This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Hong Phuc - Emergency Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the treatment of respiratory medicine.A lung abscess is a lung infection caused by bacteria that enter through the bronchi, through the bloodstream. When signs of lung abscess appear, the patient should immediately go to the hospital for timely diagnosis and treatment.
1. What is a lung abscess?
A lung abscess is an infection of the lungs. Acute necrotizing inflammatory disease causes purulent foci, purulent swelling, widespread tissue necrosis in the lung parenchyma and the formation of compartments and foci containing necrotic debris. Lung abscess can create one or more pus-filled pus-filled cavities over 2cm in size. When medical treatment fails for more than 6 weeks, it is called a chronic lung abscess. The formation of multiple abscesses can lead to pneumonia or lung necrosis.There are 2 types of abscess: Primary lung abscess and secondary lung abscess.
Primary lung abscess : occurs in healthy children - previously normal lungs. The cause of lung abscess is pneumococcal bacteria, staphylococcus aureus, and streptococcus. Bacteria enter through the bronchi, by the blood, by pneumonia or through the diaphragm. Children are susceptible to lung abscess in cases of congenital or acquired immunodeficiency (HIV/AIDS), which may also be due to immunosuppressive drugs, cancer treatment; thoracic malformations, congenital lung defects, children are easily aspirated into the lungs, especially when there is poor oral hygiene: cerebral palsy, neuro-muscular diseases; after anesthesia, intubation, mechanical ventilation; swallowing disorder; abnormal functioning of the esophagus; Thoracic trauma, forgotten airway foreign body. Secondary lung abscess: occurs in children with congenital or acquired lung abnormalities (such as after pneumonia, aspiration pneumonia, complications after surgery...). If lung abscess is not treated in time, dangerous complications will appear. Many patients become exhausted and can be fatal. Complications may occur such as: empyema , empyema due to ruptured abscess spread; brain abscess, meningitis; bronchiectasis around the abscess; severe hemoptysis (called lightning hemoptysis); universal fungus.
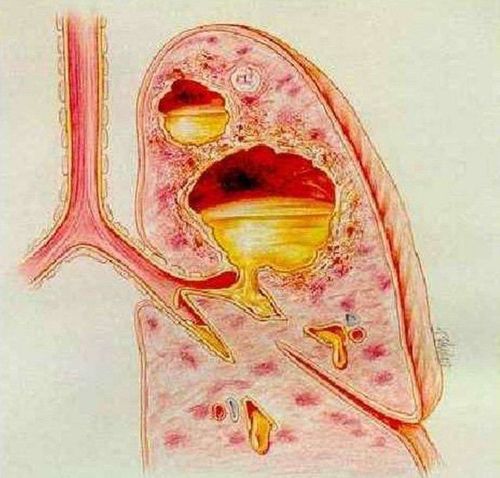
2. Causes of lung abscess
Inhalation of foreign bodies, bacteria, pulmonary infarction, superinfected primary cancer are the causes of lung abscess formation.
Inhalation of foreign bodies: Commonly inhaled foreign bodies are food, drink, vomit or oral secretions that are inhaled into the lungs. When inhaled foreign bodies lead to swelling, pneumonia, after only 7-14 days an abscess can form. Stroke, epilepsy, drug abuse, alcoholism, dental diseases, emphysema, lung cancer, and esophageal disorders can all lead to aspiration of foreign bodies. Bacteria: Bacteria, fungi, and parasites are the main causes of lung abscesses. These bacteria are usually anaerobic (do not require oxygen to grow) and originate in the mouth. Other microorganisms such as parasites and fungi can also infect the lungs and cause an abscess. Bacteria that cause pus in the lungs such as: Staphylococcus aureus, klebsiella, group A streptococcus, Bacteroides sp, Actinomyces, blue pus bacillus, E. Coli, Proteus, Fusobacterium and other anaerobic cocci.
Fungi such as: Aspergilus, Candida Abicans, Mucor. Parasites: amoeba, lung fluke.
Patients with vascular diseases, vasculitis (periarterial noditis, granulomatous disease) leading to pulmonary infarction also form pulmonary infarction.
In addition, lung abscess will increase the risk of being formed due to:
Superinfected air cocoon Necrosis in pneumonitis nasopharyngeal, maxillofacial, central venous access for a long time Having other medical diseases: diabetes, chronic lung diseases, bronchiectasis Alcoholism, injecting drug use, smoking.

3. Methods of diagnosing lung abscess
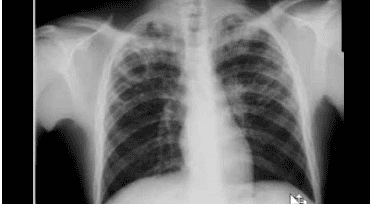
3.1 Definitive diagnosis The stage of closed pustulosis is often difficult because of poor, atypical symptoms. Therefore, before starting treatment, the doctor will use a definitive diagnosis method such as:Some patients have a fever from 38 degrees C - 39 degrees C or higher, maybe with chills or not. The body is tired, the mood changes a lot. In patients with lower lobe lung abscess, there is chest pain on the side of the lesion. The patient coughs up pus-filled sputum (purulent), foul-smelling or rotten sputum, sometimes coughing up blood mixed with pus, sometimes dry cough; Shortness of breath, rapid breathing, respiratory failure such as tachypnea, cyanosis of the lips, extremities, decreased PaO2; Pulmonary examination: Can see snoring, moist rales, sometimes cavernous syndrome, coagulation syndrome; Complete blood count: If due to bacteria, there may be an increase in white blood cells, the white blood cell count will turn left. Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate; Chest X-ray: Cavity usually has a relatively regular wall, water-vapor level. There may be only one abscess, or many. It is necessary to take a lateral film (sometimes with a computerized tomography) to accurately determine the location of the abscess to help choose an appropriate method of pus drainage. Need to take blood, sputum or aspirate from the bronchi for staining, bacterial culture. Based on the results of the antibiogram to use antibiotics accordingly. 3.2 Differential diagnosis In this case, the patient showed symptoms of choking, hoarseness, cupped fingernails, clubbing fingers, coat edema... It could be a sign of lung abscess. The doctor will order a chest X-ray to show that the cave wall is thick, often eccentric, surrounded by thorny tentacles, and the inside is convex and bumpy, rarely with horizontal water levels. Subjects with abscessed lung cancer are usually > 45 years old, have a history of smoking, pipe tobacco.
Superinfected pneumococcal cyst: Clinical manifestations are similar to lung abscess, chest X-ray shows thin-walled caverns < 1mm, air-fluid levels and after treatment, air cysts still exist.
When the patient has signs of cough, sputum or sometimes hemoptysis lasting for many years, the lungs have moist rales, crackles that persist for a long time and X-ray is indicated.
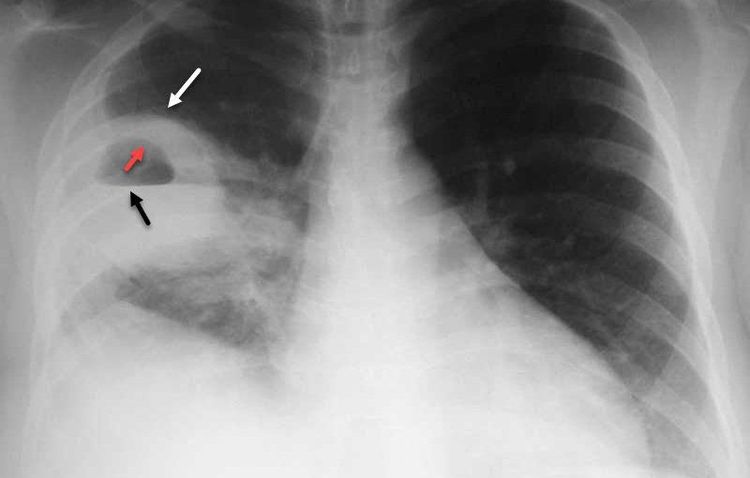
Some patients are in general condition, emaciation, collapse, fever in the afternoon, cough with sputum, or blood are clinical signs of cavernous tuberculosis. When chest x-ray shows a background of infiltrative or fibrotic lesions with one or more caverns, the localization is usually at the apex of the lung. The tuberculin reaction in many cases is strongly positive, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.