus greatly influencing the diagnosis and prognosis. However, with early screening and diagnosis, Digeorge syndrome offers the following benefits:
Alleviation of symptoms and reduction in fetal and neonatal mortality with early surgical treatment after birth. Prepare well psychologically and choose a medical facility for delivery, treatment, and good postpartum care. Monitoring and preventing brain damage, causing epilepsy syndrome and behavioral and cognitive disorders. Children diagnosed with Digeorge Syndrome will be advised not to receive any live virus vaccines until their immune systems are fully developed. Children are checked for defects in the mouth, nasopharynx to prevent the effects of the syndrome on eating and language ability.
2.2 Subjects that need to be tested for the gene causing DiGeorge Syndrome The subjects that need to be tested for the gene causing Digeorge syndrome are children, adults, and pregnant women who are suspected of having DiGeorge syndrome when there are manifestations of DiGeorge syndrome. Heart defects, thymus, ... are detected through clinical examination and imaging tests.
2.3 Genetic testing techniques for DiGeorge Syndrome Current genetic testing techniques for DiGeorge Syndrome include:
NIPT (Non invasive prenatal testing): A non-invasive prenatal screening method, performed by taking blood from a pregnant mother. Test results indicate fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) is a genetic testing method that allows the detection of abnormalities in genes in terms of copy number and different sequences in a nucleotide. This method is also done by taking the blood of the pregnant mother for testing. Microarray: A hybrid method that compares the patient's genome with the reference gene to look for differences. Microarray is a molecular cytology technique that allows the detection of chromosomal abnormalities such as deletions or duplications.
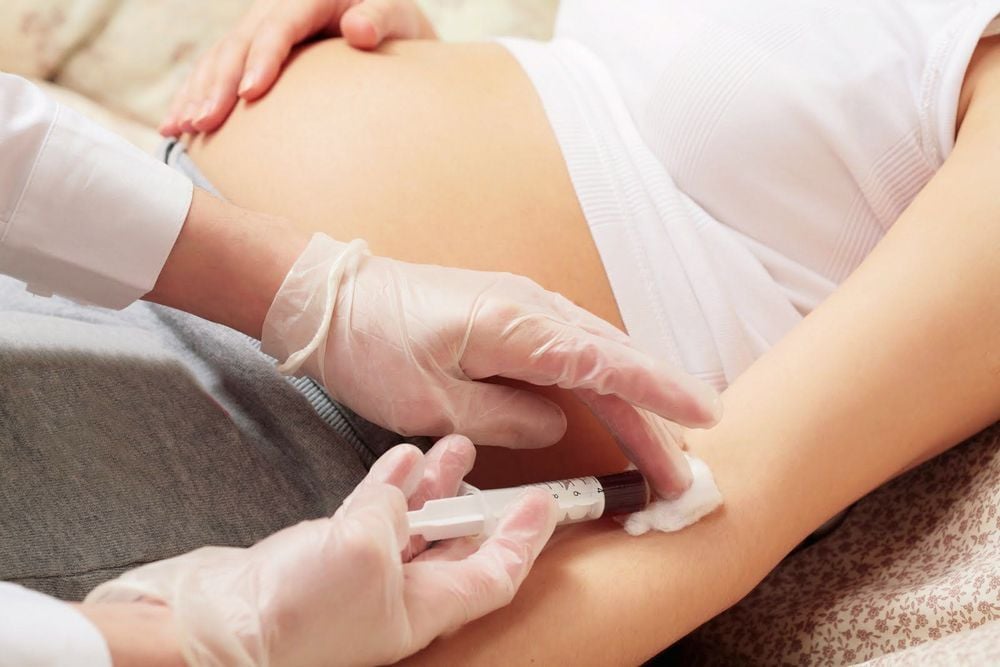
NIPT được thực hiện bằng cách lấy máu của người mẹ mang thai
DiGeorge syndrome gene testing includes techniques such as NIPT, MLPA, Microarray, allowing to detect abnormalities on chromosomes, helping to screen and diagnose the syndrome.
Prenatal and neonatal screening is a simple, inexpensive but very effective method. When detecting fetal abnormalities, doctors will advise the mother that she can choose to terminate the pregnancy in some cases for reasons such as the fetus will die while in the womb and at birth. children do not have much chance of survival or counseling to treat the fetus in the womb. From there, medical experts will advise the family to choose the appropriate treatment, avoiding the situation where they will be born with congenital diseases with a poor prognosis or become a burden to the family and society.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital applies prenatal and newborn screening methods. Among them are advanced prenatal screening methods such as Non-invasive prenatal screening. Compared with traditional methods, non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPT) gives more accurate results (especially for Down syndrome), and reduces the proportion of pregnant women who are indicated for amniocentesis. necessary. The outstanding advantage of this method is that it is non-invasive and can be carried out as early as the 9th week of pregnancy. In addition, 100% of babies born at Vinmec are screened for hearing and other newborn screenings.
To learn about Prenatal and Newborn Screening, as well as the all-inclusive Maternity Care program at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can go directly to Vinmec Health system nationwide or online registration.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.