This is an automatically translated article.
Epidural abscess is still a rare condition, however, if not detected early and treated aggressively, the patient is completely at risk of disability. So what is an epidural abscess and how should it be overcome?
1. Learn about epidural abscess
Epidural abscess is a serious infection that occurs in the epidural space, which can lead to major neurological damage and death. Until now, epidural abscesses were considered rare, but over the past two decades, the incidence of this type of disease has doubled.
Experts say that the problem of epidural abscess does not lie in treatment, but in early diagnosis and therefore appropriate intervention solutions, limiting the risk of developing neurological symptoms. big.
2. Risk factors for extramembranous abscess
Most of these abscesses are idiopathic. Some of the following risk factors and sources of infection can increase the likelihood of infection:
2.1 Local or systemic infections (44%)
Skin and soft tissue abscesses; Osteomyelitis / discitis; Intestinal, lung, urinary tract infections; Sepsis ; Pharyngitis, endocarditis.
Nhiễm trùng huyết gây áp xe ngoài màn tủy
2.2 Immunodeficiency (29%)
The immune system can be weakened due to many causes and diseases such as:
Diabetes; Social disease; Abuse of intravenous drugs; Alcohol and drug abuse.
2.3 Due to surgery or invasive treatments (22%)
Some procedures such as epidural anesthesia, spinal surgery, corticosteroid injection, paravertebral injection... can also cause epidural abscess.
2.4 Other causes
Due to spinal cord injury, chronic spine disease, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic kidney failure...
3. Clinical manifestations of extramedullary abscess
Most of the symptoms of the disease are not obvious, especially in the early stages. So a lot of patients were subjective. These signs include:
Common neck and back pain; There are about 30% cases of extramembranous abscess with fever; Numbness in the limbs and gradual loss of sensation; Paralysis of limbs or even disability at a later stage; Urinary tract disorder; Respiratory disorder.
4. How to diagnose epidural abscess?
The diagnosis of an epidural abscess can be based on many imaging criteria. In particular, the diagnostic images from X-rays often have little diagnostic value, but only show images of the spine/vertebrae... thereby determining whether an infection occurs or not.
Therefore, in order to more accurately diagnose an extramedullary abscess, doctors often prescribe:
Computed tomography (CT) with contrast injection: a clear image allows to see whether the pulp is compressed or not. are not. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): this technique has a high diagnostic value for extramedullary abscesses because it allows the lesions to be seen through images, thus supporting early diagnosis. Check leukocyte levels, CRP protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate...: these tests will help identify an infection, however, there is no specific test for an extramedullary abscess. If the patient is suspected of having an epidural abscess, a lumbar puncture is not permitted. This increases the risk of meningitis as well as a dural infection as the needle passes through the abscess.
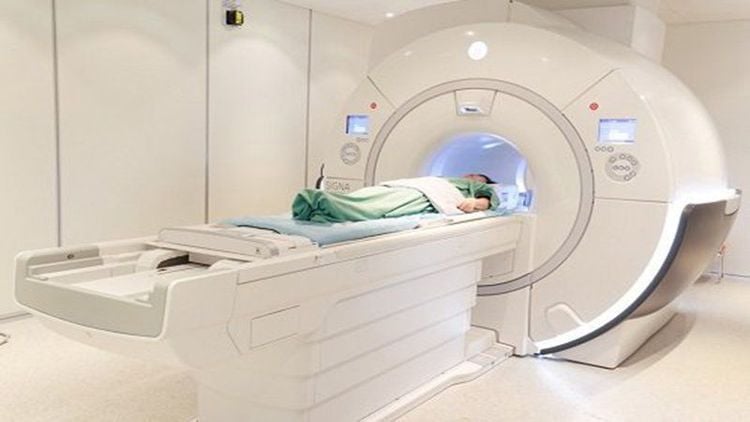
Chụp MRI giúp chẩn đoán hình ảnh áp xe ngoài màng tủy
5. How to treat epidural abscess?
5.1 Surgery (surgical treatment)
By far, the best treatment for epidural abscesses and limiting the risk of disability for this type of pathology is to remove the abscess, and at the same time destroy the foci of infection/microorganism/ infectious agent.
In which, surgical removal of infected tissue is the first method of choice. These surgeries must be performed as soon as possible after the disease is detected.
Next, the doctor will give antibiotics intravenously for about 4-6 weeks. Depending on the stage of the disease when detected, the recovery rate of each patient can vary.
5.2 Medical treatment
Not all patients can meet the conditions for surgery. Therefore, antibiotic therapy will be used but comprehensive results cannot be guaranteed compared to surgery.
In patients with intact nerves (not yet damaged), doctors will treat conservatively with intravenous antibiotics. Treatment is considered successful when the results of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in 4-6 weeks show changes in soft tissue.
In short, early intervention will help to improve symptoms and complications from epidural abscess, and at the same time reduce the risk of disability from this disease. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has a full range of modern and advanced CT and MRI equipment to help detect and diagnose diseases quickly and accurately, actively support in the treatment process for patients. core.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.
References: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov