This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General HospitalFatty liver disease is a common problem caused by the accumulation of certain fats in the liver. In most cases, fatty liver does not cause serious symptoms, but it can lead to liver damage.
1. What is fatty liver?
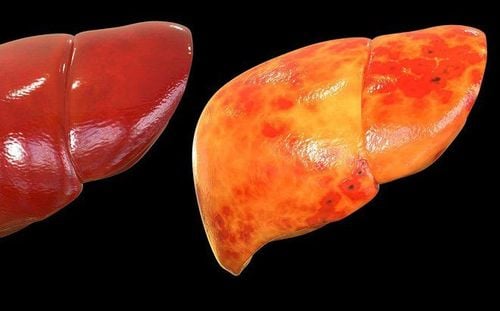
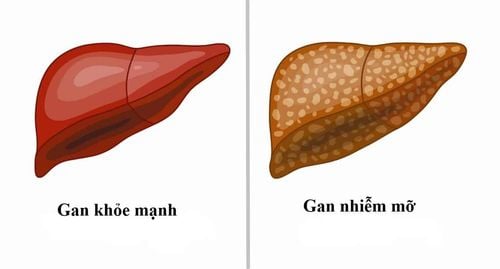
Fatty liver disease (steatosis) is a common problem caused by the accumulation of certain fats in the liver. The liver usually contains a small amount of fat. However, if fat makes up more than 5 to 15% of the liver's weight, you have fatty liver disease.
There are two main forms of fatty liver disease:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver : Fat accumulation in the liver that is not related to alcohol consumption. Alcoholic fatty liver: Fat builds up in the liver from drinking large amounts of alcohol. In most cases, fatty liver disease does not cause any serious problems or prevent the liver from working properly. However, it can lead to liver damage in some cases.
2. Symptoms of fatty liver
People with fatty liver disease often do not have any symptoms. If symptoms appear, they may include:
A feeling of fullness in the middle or upper right side of the abdomen Abdominal pain
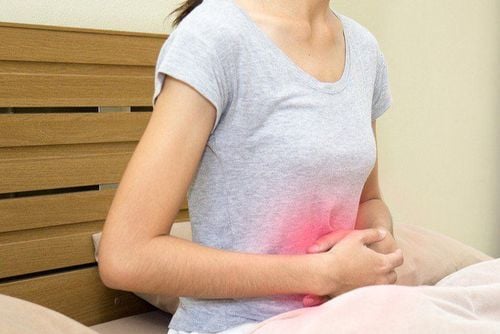
Đau bụng là một trong các triệu chứng của gan nhiễm mỡ
Loss of appetite or weight loss Nausea Fatigue Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes) Edema (abdomen, legs) Discomfort
3. Who is prone to fatty liver disease?
People at high risk of fatty liver, such as:
Alcoholics. Alcohol undergoes metabolic breakdown in the liver, which can lead to problems with fatty acid breakdown and metabolism. People who are obese or overweight People with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance People with metabolic syndrome (excess body weight, insulin resistance, high blood pressure and high triglyceride levels) People with certain diseases or Taking medications such as amiodarone, diltiazem, steroids, and tamoxifen can also increase your risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. If you are taking one of these medicines and are diagnosed with fatty liver disease, your doctor may substitute another medicine. Older adults: The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and severity of liver disease increases with age. Gender: The rate of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in men is twice as high as in women.

Những người thừa cân thuộc nhóm đội tượng dễ mắc bệnh gan nhiễm mỡ
4. How to prevent fatty liver disease?
Maintain a healthy weight. If you are overweight or obese, lose weight gradually. Eat a balanced diet: lots of vegetables, fruits and good fats, which can help lower bad cholesterol and triglyceride levels Exercise regularly Limit alcohol, or don't drink at all. Take medication as prescribed by your doctor.

KIểm tra sức khỏe gan mật giúp người bệnh phát hiện sớm bệnh lý và kịp thời điều trị
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.