This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Hemophilia is an X-linked hereditary bleeding disorder caused by a decrease in factor VIII (hemophilia A) or factor IX (Hemophilia B) leading to thromboplastin production, which slows blood clotting. The frequency of hemophilia is about 20/100,000 men, 80-85% of patients are Hemophilia A.
Below is the assessment of bleeding in patients with hemophilia:
1. Patients with hemophilia bleeding in many places
Common joint bleeding:
Two bones that meet are called joints. The ends of the bones are covered by a smooth layer called cartilage, the bones are held together by a joint capsule. The joint capsule contains a space called the synovial capsule with many small blood vessels and mucus and slippery secretions that facilitate joint movement. When the capillaries in the synovium are damaged, the joint will bleed. In people without hemophilia, blood will stop bleeding quickly, but in patients with hemophilia, the bleeding will stop for a long time, leading to swollen and painful joints, difficulty in movement. The joints that bleed most often are the ankle, knee, and elbow joints. Bleeding can also occur in the shoulder, hip, and toe joints. Hand joints are uncommon without trauma.
Long-term consequences of joint bleeding:
Repeated bleeding in the joint causes swelling of the bursa, making it easier to bleed. The synovial fluid does not produce mucus and is slippery, allowing the joints to move more easily. This damages the cartilage that covers the ends of the bones. Joints become rough, painful when moving and the muscles around the joints become weaker, over time the cartilage breaks down, the bones wear down, making it impossible to move this phenomenon called hemophilia arthritis. When bleeding occurs repeatedly in the joints, the patient will have limited mobility, joint deformity, and muscle atrophy leading to disability.
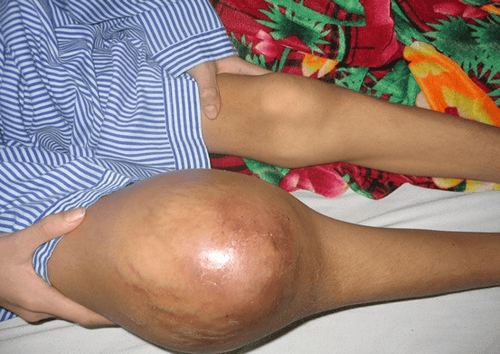
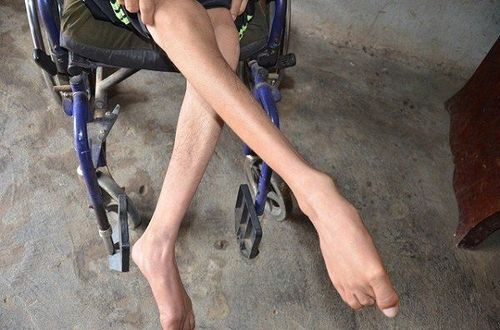
2. Muscle bleeding
Due to damage to the blood vessels in the muscle, it can be traumatic, or spontaneously due to intramuscular injection. The bleeding muscle will be solid, painful, hot, and hemorrhagic on the skin. Bleeding muscles in the area near the joint will make it difficult to move the joint. The muscles that bleed often are the calf muscles, thighs, arms, and the back muscles, the forearms, which compress nerves and blood vessels, leading to permanent damage.
Long-term consequences of muscle bleeding: Repeated muscle bleeding causes muscle weakness, scar wall shortens muscle, so it affects joint movement, which makes it easy to atrophy. If nerves are damaged during muscle bleeding, paralysis can occur. As a result, the patient will have difficulty with movement such as walking, standing and sitting.
3. Visceral bleeding that threatens the patient's life
Bleeding into the brain is often the result of trauma, which is the cause of death in patients with hemophilia, with symptoms such as headache, vomiting, somnolence, confusion, loss of consciousness, coma.
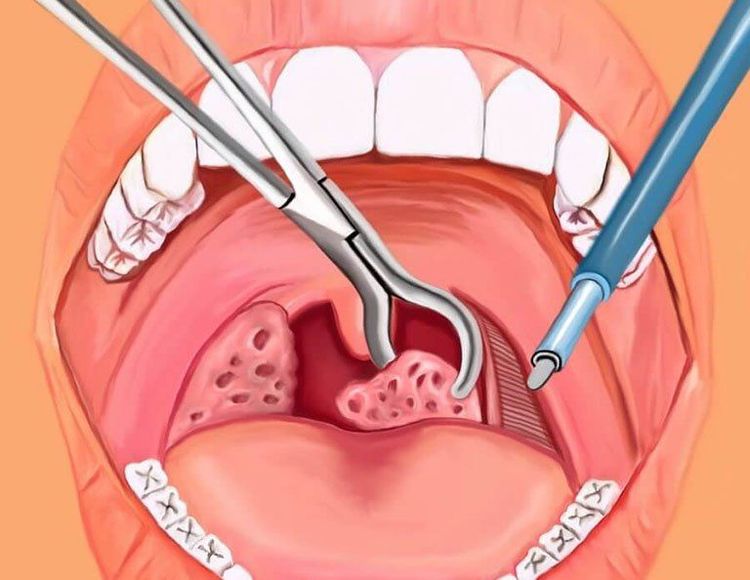
Bleeding in the throat due to inflammation, due to surgery such as tonsillectomy, curettage VA. Long-term bleeding when extracting teeth, circumcision. In children, it is easy to bleed from the skin due to crawling, learning to walk, etc.
Bleeding in the kidneys, bladder causing hematuria. Hemorrhage of the retina of the eye or lumbar muscle can be severe but is not life-threatening.
Bleeding will lead to severe anemia, which is life-threatening, so it should be treated early to quickly stop bleeding and prevent anemia, especially in cases of suspected internal bleeding.
Thus, hemophilia, the main symptom is bleeding organs, should be detected and treated promptly. Preventive treatment is very important. The patient's family needs to be closely monitored, have a special care regimen for their children and younger siblings, to avoid injuries such as not climbing, pushing, or fighting. When bleeding is correct, then take the patient to a specialized medical facility for treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.