This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Thu Hang - Dermatologist, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Hair fungus is an inflammatory condition, causing damage to the hair, scalp hair follicles and surrounding skin due to fungus. The disease occurs mainly in children but is rarer in adults. The disease is more common in rural areas than in urban areas. The disease is contagious.
1. Causes of hair fungus
Dermatophyte fungus is the main cause of hair fungus. Among them, the most common fungi are Microsporum and Trichophyton. In the UK and North America, the most common cause is Trichophyton tonsurans (90%). However, research in Vietnam shows that M. canis is more common. White Piedra is caused by the fungus Trichophyton beigelii. Black Piedra is caused by the fungus Piedraia hortae. Along with the HIV pandemic, Piedra fungal infections are also on the rise. In addition to manifesting in the hair, Piedra's hair fungus can also cause fungal infections of the blood and internal organs. Classification of dermatophyte fungi based on mode of transmission:
2. Symptoms of hair fungus
2.1.Clinical Manifestations
Piedra hair fungus: there are two main forms: Black Piedra and White Piedra:
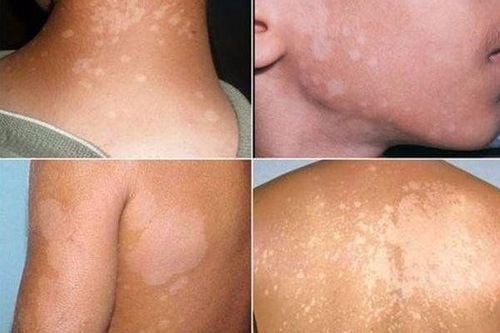
Black Piedra patients often present symptoms of brown or black nodules along the hair shaft. Fungal infections usually start under the cuticle of the hair shaft and spread outward. Hair breakage can occur due to broken nodules at the hair shaft. When the nodules are large, they can cover the hair shaft. In white piedra, the fungal infection also begins below the cuticle and grows through the hair shaft causing hair loss and breakage. The nodules are soft, less sticky, white but can also be red, green, or light brown. The incidence of white Piedra has increased since the beginning of the HIV pandemic. In immunocompromised patients, T. beigelii can cause severe systemic fungal infections with fever, bacteremia, pulmonary infiltrates, skin lesions (vesicular and hemorrhagic papules, central necrosis) and disease kidney.
Tinea capitis:
Manifestations can be mild, non-inflammatory similar to seborrheic dermatitis (common cause is T. tonsurans) to severe pustular reaction with hair loss, known as kerion ( honeycomb). Hair loss with or without scabs. As a result of the body's overreaction, it manifests as wet, pus-filled patches, with the formation of small abscesses and hair loss. Some patients have symptoms of the whole body, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes. Hair in the damaged area can regrow, but when damaged for a long time, it can leave scars and cause permanent hair loss. T. Tonsurans carrier status is a condition that is not clinically apparent but when culture is positive. This condition is common in adults, people who have contact with sick children. Fungal carriers can also be considered infectious and should be treated to limit recurrence in young children.

Dermatophytes enter and exist in the hair in three ways: endofilaments, extrins and favus.
Extrafibrous form: the outer cuticle of the hair is destroyed. Ectopic fungal infections may appear fluorescent (Microsporum) or not (Microsporum and Trichophyton) under Wood's light. Clinical manifestations vary from scaly patches of skin or alopecia areata with mild to severe inflammation, to kerion formation. The Favus form is the most severe form of hair dermatophyte infection. The main cause is T. Schoenleinii. Under Wood's lamp a bluish white fluorescent light can be seen. Favus presents as thick, yellow scaly patches containing fibers and patches of dead skin. Chronic fungal infections can cause hair loss and scarring.
2.2 Subclinical
Fresh examination: specimens and scales of skin and hair. Scan directly in 10-20% KOH, can be used with blue ink. Combine staining with acridin orange, calcofluor white and blankophor and using fluorescence microscopy detect polysaccharides of fungal cell walls. On the direct microscope, the mycelium is divided and branched. Culture: Sabouraud's basal medium. Culture time for positive conclusion is 7-14 days and for negative conclusion is 21 days.

2.3 Treatment
a, Principle of treatmentShort haircut. Wash your hair with antiseptic and antifungal solutions. Use antifungal agents with caution and with close monitoring. Treatment of associated infections. b, Specific treatment
Piedra hair fungus: pull out hair with nodular lesions along with shampooing with sulfur, Ketoconazole 2%. Oral terbinafine is effective. Scalp fungus: Adults take one of the following drugs:
Fluconazole 6mg/kg/day x 3-6 weeks Griseofulvin 20mg/kg/day x 6-8 weeks Itraconazole 5mg/kg/day x 4-8 weeks Terbinafin 250mg/ days x 2-4 weeks

Children: use one of the following drugs:
Fluconazole 6mg/kg/day x 6 weeks Griseofulvin 20-25 mg/kg/day x 6-8 weeks Itraconazole 3-5 mg/kg/day x 6 weeks Terbinafin 62.5 mg /bgatf (<20kg), 125 mg/day (20-40 kg) or 250 mg/day (>40 kg) x 2-6 weeks.
3. Prevention of hair fungus
Wash your hair regularly. Limit washing your hair at night. Keep hair dry. Limit children's play with animals.

Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
If you notice any unusual health problems, you should visit and consult with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.