This is an automatically translated article.
Translated by Dr. Truong Ngoc Hai - Resuscitation Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Heart failure is the ultimate common pathway of cardiovascular diseases. Heart failure is divided into two types, acute heart failure and chronic heart failure. Acute heart failure can be a new-onset heart failure, but it can also be an aggravation of chronic heart failure.
Here are 10 notes according to the European Society of Cardiology guidelines 2021 on the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure:
ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-neprilysin receptor blockers, blockers beta, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors are recommended as cornerstone therapy to reduce mortality and hospitalization for heart failure for all patients with reduced ejection fraction. and as therapy may be considered in patients with mildly reduced ejection fraction. In patients with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≤35%, in sinus rhythm, cardiac resynchronization therapy is recommended in the presence of left bundle branch block (LBBB) and QRS duration > 150 ms; should be considered in the case of LBBB time and QRS time between 130 and 149 ms or no LBBB and QRS time > 150 ms; and can be considered in patients without LBBB and a QRS duration of 130–149 ms. In patients with an LVEF 35%, an implantable defibrillator-converter should be used in ischemic cases and should be considered in non-ischemic cases, if appropriate. fit. In some patients with advanced heart failure unresponsive to medical therapy, heart transplantation is recommended and mechanical circulatory support is considered. Treatment of acute heart failure includes treatment of specific causes (eg, acute coronary syndromes, hypertensive emergencies, arrhythmias, mechanical complications, pulmonary embolisms, infection, compression). acute heart failure) and the use of diuretics, vasodilators, vasopressors, vasopressors, short-term mechanical supportive therapy, renal replacement therapy. Indications for these treatments and duration of implementation vary according to the patient's clinical presentation (eg, acute decompensated heart failure, acute pulmonary edema, right ventricular failure, cardiogenic shock) and severity severity of acute heart failure. It is recommended that patients with heart failure be examined before discharge and have an early follow-up, at 1–2 weeks after discharge, to assess for signs of congestive heart failure, tolerability, and to initiate and /or tailor evidence-based therapies. It is recommended that patients with heart failure be periodically screened for anemia and iron deficiency. Intravenous iron supplementation with carboxymaltose salts should be considered if serum ferritin <100 ng/mL, or if serum ferritin is 100–299 ng/mL and transferrin saturation <20% in patients with LVEF < 45% were symptomatic to improve symptoms and quality of life, and in patients recently hospitalized for heart failure had an LVEF <50% to reduce the risk of re-hospitalization. Pulmonary venous ablation should be considered for rhythm control when atrial fibrillation is associated with worsening symptoms of heart failure. Heart failure patients with secondary mitral regurgitation should be evaluated by a Cardiologist (Team). If the criteria for an improved prognosis are met, the patient should be considered for an edge-to-edge technique for percutaneous mitral valve repair. Patients with 'danger warning signs', such as patients ≥65 years of age with heart failure with left ventricular wall thickening, should be screened for cardiac amyloidosis. Tafamidis is recommended in patients with symptoms of NYHA class I or II heart failure and transthyretin-cardiac amyloidosis for the relief of symptoms, hospitalization, and mortality.
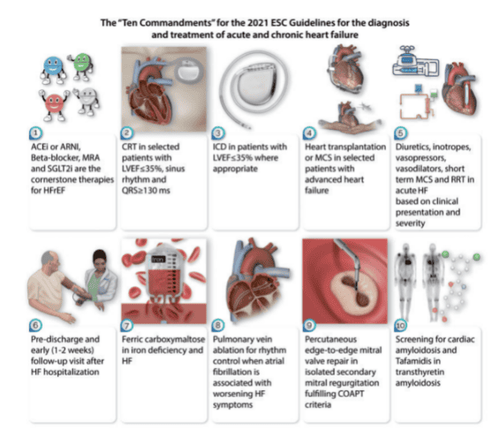
Lưu ý của Hướng dẫn ESC năm 2021 về chẩn đoán và điều trị suy tim cấp và mạn tính.
Acute heart failure in patients with chronic heart failure is more common clinically. Patients who come to the hospital in the context of acute heart failure need emergency treatment, if delayed, they may fall into cardiogenic shock, the mortality rate is very high.
Together with cardiovascular health care for the community, Vinmec has implemented many packages of examination, diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases such as the basic Cardiovascular examination package; package of examination and screening for coronary artery disease, hypertension, heart failure... for different risk groups. Besides, Vinmec is fully equipped with modern equipment such as high standard testing system, electrocardiogram machine, echocardiogram, stress electrocardiogram, Aquillion 640 slice CT scanner, technical angiography machine modern digital number (DSA)... makes examination and treatment easier. Especially, the medical team with many years of experience in diagnosing and treating cardiovascular diseases in general and coronary artery disease in particular is the decisive factor in bringing satisfaction to all customers. .
Summary of the article: “Marianna Adamo, Roy S Gardner, Theresa A McDonagh, Marco Metra, The 'Ten Commandments' of the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure, European Heart Journal , 2021; ehab853”
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.