This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Hong Phuc - Emergency Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the treatment of respiratory medicine.Pleurisy is an overflow of pus in the pleural space. When the patient is not treated adequately and promptly, dangerous complications will occur. One of the treatments for pleurisy is thoracotomy - drainage and decapitation of the lung.
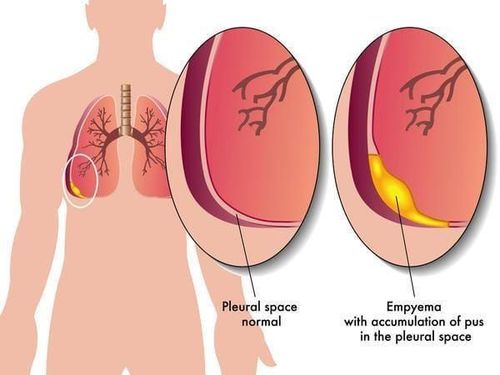
1. What is empyema?
Empyema is the presence of true pus in the pleural space and the presence of pus in the pleural space. When pleural puncture sucks out real purulent fluid, it can be cloudy, or clear fluid. However, there is a neutrophil (N) count of 60% or more in the pleural fluid. Purulent pleurisy is often associated with infection of the lung parenchyma, but may also be associated with bacteremia, thoracic surgery, trauma, intra-abdominal infection, or neoplasm.As mentioned above, if the patient is not treated adequately and promptly, it will lead to dangerous complications such as:
Local complications: Pus will break into the chest wall or leak in the posterior axillary line. low in the lying position, here the soft part is thinner. Bronchopleural fistula: The patient suddenly has chest pain, shortness of breath, and then vomits pus, which can be a lot or a little, lasting. Very rarely, pleural effusion ruptures through the diaphragm into the abdomen. Systemic complications: Possible heart failure, first of all right heart failure, exhaustion due to prolonged severe toxic infection, sepsis, abscesses of other organs (brain abscess, kidney abscess).. .
2. Causes of empyema
Common bacteria causing empyema are: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichiacoli, Aerobacteraerogenes, Proteus, Bacteroides, Salmonella... In addition, had empyema caused by tuberculosis bacteria. Disseminated infection from the bloodstream or to any site of the thorax or abdomen (mediastinitis, esophagitis, spinal epidural abscess, osteomyelitis, lymphadenitis, pericarditis, tracheitis biliary tract, diverticulitis...).Letting the body catch pleurisy depends on the number of bacteria, the toxicity of the bacteria, the general health of the body, the body's resistance and immunity... Because of the fact The human pleura has very good resistance, so normally bacteria can't cause pleurisy.
In addition, pleurisy can occur due to the following reasons:
Often accompanied by pneumonia, especially aspiration pneumonia. Bronchopleural fistula. Abscesses around the amygdala, around the jaw, or around the pharynx. Infection of the anterior cervical spine. Thoracic surgery, trauma, hemothorax. Fistula due to bronchial snout after pneumonectomy. Non-sterile technical pleural puncture. Esophageal rupture.
3. Diagnosis of empyema
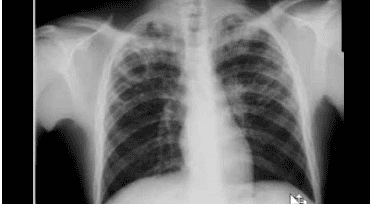
Diagnosis of empyema is based solely on pleural fluid analysis. Diagnosis is urgent because of the risk of pleural fibrosis and localized pus formation that cannot be drained. If the pleural fluid is diagnosed as reactive fluid adjacent to the pneumonia, there is still the possibility of subsequent empyema.Empyema due to treatment of pneumothorax secondary to cavernous TB.
Left film: Large right pleural mass with sharp edges and obtuse angle adjacent to chest wall. Pulmonary calcification. The right flank angle is blurred. Right film: CT scan shows large fluid accumulation in right lung, with clear calcification of parietal pleura and visceral visceral. Courtesy of Paul Stark, MD. Straight film: uniformly blurred right lung, pulmonary blood vessels can also be seen, this is called filter effect, characteristic of pleural disease. Tilt film: characteristic of pleural mass: mass has only one border (one-edged), sharp border, created with obtuse angle of chest wall. Courtesy of Paul Stark, MD.
4. Principles of treatment
4.1. Antibiotics Choosing antibiotics to treat diseases requires research on the causative agents and causes of pneumonia. At the same time, the antibiotics selected should be based on the Gram stain to predict the bacteria according to the clinical situation, and then adjust the antibiotic according to the results of the bacterial culture. Antibiotics enter the patient's body, mostly enter the pleural cavity, some are inactivated at low pH of pleural fluid such as aminoglycosides.
Those antibiotics include: penicillin, clindamycin, broad-spectrum PNCs (ticarcillin, piperacillin, ampicillin-sulbactam, or piperacillin-tazobactam), or imipenem
The use of topical antibiotics (eg, inhalation) is not required necessary and may cause irritation. Inject antibiotics into the pleural space only when pleural adhesions are needed, erythromycin can be used.
4.2. Pleural drainage When pleural drainage needs to be conducted promptly, if it is too late, it will cause thickening of the pleura. 10-20% of pleural effusions require drainage or surgical intervention. If drainage is too late, it will cause thickening of the pleura. Cases in which the doctor prescribes pleural drainage: Purulent effusion, infected pleural fluid, pleural fluid pH < 7.0. In the remaining cases, another closed pleural drainage will be indicated. It is necessary to aspirate negative pressure to remove gel-like substances, pus... so that the lung expands quickly and clears the pleural empyema. The thoracoscopic drainage technique also gives good results, especially in children, this technique is considered a delayed procedure (eg, after rupture of a lung abscess into the pleural space). In the treatment when the patient is stable and the condition is open to drainage, or the situation shows that the pleural effusion requires prolonged drainage, surgical intervention is required. 4.3 Occupational therapy Needs to be implemented early and in the long term, with the aim to avoid serious sequelae such as severe restrictive ventilation, chronic respiratory failure, bronchiectasis and bronchial consequences such as bronchiectasis. esophagus, atelectasis. But exercise therapy needs to be combined with good bronchial circulation for good lung expansion.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.