This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc.BSCK II Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist, Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.In Vietnam, it is estimated that more than 7 million people are suffering from gastroesophageal reflux disease. Choosing the right foods will reduce the unpleasant symptoms caused by this disease in daily life but also help limit the complications of this common disease.
1. What is Gastroesophageal Reflux?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, also known as acid reflux, is the occasional or frequent backflow of gastric juices into the esophagus. Gastroesophageal reflux can be physiological, functional (doesn't affect the body's daily activities and physical development) or pathological can cause malnutrition, esophagitis, and some respiratory complications. other, even death.Trắc nghiệm: Bận rộn có ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe của bạn không?
Cuộc sống hiện đại khiến chúng ta vì quá bận rộn mà quên chăm sóc sức khỏe cho chính mình. Ai cũng biết rằng lịch trình làm việc cả ngày có thể khiến bạn kiệt sức, nhưng cụ thể bận rộn ảnh hưởng thế nào tới sức khỏe? Hãy cùng làm thử bài trắc nghiệm dưới đây.
2. Manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux
gas, heartburn, heartburn Ợ frequent fasting is a symptom to think about gastroesophageal reflux disease . Heartburn is a burning sensation from the stomach or lower chest that radiates up to the neck. Heartburn occurs most in the morning when brushing teeth. Heartburn, heartburn also often go together. The patient has a feeling of belching, accompanied by a sour taste in the mouth. The symptoms of burping mentioned above may increase when you eat full, when you drink water, when you have an upset stomach or when you bend forward, lie down, or sleep at night. Nausea, vomiting This symptom usually appears when eating too much or lying down immediately after eating. Patients are prone to vomiting, nausea or a feeling of choking on food. Patients are also more prone to vomiting when suffering from motion sickness, morning sickness, or taking certain medications...
Pain, tightness in the chest The patient has a feeling of pressure, tightness in the chest, through the back and arms. This symptom is the cause of gastroesophageal reflux disease - easy to be confused with cardiovascular diseases. This pain is pain in the part of the esophagus that runs through the chest. The refluxed acid irritates the nerve endings on the surface of the lining of the esophagus, causing a pain-like sensation in the chest.
Difficulty swallowing Gastroesophageal reflux disease when it becomes severe causes stomach acid to back up with great frequency. This will cause edema, swelling of the lining of the esophagus. Therefore, the patient has a feeling of difficulty swallowing, choking and stuck in the neck.
Hoarseness and cough People with GERD may experience hoarseness and persistent cough. This phenomenon is because the vocal cords when exposed to stomach acid cause swelling. The patient will have hoarseness, difficulty speaking and long-term cough.
Mouth secretes a lot of saliva This is a natural reflex of the mouth to encounter sour acid after heartburn. Saliva will produce more than usual to neutralize the acid.
Bitter mouth When the gastric juice overflows with bile, the patient feels bitter in the mouth. This is a manifestation of gastric nerve disorder, causing the body to open too much of the pyloric valve and bile to leak out.
In addition, the patient may have anorexia, weight loss, anemia, or gastrointestinal bleeding
3. Causes of Gastroesophageal Reflux
There are causes from the esophagus, from the stomach and effects from other organs in the body
Esophageal causes Lower esophageal sphincter failure Lower esophageal sphincter is the lowest muscle of the esophagus that connects to the stomach thick. Normally, the lower esophageal sphincter only relaxes and opens when swallowing, then contracts and closes to prevent gastric juice from backing up into the esophagus. However, there are times when muscle tone is reduced and gastric juices back up into the esophagus. When there is reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus, esophageal mucus with bicarbonate and saliva due to its alkaline nature will neutralize the acid of gastric juice, reducing or losing the stimulation of gastric juice to the esophageal mucosa. Peristalsis of the esophagus will push the reflux back into the stomach. When there is a failure of the lower esophageal sphincter, it will lead to gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Factors causing esophageal sphincter failure: esophageal motility disorders, reduced salivary secretion (smoking, ..), drugs that stimulate β receptors, α inhibitors, anticholinergics, theophylline; caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, chocolate or fatty foods.
Diaphragmatic hernia The diaphragm is a dome-shaped flat muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavity. When the diaphragm contracts, it strengthens the lower esophageal sphincter to prevent gastroesophageal reflux. When there is a diaphragmatic hernia, part of the stomach extends to the diaphragm. At this time, the lower esophageal sphincter is not at the same level as the diaphragm, so reflux is likely to occur.
Causes in the stomach Food stagnation in the stomach: Gastritis, stomach cancer, pyloric stenosis... slows down the contents of the stomach to the intestines, thereby increasing the pressure in the stomach. thick. Sudden increase in intra-abdominal pressure: Coughing, sneezing, or exertion can also cause acid reflux. Some other causes Stress increases cortisol secretion: Cortisol increases acid in the stomach, increases the contraction force of the stomach, pushes gastric juice back up into the esophagus. Stress disrupts esophageal motility, causing the esophageal sphincter to become sensitive, the muscle relaxation occurs frequently and for a long time, causing gastric juice to back up into the esophagus. Unhealthy eating habits: Eating too full, eating at night, eating acidic fruits (oranges, lemons...) when hungry, eating fast food, fried foods... put pressure on muscle tone esophageal stricture, leading to this muscle weakening, opening and closing abnormally, causing reflux. Congenital factors: Weak lower esophageal sphincter, patients with gastric prolapse, or diaphragmatic hernia, accidental trauma... Gastroesophageal reflux in young children is usually considered physiologically normal with Typical symptom is vomiting. This symptom will gradually decrease as the child gets older and will disappear completely in adulthood. Obesity: Weight puts pressure on the stomach and lower esophageal sphincter, weakening the tone, making it easier for stomach acid and substances to back up.
4. Harm of gastroesophageal reflux
Esophageal Inflammation and Ulcers: Stomach juices back up into the esophagus, often damaging the lining of the esophagus, causing inflammation. The patient may experience symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, painful swallowing, chest pain. Especially pain behind the sternum when eating, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite. Esophageal stricture: Inflammatory esophagitis will cause esophageal contraction, Barrett's esophagus (esophageal pre-cancerous): This is a condition in which the cells lining the lower esophagus become discolored. due to repeated exposure to stomach acid. Only a small percentage of people with GERD will develop Barrett's esophagus. Esophageal cancer: Gastroesophageal reflux that leads to Barrett's esophagus and causes esophageal cancer is a rare, serious complication. Accompanied by symptoms such as choking, regurgitation, pain behind the sternum, persistent pain, hoarseness, persistent cough, chest pain, prominent infectious syndrome. Enlarged lymph nodes are sometimes palpable in the left supraclavicular fossa or bilaterally. After a period of illness, the patient's whole body is thin, within 1 month, he can lose > 5kg due to choking, malnutrition. Dull, dry skin with prominent wrinkles. The face and hands have the most prominent and noticeable wrinkles. Even a small amount of acid that reaches the upper respiratory tract can also cause pharyngitis, rhinosinusitis, bronchitis, or pneumonia. The patient has persistent cough and wheezing but does not respond or responds poorly to conventional treatments. Some people develop hoarseness due to thickening of the vocal cords in the throat. In addition, people with reflux disease may have worn teeth, ear infections, thyroiditis...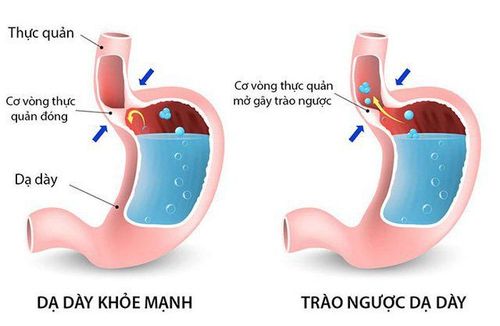
>> See more: Prolonged cough - Beware of causes due to gastroesophageal reflux - Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
5. How to cure gastroesophageal reflux?
The doctor will advise you on measures to treat gastroesophageal reflux including: Lifestyle changes, medical treatment, surgical treatment and other procedures.
Choose alkaline, acid-neutralizing foods: starchy foods such as bread or oatmeal, or easily digestible proteins, ... because these foods help avoid the erosion of the mucus layer in the skin. stomach acid, limiting esophageal sphincter rhythms with acid reflux. Limit foods that stimulate acid secretion or stimulate the lower esophageal sphincter: fruits with high acid content (lemon, orange, pineapple...), carbonated water, spicy, hot foods, chocolate... Necessary abstain from alcohol, coffee, tobacco. Do not wear clothes that are too tight, do not eat too much, do not eat late in the evening, do not bend for too long, do not lie down for 2 hours after eating, do not drink too much water while eating. Sleep with your head 15 cm above your feet. Lose weight if overweight or obese.
6. Choosing foods suitable for people with gastroesophageal reflux disease
Bread, oatmeal This food is very good at reducing excess acid in the stomach, helping to limit the damage to people with gastroesophageal reflux disease.Beans, peas, green beans, red beans, ... contain high levels of fiber and amino acids ... are the best choice for people with gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Easy-to-digest protein Easy-to-digest proteins include: pork loin, goose meat, pork tongue. These proteins help neutralize acid, limiting the symptoms of the disease for people with acid reflux.
Yogurt Yogurt helps digest food faster, not only that, yogurt contains probiotics that improve digestion. People with acid reflux should use yogurt daily, but should not eat on an empty stomach.
Turmeric & honey Turmeric, honey is used as a popular spice in daily meals, but it also supports the treatment of people with gastroesophageal reflux disease very effectively.
When adjusting with lifestyle and nutrition without improving symptoms, you need to treat with internal and external methods, ie using drugs or surgery. Which method to choose, should be based on the cause of gastroesophageal reflux disease and symptoms of the disease, the doctor will conduct step-by-step treatment with the following objectives: Control symptoms, improve quality of life; Heal the scars if any; Control and reduce the risk of complications...
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Hospitals under the national health system, please make an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.