This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by a Doctor of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Gallstones are solid crystals made up of components in bile. Without early treatment, gallstones will continue to grow in size and number. At that time, gallstones will become the source of pathological conditions when they block the cystic duct, obstructing the process of bile secretion, which can backfire and affect liver and pancreatic function. .
1. What are gallstones?
The "starter" of gallstones is bile - a compound produced by the liver that helps the body digest fats and many vitamins. Bile aids digestion by breaking down fats, and also acts as a solvent to dissolve toxic wastes released by the liver.Bile is secreted by the liver and transported to the gallbladder, which performs the role of preserving and condensing bile. When the body recognizes the presence of fat in the food ingredients in the digestive tract, it will initiate a hormone response, commanding the gallbladder to contract to secrete bile into the intestinal lumen (duodenum) to participate in food digestion.
Gallstones are solid crystals made up of components in bile. Without early treatment, gallstones will continue to grow in size and number. At that time, gallstones will become the source of pathological conditions when they block the cystic duct, obstructing the process of bile secretion, which can backfire and affect liver and pancreatic function. . In some cases, gallstones are also the direct cause of other diseases such as cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis ....
Gallstones may initially be as small as a grain of sand but can grow. to the size of a pea, in some cases gallstones the size of a golf ball. A person can have one or more stones at the same time. In the West, most gallstones are of a crystalline nature formed mainly from cholesterol, bile salts and calcium. In Vietnam, most of them are pigment stones, the origin (nucleus of stones) is eggs and/or intestinal parasites. In general, biliary tract worms and infection play an important role in the mechanism of stone formation.
2. Who is prone to gallstones?
Đái tháo đường hoặc những bệnh khác hạn chế chức năng của túi mật làm gia tăng nguy cơ hình thành sỏi túi mật
With increasing age, the amount of female sex hormones also decreases, so the incidence of women decreases with age. Before the age of 40, the rate of gallstones in women is nearly three times higher than in men; In particular, the risk of disease increases markedly during pregnancy. After the age of 60, the incidence of the disease in women does not increase significantly.
Hormone replacement therapy (estrogen) also increases the risk of the disease, especially in cases where the hormone is taken orally rather than indirectly through the skin (via a patch). Birth control pills also increase the risk of gallstones, especially during the first 10 years of use.
Obese people also have a higher risk of gallstones than people of normal weight due to a higher risk of cholesterol crystal deposition, especially in women (tissues in the body that contain more fat also produce more cholesterol). more estrogenic). However, there is a paradox that cases of sudden weight loss due to fat loss or due to the application of a low-calorie diet that inhibits the mechanism of bile production, makes the cholesterol precipitation process take place faster. The occurrence of gallstones after liposuction or gastric bypass surgery to reduce appetite is also common, many patients have to have their gallbladder removed immediately after performing the above techniques.
Diabetes or other conditions that limit gallbladder function or slow bowel movements (eg, spinal cord injury) increase the risk of gallstones.
3. Warning signs of gallstones?
Gallstones may have no signs or symptoms. However, if the stone moves and becomes stuck in the common bile duct, becoming the cause of obstruction, then there will be very aggressive clinical signs and symptoms:Liver colic, also known as pain biliary colic is manifested as severe pain or severe pain in the right epigastrium or lower abdomen with an upward direction between the shoulders or right shoulder, in pain the patient often rolls or leans over the buttocks to find a position to relieve pain. The pain usually starts quite suddenly, lasts from 30 minutes to 5 hours, then subsides or disappears very quickly. Such an episode of biliary colic is often accompanied by a feeling of tenderness and tightness in the lower ribs for a day or more. Nausea and vomiting often occur during the pain. Symptoms of digestive disorders such as fear of greasy foods. In addition to me, the patient may be accompanied by heartburn, belching or bloating. Signs and symptoms when gallstones are complicated. If there is fever or chills in pain, it is necessary to think of complications of gallstones such as cholecystitis, intrahepatic cholangitis, acute pancreatitis... Jaundice: when gallstones cause biliary obstruction. Abdominal distention accompanied by persistent abdominal pain 🡪 thinking a lot about complications of acute pancreatitis.
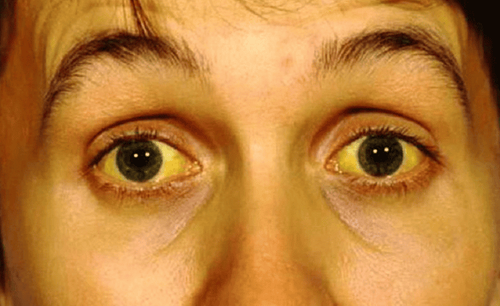
Hiện tượng vàng da có thể gặp khi sỏi gây tắc mật
4. When to treat gallstones?
For cases of gallstones without symptoms, there may be no treatment at all and the patient can live peacefully with the disease. In fact, gallstones of this type are often discovered incidentally and the carrier has lived with the stone for many years without symptoms.However, when gallstones have symptoms, cause frequent pain, recurrent cholecystitis or have complications that threaten the patient's life (eg, acute pancreatitis) Early surgery is warranted, regardless of the size or number of gallstones. In addition, cases of gallstones are asymptomatic but patients have stones larger than 25mm, gallbladder has many stones, gallbladder stones are accompanied by gallbladder polyps larger than 10mm or are at risk of gallbladder cancer. also require early surgery (cholecystectomy).
Women of childbearing age with gallstones are advised to proactively have gallstone surgery before pregnancy because if there is a complication of gallstone cholecystitis during pregnancy, the treatment will become difficult. very complicated, especially if cholecystectomy is required at this stage, there will be many risks to the fetus at any stage of pregnancy.
5. What are the treatments for gallstones?
Patients can choose to treat gallstones such as: Surgery (open or laparoscopic surgery); the use of stone-dissolving drugs; extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy; dissolve stones and remove stones through the skin; Endoscopic removal of gallstones.Method of using drugs to dissolve stones:
Oral medicine is the main method of medical treatment in Vietnam. However, this method has the disadvantage that the treatment time is long, up to 12 months. Prolonged treatment time reduces the patient's ability to adhere to treatment. Moreover, the drug is only effective for people with cholesterol stones while patients with gallstones in our country are mainly bile pigment stones, so the effectiveness of drug treatment is often not high. Mainly used to prevent stone formation in high-risk subjects (For example, gastrectomy for fat loss) Methods of cholecystectomy or endoscopic endoscopic removal of gallstones have not been applied. Widely used because of difficult patient selection, long course and complicated technique.
The above treatment methods have a common feature of leaving the gallbladder, creating favorable conditions for the recurrence of gallstones in the future, which is time-consuming and expensive for treatment, but the effectiveness is not high.
Surgery is the most used treatment for people with gallstones, especially when there are complications. Currently, in the world, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is considered as the only method of choice in surgical treatment of gallstones. Cholecystectomy by laparoscopic surgery to completely remove the cause of the disease. Only a very few cases of force majeure have open surgery or just remove the stone and leave the gallbladder.

Dùng thuốc uống là phương pháp điều trị nội khoa chủ yếu ở Việt Nam
6. When to operate gallstones?
This treatment is indicated for symptomatic or complicated gallbladder stones. It is still controversial about indications for surgery for gallbladder stones that have not caused symptoms and have not caused damage to the gallbladder. If surgery is indicated, the method of choice in most doctors is still cholecystectomy.After surgery, the patient still eats normally because there is still enough bile from the liver through the bile duct to go to the intestines to help digestion, normal activities and work, the "marital relationship" is not affected, does not reduce life expectancy. , no need to take other digestive aids.
7. Prevention of gallstones?
Follow a low-fat diet. Eat a diet rich in fiber which includes healthy fats. Choose a diet that's full of a variety of fruits and vegetables. High-fiber foods help block the reabsorption of cholesterol by the “liver-intestinal cycle” in the small intestine, which can help prevent additional gallstones from forming. Healthy fats include unsaturated fats in the diet. Foods that contain unsaturated fats include fish and nuts. Eat three balanced meals a day, do not skip meals. Skipping or fasting can increase the risk of gallstones. Maintain a weight that does not exceed the age norm. If you are overweight or obese, you should take measures to lose weight. If you need to lose weight, do it slowly. Rapid weight loss can increase the risk of gallstones. The goal is to lose 0.5 to about 1 kg a week. Regular exercise (eg walking, cycling...) for at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Patients with blood diseases should be monitored for gallstones by ultrasound (due to the risk of bile pigment deposition). When you have gallstones, you should eat less fat to reduce gallbladder spasms and slow the development of gallstones. To help protect customers' health in a comprehensive way, Vinmec International General Hospital has launched Hepatobiliary Screening Packages with different levels of intensive screening, depending on the specific needs of the patient. diseases, help customers assess liver function, comprehensive bile, perform tests to help detect liver and bile problems at the earliest, from which the doctor will give appropriate treatment advice.Screening results are guaranteed to have the highest accuracy when performed by a team of highly qualified and experienced medical doctors; modern and advanced technological equipment; Professional quality service, methodical.
Doctor Nguyen Quoc Lan has experience and strengths in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy, worked at the Department of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy at Family General Hospital until 2016. Currently, he is a Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Doctor of the Department of Medical Examination. and Internal Medicine, Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.