This is an automatically translated article.
Drumstick finger, also known as Hippocratic finger or watch glass nail, is an abnormal condition that occurs in a number of diseases, especially lung and cardiovascular diseases.The clubbing finger (foot) sign is a warning sign of an underlying medical condition that should be quickly seen by a doctor for timely diagnosis and treatment.
1. What is a drumstick finger?
Clubbing fingers are physical changes in the fingernails (sometimes in the toenails) caused by one or more underlying health problems. Depending on the cause, finger and nail changes can develop over weeks or years.Clubbing fingers are fingernails or toenails that grow larger than normal and look like an upside down spoon, the tips of the fingers tend to swell and turn red. This is an abnormal condition of the fingers and nails.
The signs of clubbing are identified as follows:
Fingernails or toenails grow abnormally large and round; Drumstick-shaped nails often tend to curve significantly downwards, and fingernails grow convex The nail bed becomes soft, creating a spongy feeling when pressed against the nail. Fingertips are swollen, often red and may be hot at this site Wrinkles of the nails and skin appear.
2. Drumstick Diagnosis
The angle between the nail bed and the nail is usually 160 degrees, but when it is greater than 180 degrees, it is a sign of clubbing. In healthy nails, the ratio between distal phalangeal height (DPD) and distal interphalangeal space. (IPD) usually has a result less than 1. But when the DPD/IPD ratio > 1, the finger is clubbing Schamroth's sign: when the two nails of the two index fingers are pressed together, the space between the two nails is very large. Small or absent is a normal finger. Appears a large gap is the finger drumstick or the angle formed by the two faces is greater than 30 degrees.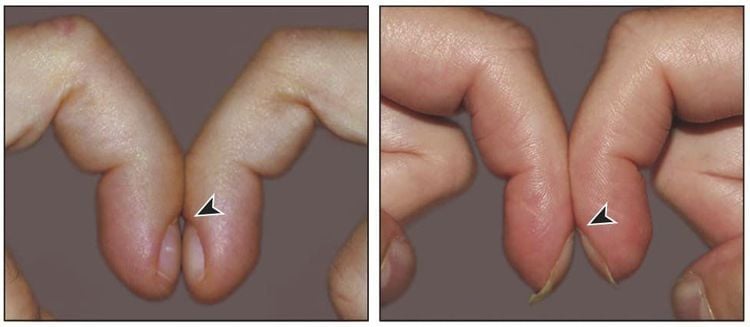
Sự khác biệt giữa ngón tay bình thường và ngón tay dùi trống
3. Drumstick finger formation mechanism
There are many theories to explain the mechanism that produces clubbing fingers, however, it is still unclear. The currently most accepted hypothesis is the one related to platelets and platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF for short). However, it does not explain unilateral clubbing and does not apply to all cases of clubbing.In healthy people, some macrophages escape from the bone marrow but are blocked in front of the pulmonary capillaries because of their large size, then it breaks into many pieces of platelets in the lungs and becomes platelets. However, when a shunt does not pass through the pulmonary capillary, the macrophage can enter the systemic circulation and become trapped in the small capillary of the fingertip.
They then release PDGFs - platelet-derived growth factor, which aggregates many cells and promotes the proliferation of muscle cells and fibroblasts, causing the characteristic expression of club fingers .
Another theory is that clubbing is caused by vasodilation. In congenital heart diseases, tissues that are far from the center, such as those in the extremities, are often not supplied with enough oxygen, causing blood vessels to dilate to increase blood flow and increase oxygen supply to tissues. will form a drumstick phenomenon.
Similar to the above, in lung cancer or other cancers, in addition to the mechanism of vasodilation due to lack of oxygen in the tissue, clubbing is also affected by the cancer, but the mechanism of action is still not very clear. In fact, the mechanism of vasodilation cannot be explained in cirrhosis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis...
Some causes of club-shaped fingers Cancer: lung cancer (29) % of people with lung cancer have signs of clubbing ), bronchial carcinoma, lymphoma, tumor of the pleura

Một khảo sát cho thấy 29% người bị ung thư phổi có dấu hiệu ngón tay dùi trống
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.