This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc, BS. Dang Manh Cuong - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has over 18 years of experience in the field of ultrasound - diagnostic imaging.Osteoporosis is a disease identified by imaging studies. Therefore, the role of CT, X-ray, and MRI is very important in the diagnosis of common osteoporosis in women and the elderly.
1. What is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by damage to bone tissue structures and reduced bone mass. The disease progresses over time, reducing bone function.Osteoporosis manifested by changes in bone structure (gradual porous) and more easily broken. When viewed under a microscope, while normal bones have a honeycomb-like structure, osteoporotic bones have larger holes and gaps in the honeycomb.
Women and the elderly are the two main groups at high risk of osteoporosis. In addition, osteoporosis is also affected by other factors such as genetics, low BMI, smoking and use of drugs to treat chronic diseases (such as steroids).
People with osteoporosis are prone to fracture when lifting, bending, bumping into furniture, even sneezing in critically ill patients. Any bone in the body can be broken, with the most common being the pelvis, spine, and wrists.
Osteoporosis can present for years without any noticeable symptoms until the person experiences the following warning signs:
Severe back pain Loss of height over time Crooked posture Back Fracture due to minor trauma.

2. The role of imaging in the assessment of osteoporosis
To evaluate osteoporosis and determine the need for treatment, the most commonly used indication is bone density measurement. This technique helps determine bone mineral density (BMD). It is usually performed using dual X-ray energy absorptiometry (DEXA-DXA) and quantitative computed tomography. The results show that the more X-rays penetrate, the lower the bone density and vice versa.Bone density information is converted to T-scores and Z-scores. T-scores show the amount of bone compared to a young person of the same sex with the highest bone mass. It is used to estimate the risk of fracture and determine the need for medication. The Z-score reflects the number of bones compared to others in the same age group, with the same body size (in cm2) and gender. If the Z-score is abnormally high or low, further testing may be needed.
Some of the following imaging tests may be done to identify osteoporosis fractures :
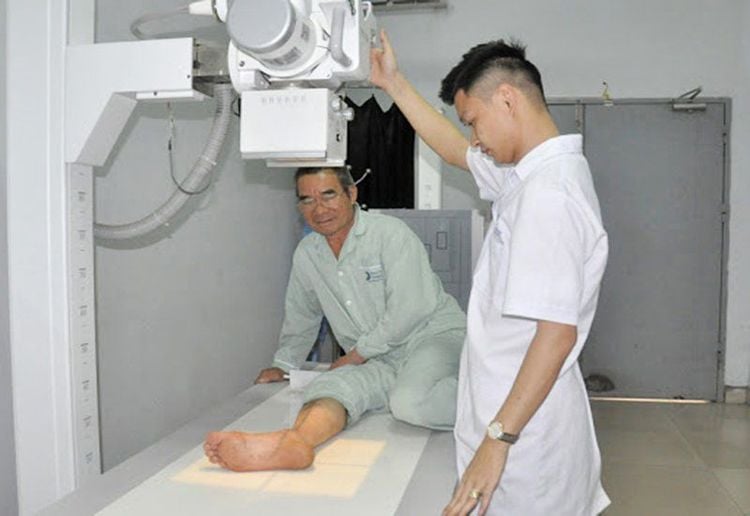
Bone X-rays : A bone X-ray helps to look at bone structures in the body, including the hand, wrist, arm, elbow, shoulder, foot, ankle, shin, knee, thigh, hip, pelvis or spine. It aids in the diagnosis of fractures. CT scan of the spine: CT of the spine is used to measure bone density and determine if a vertebral fracture is likely. MRI of the spine: Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine helps to evaluate vertebral fractures, to find the cause of diseases such as cancer, and to assess whether the fracture is old or new. New fractures often respond better to two percutaneous chiropractic treatments, vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.
3. How to treat osteoporosis?
There are many FDA-approved drugs to choose from for the treatment of osteoporosis including:Bisphosphonate Calcitonin Hormone replacement therapy RANK ligand inhibitors Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) Parathyroid hormone analogues Thyroid Medications should be prescribed as indicated, following specific clinical and laboratory evaluation of the osteoporosis status. The occurrence of vertebral compression fractures may be the result of osteoporosis. There are two techniques applied in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures:
Transdermal vertebroplasty technique with bio-cement pump (Vertebroplasty): Under the guidance of a fluorescent screen, bio-cement mixture A special cement mixture is applied to the broken bone through a hollow needle to repair the damaged vertebra. Kyphoplasty: A specialized needle with a ball at the tip pokes into the vertebral body and is inserted into the broken bone. The balloon is stretched to expand the vertebrae, returning it to its original shape. After the ball is removed, the bio-cement mixture is injected into the bone cavity. In some cases of compression fractures, surgical treatment may be required, especially if there is evidence of severe spinal stenosis.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. Examination and treatment of osteoporosis at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org
SEE MORE
Causes of osteoporosis - know early, prevent early Osteoporosis prevention What should people with osteoporosis eat?