This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Dr. CKII Nguyen Bang Phong - Internal Medicine - Interventional Cardiology cum Head of Heart Failure Clinic, Cardiovascular Center, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Pulmonary artery pressure is abbreviated as PAP (Pulmonary artery pressure). This is a quantity widely used in clinical practice in the diagnosis, prognosis, treatment indications and evaluation of treatment results for many cardiovascular diseases.
1. What is pulmonary hypertension?
The concept of pulmonary hypertension is defined when the mean pulmonary artery pressure is ≥ 25 mmHg. Pulmonary hypertension can be primary, but it can also be the result of many diseases: left heart failure, congenital heart disease, certain genetic mutations, valvular heart disease, lung disease, thoracic malformations, arterial occlusion. pulmonary vascular disease, systemic disease, sleep apnea, AIDS, drugs, parasites. Severe pulmonary hypertension has a poor prognosis.
The most accurate assessment of pulmonary artery pressure is to measure pulmonary artery pressure directly through a catheter in the catheterization room. At cardiopulmonary resuscitation or intensive care facilities, pulmonary artery pressure can be measured using the Swan Ganz method. However, the most common method of measuring pulmonary artery pressure, and the most commonly used, is the calculation of pulmonary artery pressure via Doppler ultrasound. This technique is easy to implement, cheap and has a high accuracy. There are 3 parameters of pulmonary artery pressure: systolic pulmonary artery pressure (ALDMP tt) is calculated by analyzing the spectrum of tricuspid regurgitation, and mean pulmonary artery pressure (APDMP tb) and pulmonary artery pressure The diastolic pressure (ALP ttr) was calculated by analyzing the pulmonary valve regurgitation spectrum.

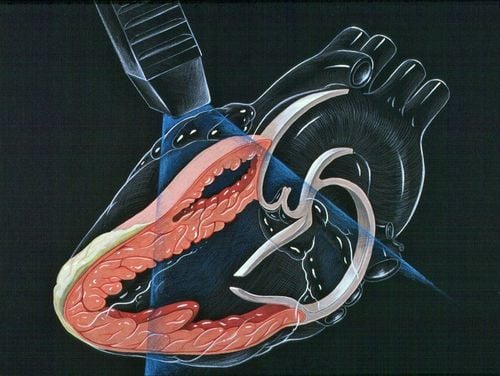
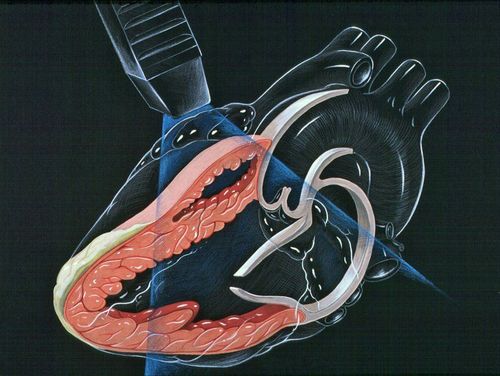
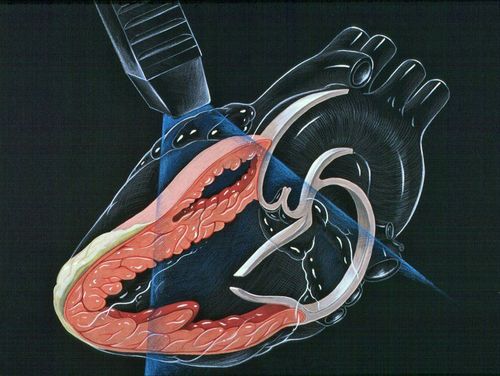
2. Calculation of systolic pulmonary artery pressure through analysis of tricuspid regurgitation spectrum
In the absence of right ventricular outflow tract stenosis or pulmonary stenosis, pulmonary artery pressure = right ventricular pressure during systole. Through the spectrum of tricuspid regurgitation, pulmonary artery pressure can be calculated by the formula: Pulmonary arterial pressure = pressure difference between P ventricle and P atrium + right atrial pressure.
Measurement of the pressure difference between the right ventricle and the right atrium is manipulated as follows: the patient is lying on the left side, taking a four-chamber cut from the apex of the heart; identify tricuspid regurgitation by color Doppler spectrum, then turn on continuous Doppler mode, to locate (cursor) in the middle of the color spectrum of tricuspid regurgitation and then record continuous Doppler spectrum. Measure the peak gradient of the continuous Doppler spectrum obtained, this parameter = pressure difference between right ventricle and right atrium across tricuspid regurgitation.
Estimation of right atrial pressure: Because the right atrium receives blood from the inferior vena cava, right atrial pressure affects the size of the inferior vena cava: Large right atrial pressure increases the size of the inferior vena cava. Normally, the maximal diameter of the inferior vena cava is ≤ 2.1 cm. In addition, because the size of the inferior vena cava varies with the respiratory cycle: the size of the inferior vena cava decreases with inspiration. The change in size of the inferior vena cava with the respiratory cycle is reflected by the IVC collapsibility index: (max IVC diameter – min IVC diameter)/max IVC diameter
Normally, the collapse index is ≥ 50%. If the right atrial pressure is high, the collapse index will decrease. Based on the size of the inferior vena cava and the collapse index, the right atrial pressure can be estimated according to the following table:
These are the parameters of the American Society of Echocardiography. For Vietnamese people of smaller height and weight, using the inferior vena cava size parameter may not be accurate. We can use the collapse index to estimate right atrial pressure.
Estimating the right atrial pressure through the parameters of the inferior vena cava is done as follows: The patient is in the supine position, taking a cut below the costal margin, measuring the diameter of the inferior vena cava below the empties. into the right atrium 1-1.5 cm in 2 maximal inspiration and expiration.
Example: Maximum pressure difference across the tricuspid regurgitation spectrum = 30 mmHg; The maximal size of the inferior vena cava = 2.3 cm, the index of lower vena cava collapse < 50%, equivalent to an ALNP of 15-20 mmHg. ICP tt = 45 – 50 mmHg.
3. Calculation of pulmonary diastolic pressure through analysis of pulmonary valve regurgitation spectrum
On echocardiography, the diastolic pulmonary artery pressure is calculated by the formula: ALDMP ttr = Pressure difference between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle at the end of diastole + right ventricular pressure (ALTP). During diastole, the right ventricular pressure is roughly equivalent to the right atrial pressure. Therefore, the right ventricular pressure can be replaced by the right atrial pressure in the above formula. Calculation of the pressure difference between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle at the end of diastole is done as follows: Take a cross-section of the left side of the breast, determine pulmonary valve regurgitation by color Doppler. Continuous Doppler on, to locate (cursor) in the middle of the pulmonary regurgitation spectrum. Measure the end-diastolic gradient of the obtained pulmonary regurgitation spectrum.
Example: The end-diastolic pressure difference across the pulmonary valve regurgitation spectrum = 10 mmHg; max size of inferior vena cava = 1.9 cm; vena cava collapse index less than 50%. ICP ttr = 10 – 15 mmHg
4. Calculate mean pulmonary artery pressure by analyzing pulmonary valve regurgitation spectrum
On echocardiography, mean pulmonary artery pressure is calculated according to the formula: ALPMP tb = pressure difference between pulmonary artery and right ventricle at end-diastolic + right ventricular pressure. Calculation of the mean pressure difference between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle is done as follows: Take a cross-section of the left parasternal axis, determine the pulmonary valve regurgitation by color Doppler. Continuous Doppler on, to locate (cursor) in the middle of the pulmonary regurgitation spectrum. Measure the maximal differential pressure of the obtained pulmonary regurgitation spectrum.
Example: Maximum pressure difference of pulmonary open spectrum = 30 mmHg; maximal size of inferior vena cava = 2 cm; The index of vena cava collapse is less than 50%. Pulmonary edema tb = 30-35 mmHg.
There are 3 parameters of pulmonary artery pressure: ALDMP tt; ALDMP tb; However, in clinical practice, ALP parameter tt is often used because the spectrum of tricuspid regurgitation is more common and easier to perform. There are 3 degrees of pulmonary hypertension: Mild pulmonary hypertension when pulmonary systolic pressure is from 25 to 45 mmHg; Mean pulmonary arterial pressure increases when systolic pulmonary arterial pressure is 46 to 65 mmHg; Severe pulmonary hypertension when pulmonary systolic pressure > 65 mmHg.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.