This is an automatically translated article.
Although colon polyps are inherited, they are quite rare, usually only in subjects who inherit the genetic mutation that causes colon polyps. Among colon polyps is a type known as familial adenomatous polyposis, abbreviated as FAP.
1. What is familial adenomatous polyposis?
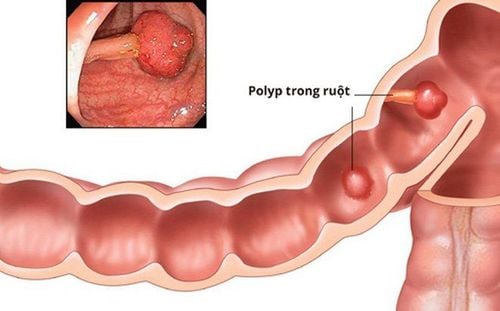
Familial adenomatous polyposis is a rare form of colon polyposis, which is an inherited condition, known as classic FAP or FAP. When suffering from this disease, the patient has more than 100 colon polyps in the form of adenomatous polyps. Each adenomatous polyp is a mass in the colon made of normal cells of the colon. People with FAP often develop colon polyps in middle age. If the disease is not detected and treated, the patient has a very high risk of developing colorectal cancer.People with FAP also have an increased risk of developing cancer in other organs such as the stomach, small intestine, pancreas, and gallbladder. They also have an increased risk of hepatoblastoma, a type of liver cancer. Desmoid tumor/fibromatosis - a locally invasive tumor that has not metastasized and a brain tumor called medulloblastoma may also be present in some of these patients. They also have a higher risk of thyroid cancer than other people.
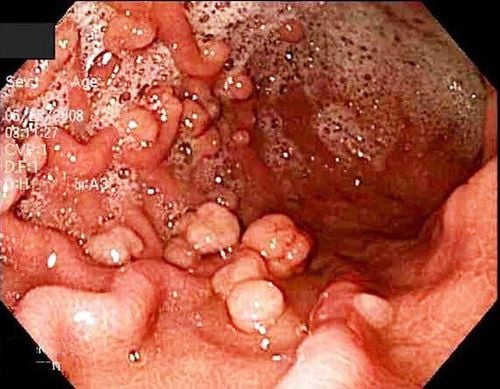
Hình ảnh đa polyp tuyến gia đình
Not all symptoms of FAP are related to cancer and colon, but they can also have other symptoms such as:
Bone dysplasia, which is a noncancerous bone growth, is often found found in the jawbone. Missing or excess teeth or not yet erupting. Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE): this is a condition that occurs in the eye at birth, does not affect vision, but can be seen by a doctor when examining the eyes with an ophthalmoscope. Benign skin changes such as epidermal cysts, fibroids,... Adrenal mass. Thus, familial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited form of colon polyps. The disease is characterized by hundreds of adenomatous polyps co-occurring in the colon. The disease usually begins in middle age. The disease increases the risk of cancer in the colon and many other organs, but it also has noncancerous manifestations in some organs.
2. What types of familial adenomatous polyposis are there?
Familial adenomatous polyposis can be divided into the following types:
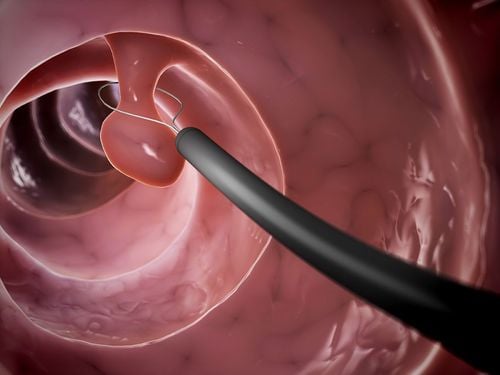
2.1. Classical FAP Classical FAP is typically characterized by more than 100 colonic polyps. Treatment for this form is usually a colectomy, which is the most effective for reducing the risk of colorectal cancer.
Tình trạng bệnh polyp đại tràng
2.2. Impaired FAP (AFAP) Impaired FAP usually has between 20 and 100 colorectal polyps. In people with this form, colon polyps often continue to grow throughout their lives and increase the risk of colorectal cancer if the polyps are not removed. People with attenuated FAP tend to develop the disease later than those with classic FAP. The risk of other cancers with impaired FAP is currently unknown.
2.3. Gardner syndrome Gardner syndrome is a variant of FAP, people with this syndrome also develop many colon polyps, in addition, they also develop other tumors outside the digestive organs such as:
Epidermoid cyst: is a tumor in or under the skin. Fibroids. Scleroderma: A fibroid tumor that can develop anywhere in the body. Bone tumors. 2.4. Turcot syndrome Turcot syndrome is also a variant of FAP or Lynch syndrome, rather than a separate genetic condition. People with this syndrome tend to have more colon polyps, an increased risk of colorectal cancer, and an increased risk of brain tumors. The two most common brain tumors in Turcot syndrome are: Glioblastoma: a type of astrocytoma, often found in families with features of Lynch syndrome. Mediastinal tumor: This type of tumor begins in the cerebellum, the back of the brain. This type usually occurs in children and is often found in families with the condition of FAP.

U nguyên bào thần kinh đệm (Glioblastoma)
3. What causes classical familial adenomatous polyposis?
Classical familial adenomatous polyposis is a form of colon polyp that is passed down from generation to generation in a family. Mutations in the APC (Adenomatous polyposis coli) gene are associated with FAP, AFAP, Gardner syndrome, and Turcot syndrome. Mutations in the APC gene increase the risk of colorectal or other gastrointestinal cancers.
Some patients with colon polyps have been found to have 2 mutations in the MUTYH gene, also known as the MYH gene, which is associated with MUTYH-associated polycystic disease (MAP).
People with FAP or AFAP can have blood tests to look for mutations in the APC gene or the MUTYH gene. If they have a gene mutation, other family members need to be tested to see if they have FAP or AFAP.
4. How is familial adenomatous polyposis inherited?
Normally, each cell has 2 copies of each gene: one inherited from the mother and one inherited from the father. FAP with mutations in the APC gene follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Therefore, a child whose mother has a mutation in the APC gene has a 50% chance of inheriting that mutation. Siblings or parents of someone with an APC gene mutation also have a 50% chance of having it. However, if the patient's parents do not have the gene mutation, the risk of the patient's brothers and sisters is also significantly reduced, but their risk is still higher than the general population. .
Bệnh polyp đại tràng dạng đa polyp tuyến gia đình mang yếu tố di truyền
Today, preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is a medical procedure performed in conjunction with in vitro fertilization (IVF). This helps children reduce the risk of inheriting mutated genes from their parents. The mother's egg is removed and fertilized in vitro, when the embryo reaches a certain size, a cell will be removed to check the genetic status, then the parents can choose to transfer the embryo without mutation.
5. How is familial adenomatous polyposis diagnosed?
Classical familial adenomatous polyposis is a clinical diagnosis. Usually diagnosed when a doctor finds more than 100 colon polyps.
A person is suspected to have AFAP when there are more than 20 colon polyps but less than 100. A person is suspected to have Gardner syndrome when there are multiple colon polyps and/or colorectal cancer along with some benign tumors mentioned above. A person is suspected of having Turcot syndrome when there are multiple colonic polyps and/or colorectal cancer, along with a glioblastoma or medulloblastoma. Blood tests may be done to look for a mutation in the APC gene and/or the MUTYH gene if these conditions are suspected.

Một số xét nghiệm có thể phát hiện bệnh polyp đại tràng loại đa polyp tuyến gia đình
The risks associated with hereditary colon polyps that need to be checked are:
Colorectal cancer up to 100% if the polyps are not removed. Fibroid tumor (desmoid) 10 - 20% Small intestine: 4 - 12%. Pancreatic cancer: 2%. Papillary thyroid cancer: 2 - 25%. Hepatoblastoma: 1.5% Brain or central nervous system tumor: < 1%. Stomach cancer : 0.5% Bile duct cancer . Adrenal cancer. Hereditary colon polyps is a complex disease that can turn into many other cancers. Therefore, when a person is diagnosed with familial adenomatous polyposis, family members should be tested for the disease. If so, it should be treated early to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.